Summary
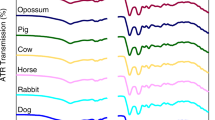
A reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic method for species identification of blood and bloodstains is described. The method employs a 300 Å pore SynChropak RP-4 column and ternary solvents (acetonitrile-trifluoroacetic acid-water) and can not only identify a species by its characteristic chromatogram, but also simultaneously demonstrates that it is of blood origin by the existence of the heme peak. Deformations in chromatographic profiles obtained with older bloodstains were observed, but the retention times of heme and the major peaks showed only minor changes. The species could be identified from bloodstains at least 3 months old and the present method has the advantage of simplicity, speed and sensitivity in the practice of forensic science.
Zusammenfassung
Beschrieben wird eine „reversedphase” HPLC-Methode zur Identifizierung und Spezifizierung von Blut und Blutspuren. Die Analysenmethode besteht aus einer SynChropak RP-4-Säule und einem ternären Lösungsmittelgradientensystem (Acetonitril/Trifluoressigsäure/Wasser). Mit dieser Methode wird durch die Detektion des Häm-Peaks die Probe als Blut identifiziert und die Herkunft (human/tierisch) gleichzeitig durch charakteristische Chromatogramme UV-spektrometrisch spezifiziert. Deformationen der chromatographischen Profile wurden bei älteren Blutspuren beobachtet, wobei sich aber die Retentionzeiten der Hauptkomponenten nur geringfügig änderten. Der Speziesnachweis gelang bei bis zu drei Monate alten Blutspuren. Die vorgestellte Methode hat den Vorteil der Einfachheit, der Schnelligkeit und der Empfindlichkeit für die forensische Praxis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee HC (1982) Identification and grouping of bloodstains. In: Saferstein R (ed) Forensic science handbook. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, pp 267–337
Culliford BJ (1964) Precipitin reactions in forensic problems. Nature 201:1092–1094
Lee HC, Gaensslen RE, Pagliaro EM, Lee SK, Carroll-Reho J (1985) Simultaneous identification and determination of species origin. ABH antigens and isoenzyme markers in the same bloodstain. Forensic Sci Int 29: 191–198
Fletcher SM, Dolton P, Harris-Smith PW (1984) Species identification of blood and saliva stains by enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) using monoclonal antibody. J Forensic Sci 29: 67–74
Quarino L, Kobilinsky L (1988) Development of a radioimmunoassay technique for the detection of human hemoglobin in dried bloodstains. J Forensic Sci 33: 1369–1378
Smith RN (1982) Forensic applications of high-performance liquid chromatography. In: Saferstein R (ed) Forensic science handbook. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, pp 28–91
Inoue H, Takabe F, Maeno Y, Iwasa M (1989) Identification of fetal hemoglobin in blood stains by high performance liquid chromatography. Z Rechtsmed 102:437–444
Shelton JB, Shelton JR, Schroeder WA (1984) High performance liquid chromatographic separation of globin chains on a large pore C4 column. J Liq Chromatogr 7:1969–1977
Schroeder WA, Shelton JB, Shelton JR, Huynh V, Teplow DB (1985) High performance liquid chromatographic separation of the globin chains of non-human hemoglobins. Hemoglobin 9:461–482
Condò SG, Giardina B, Barra D, Gill SJ, Brunori M (1981) Purification and functional properties of the hemoglobin components from the rat (Wistar). Eur J Biochem 116:243–247
Gilman JG, Datta MC (1982) Rat hemoglobin heterogeneity: genetic variation affecting hemoglobin proportions. Hemoglobin 6:439–444
Takenaka A, Takahashi K, Takenaka O (1988) Novel hemoglobin components and their amino acid sequences from the crab-eating macaque (Macaca fascicularis). J Mol Evol 28: 136–144
Springer GF, Williamson P, Brandes WC (1961) Blood group activity of gram-negative bacteria. J Exp Med 113: 1077–1093
Cowan ME (1979) Identification of blood and other biologic stains. In: Hirsch CS, Morris RC, Moritz AR (eds) Handbook of legal medicine, 5th edn. Mosby, St. Louis Toronto London, pp 145–157
Ito S, Suzuki K, Matsui K, Matsumoto H (1987) Determination of bloodstain origin by high-performance liquid chromatography of the hemoglobin peptides. Act Crim Japon 53: 68–75
Oshima M, Inoue T, Hara M (1982) Identification of species specific hemoglobin by isoelectric focusing. Forensic Sci Int 20:277–286
Stevenson D, Bridges JW (1986) A review of analytical methods. In: Curry AS (ed) Analytical methods in human toxicology, Part 2. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim Basel, pp 1–34
Kutlar F, Kutlar A, Huisman THJ (1986) Separation of normal and abnormal hemoglobin chains by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr 357:147–153
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inouel, H., Takabe, F., Takenaka, O. et al. Species identification of blood and bloodstains by high-performance liquid chromatography. Int J Leg Med 104, 9–12 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01816476
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01816476