Summary
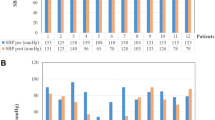
The influence of diabetic autonomic neuropathy upon the behavior of the circulatory system was investigated in 56 patients who had undergone ophthalmological surgery. A standardized test combination (variability in heart rate during deep breathing, Valsalva ratio, 30∶15 ratio, change in blood pressure from lying to standing, sustained handgrip test) was used to study the patients' cardiovascular reflectory reactions. The patients were then divided into the following groups: Group I, non-diabetics Group II, diabetics without autonomic neuropathy Group III, diabetics with autonomic neuropathy The anesthetic (induction by barbiturates and conduction by inhalation agents) and the surgical procedure (pars plana vitrectomy) were standardized and always identical. During anesthesia patients in group III experienced hypotensive reactions (systolic blood pressure below 90 mm Hg) significantly more often (72.2%) than patients in group I (25%). In order to achieve stability in blood pressure the patients of group III had to be given vasoactive drugs much more often (77.8%) than the patients of group I (12.5%) and those of group II (35.7%). We found a significant correlation between the degree of autonomic dysfunction and the largest drop in blood pressure under narcosis (r=−0.60,P<0.001). However, marked variability in heart rate and cardiac rhythm disorders during anesthesia were seen only in patients of groups I and II. These results prove the atypical hemodynamic behavior and especially the extreme instability in blood pressure in diabetic autonomic neuropathy under general anesthesia. Therefore we consider it to be very helpful to check the cardiovascular reflectory status of diabetics preoperatively.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AN:
-
autonomic neuropathy
- AV:
-
atrioventricular
- BP:
-
blood pressure
- bpm:
-
beats per minute
- cm:
-
centimeter
- f:
-
female
- HR:
-
heart rate
- m:
-
male
- PD:
-
diastolic blood pressure
- PS:
-
systolic blood pressure
References
Alberti KGMM, Thomas DJB (1979) The management of diabetes during surgery. Br J Anaesth 51:693–710
Bannister R, Davies B, Holly E, Rosenthal T, Sever P (1979) Defective cardiovascular reflexes and supersensitivity to sympathomimetic drugs in autonomic failure. Brain 102:163–176
Bellavere F, Bosello G, Cardone C, Girardello L, Ferri M, Fedele D (1985) Evidence of early impairment of parasympathetic reflexes in insulin dependent diabetics without autonomic symptoms. Diabete metab 11:152–156
Bosnjak ZJ, Kampine JP (1981) Effects of halothane on ganglionic transmission. Anesthesiology 55:A275
Burgos LG, Ebert TJ, Asiddao C, Turner LA, Pattison CZ, Wang-Cheng R, Kampine JP (1989) Increased intraoperative cardiovascular morbidity in diabetics with autonomic neuropathy. Anesthesiology 70:591–597
Ciccarelli LL, Ford CM, Tsueda K (1986) Autonomic neuropathy in a diabetic patient with renal failure. Anesthesiology 64:283–287
Derbyshire DR, Smith G (1984) Sympathoadrenal responses to anesthesia and surgery. Br J Anaesth 56:725–739
Duke PC, Trosky S (1980) The effect of halothane with nitrous oxide on baroreflex control of the heart rate in man. Can Anaesth Soc J 27:531–534
Dyrberg T, Benn J, Sandahl Christiansen J, Hilsted J, Nerup J (1981) Prevalence of diabetic autonomic europathy measured by simple bedside tests. Diabetologia 20:190–194
Ebert TJ, Kotrly KJ, Vucins EJ, Pattison CZ, Kampine JP (1985) Halothane anesthesia attenuates cardiopulmonary baroreflex control of peripheral resistance in humans. Anesthesiology 63:668–674
Ewing DJ, Campbell IW, Clarke BF (1980) The natural history of diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Q J Med 193:95–108
Ewing DJ, Clarke BF (1982) Diagnosis and management of diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Br Med J 285:916–918
Hilsted J, Parving HH, Christensen NJ, Benn J, Galbo H (1981) Hemodynamics in diabetic orthostatic hypotension. J Clin Invest 68:1427–1434
Magnusson J, Werner O, Carlsson C, Norden N, Petterson KI (1983) Metoprolol, fentanyl and stress responses to microlaryngoscopy. Br J Anaesth 55:405–413
Page MMcB, Watkins PJ (1978) Cardiorespiratory arrest and diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Lancet 1:14–16
Pascual ALC, Ganuza JR, Recio MG, Alvarez M (1984) Neuropatia autonomica, hipertension arterial y diabetes mellitus. Med Clin (Barc) 84:437–439
Skovsted P, Price ML, Price HL (1970) The effect of shortacting barbiturates on arterial pressure, preganglionic sympathetic activity and barostatic reflexes. Anesthesiology 33:10–18
Takeshima R, Dohi S, Hayasaki M, Naito H (1988) Abnormal hemodynamic responses in patients with diabetic autonomic-neuropathy during anesthesia and surgery. Jpn J Anesthesiol 37:1249–1254
Thomas AN, Pollard BJ (1989) Renal transplantation and diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Can J Anaesth 36:590–592
Triantafillou AN, Tsueda K, Berg J, Wieman TJ (1986) Refractory bradycardia after reversal of muscle relaxant in a diabetic with vagal neuropathy. Anesth Analg 65:1237–1241
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knüttgen, D., Weidemann, D. & Doehn, M. Diabetic autonomic neuropathy: Abnormal cardiovascular reactions under general anesthesia. Klin Wochenschr 68, 1168–1172 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01815272
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01815272