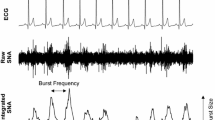
Abstract
Human muscle nerve sympathetic activity measured by microneurography during supine rest is known to vary considerably between healthy subjects, whereas in a given individual the level of muscle nerve sympathetic activity is stable over weeks and months. To further characterize long-term variability or reproducibility microneurographic recordings of muscle nerve sympathetic activity were performed in 15 healthy, normotensive subjects (mean age 51 years) who had undergone the same procedure between 10 and 14 years earlier (mean 12 years). The range of muscle nerve sympathetic activity was 9–59 in the first and 13–61 bursts/min in the second recording. Subjects maintained the level of muscle nerve sympathetic activity displayed previously, although with a slight but significant tendency to a higher outflow with increasing age.
It is concluded that muscle nerve sympathetic activity is characterized by large inter-individual differences and strong intra-individual reproducibility over many years, with a tendency to increase with age. The age relationship is only in a minor part responsible for the variability, the cause of which remains unexplained. Because of the marked difference between individuals, strict normality criteria are difficult to define when comparing groups of subjects. There remains the risk of either obtaining spurious differences or obscuring a true abnormality. This is unlikely to apply when results in individual subjects are compared.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hagbarth KE, Vallbo ÅB. Pulse and respiratory grouping of sympathetic impulses in human muscle nerves.Acta Physiol Scand 1968;74: 96–108.
Wallin BG, Fagius J. Peripheral sympathetic neural activity in conscious humans.Annu Rev Physiol 1988;50: 565–576.
Sundlöf G, Wallin BG. The variability of muscle nerve sympathetic activity in resting recumbent man.J Physiol (Lond) 1977;272: 383–397.
Sundlöf G, Wallin BG. Human muscle nerve sympathetic activity at rest. Relationship to blood pressure and age.J Physiol (Lond) 1978;274: 621–637.
Fagius J, Wallin BG. Microneurographic evidence of excessive sympathetic outflow in the Guillain-Barré syndrome.Brain 1983;106: 589–600.
Yamada Y, Miyajima E, Tochikubo O, Matsukawa T, Ishii M. Age-related changes in muscle sympathetic nerve activity in essential hypertension.Hypertension 1989;13: 870–877.
Wallin BG, Sundlöf G, Eriksson BM, Dominiak P, Grobecker H, Lindblad LE. Plasma noradrenaline correlates to sympathetic muscle nerve activity in normotensive man.Acta Physiol Scand 1981;111: 69–73.
Mörlin C, Wallin BG, Eriksson BM. Muscle sympathetic activity and plasma noradrenaline in normotensive and hypertensive man.Acta Physiol Scand 1983;119: 117–121.
Berne C, Fagius J, Niklasson F. Sympathetic response to oral carbohydrate administration. Evidence from microelectrode nerve recordings.J Clin Invest 1989;84: 1403–1409.
Fagius J, Karhuvaara S. Sympathetic activity and blood pressure increases with bladder distension in humans.Hypertension 1989;14: 511–517.
Vallbo ÅB, Hagbarth KE, Torebjörk HE, Wallin BG. Somatosensory, proprioceptive, and sympathetic activity in human peripheral nerves.Physiol Rev 1979;59: 919–957.
Mark AL, Victor RG, Nerhed C, Wallin BG. Microneurographic studies of the mechanisms of sympathetic nerve response to static exercise in humans.Circ Res 1985;57: 461–469.
Ebert TJ, Morgan BJ, Barney JA, Denahan T, Smith JJ. Effects of aging on baroreflex regulation of sympathetic activity in humans.Am J Physiol 1992;263: H798-H803.
Anderson EA, Sinkey CA, Lawton WJ, Mark AL. Elevated sympathetic nerve activity in borderline hypertensive humans.Hypertension 1989;14: 177–183.
Anderson EA, Wallin BG, Mark AL. Dissociation of sympathetic nerve activity to arm and leg during mental stress.Hypertension 1987;9 (suppl III): 114–119.
Freyschuss U, Fagius J, Wallin BG, Bohlin G, Perski A, Hjemdahl P. Cardiovascular and sympathoadrenal responses to mental stress: a study of sensory intake and rejection reactions.Acta Physiol Scand 1990;139: 173–183.
Wallin BG, Sundlöf G, Strömgren E, Åberg H. Sympathetic outflow to muscles during treatment of hypertension with metoprolol.Hypertension 1984;6: 557–562.
Fagius J, Berne C. Increase in muscle nerve sympathetic activity in humans following food intake. (unpublished observation) 1993.
Christensen NJ. Is plasma noradrenaline an index of biologic age? In: Christensen NJ, Henriksen O, Lassen NA, eds.The Sympathoadrenal System, Physiology and Pathophysiology. Copenhagen; Munksgaard, 1986: 266–272.
Lake CR, Ziegler MG, Coleman MD, Kopin IJ. Age-adjusted plasma norepinephrine levels are similar in normotensive and hypertensive subjects.N Engl J Med 1977;296: 208–209.
Rowe JW, Troen BR. Sympathetic nervous system and aging in man.Endocrinol Rev 1980;1: 167–179.
Gribbin B, Pickering TG, Sleight P, Peto R. Effect of age and blood pressure on baroreflex sensitivity in man.Circ Res 1971;29: 424–431.
Lindblad LE. Influence of age on sensitivity and effector mechanisms of the carotid baroreflex.Acta Physiol Scand 1977;101: 43–49.
Wallin BG, Kunimoto MN, Sellgren J. Genetic influence on the strength of human muscle nerve sympathetic activity at rest. (unpublished observation) 1993.
Fagius J, Kay R. Low ambient temperature increases baroreflexgoverned sympathetic outflow to muscle vessels in humans.Acta Physiol Scand 1991;142: 201–209.
Andersson B, Elam M, Wallin GW, Björntorp P, Andersson OK. Effect of energy-restricted diet on sympathetic muscle nerve activity in obese women.Hypertension 1991;18: 783–789.
Fagius J, Westermark K, Karlsson A. Baroreflex-governed sympathetic outflow to muscle vasculature is increased in hypothyroidism.Clin Endocrinol 1990;33: 177–185.
Leimbach WN, Wallin BG, Victor RG, Aylward PE, Sundlöf G, Mark AL. Direct evidence from intraneural recordings for increased central sympathetic outflow in patients with heart failure.Circulation 1986;73: 913–919.
Wallin BG, Sundlöf G. A quantitative study of muscle nerve sympathetic activity in resting normotensive and hypertensive subjects.Hypertension 1979;1: 67–77.
Rea RF, Hamdan M. Baroreflex control of muscle sympathetic nerve activity in borderline hypertension.Circulation 1990;82: 856–862.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fagius, J., Wallin, B.G. Long-term variability and reproducibility of resting human muscle nerve sympathetic activity at rest, as reassessed after a decade. Clinical Autonomic Research 3, 201–205 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01826234
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01826234