Summary
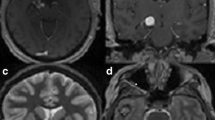
In a case of cavernous angioma, a remote gyrus, which was found to contain an epileptogenic focus by intraoperative electrocorticography (ECoG), was resected simultaneously with lesionectomy.
The patient was a 27-year-old male who was referred to our hospital because of frequent systemic tonic-clonic convulsions. ECoG revealed an epileptogenic focus not only in the cortex around the angioma-affected tissue of the left frontal lobe but also in an in addition to lesionectomy. The postoperative course was uneventful. Now (two years after surgery), the patient is seizure-free
In the surgical treatment of convulsions-accompanied by cavernous angioma, it is essential not only to detect epileptogenic foci by intraoperative ECoG but also to remove these foci together with the angioma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Awad IA, Rosenfeld J, Ahl J, Harn JF, Luders H (1991) Intractable epilepsy and structural lesions of the brain: mapping, resection strategies, and seizure outcome. Epilepsia 32: 179–186
Buckingham MJ, Crone KR, Ball WS, Berger TS (1989) Management of cerebral cavernous angiomas in children presenting with seizures. Childs Nerv Syst 5: 347–349
Fargueta JS, Iranzo R, Garcia M, Jorda M (1981) Hemangioma calcificans: a benign epileptogenic lesion. Surg Neurol 15: 66–70
Giombini S, Morello G (1978) Cavernous angiomas of the brain: account of fourteen personal cases and review of the literature. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 40: 61–82
Gloor P (1975) Contributions of electroenchephalography and electrocorticography to the neurosurgical treatment of the epilepsies. Adv Neurol 8: 59–105
Graf M, Niedermeyer E, Schiemann J, Uematsu S, Long DM (1984) Electrocorticography: information derived from intraoperative recordings during seizure surgery. Clin Electroencephalogr 15: 83–91
Kaminogo M, Nishimura S, Baba H, Matsumura H, Mori K (1986) Epileptogenesis in cavernous hemangioma: pathophysiological study. Nerv Syst Child 11: 355–360
Kasamo S, Kobayashi E, Awa H, Kanemaru R, Kusumoto K, Masaki N, Asakura T (1980) A case of cerebral venous angioma as an epileptogenic lesion detected by CT scan and surgically treated. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 20: 865–873
Little JR, Awad IA, Jones SC, Ebrahim ZY (1990) Vascular pressures and cortical blood flow in cavernous angioma of the brain. J Neurosurg 73: 555–559
Morimoto T, Takemura K, Sakaki T, Hori Y, Miyamoto S, Kyoi K, Utsumi S (1984) Clinical study on six cases of subcortical cavernous angiomas. Surg Neurol 12: 359–367
Nakayama Y, Kimura H, Yoshinaga S, Tanaka A, Tomonaga M (1989) Surgical experiences with organic lesions in refractory epilepsy, as discovered by magnetic resonance imaging: a report of two cases. Progress CT 11: 351–355
Ojemann GA (1987) Surgical therapy for medically intractable epilepsy. J Neurosurg 66: 489–499
Pozzati E, Padovani R, Morrone B, Finizio F, Gaist G (1980) Cerebral cavernous angiomas in children. J Neurosurg 53: 826–832
Rasmussen T (1975) Surgery of epilepsy associated with brain tumors. Adv Neurol 8: 226–227
Ribalric II, Janicijevic MA (1979) The electrocorticographic status and the extent of the cortical resection in epileptic patients. Acta Neurochir (Wien) [Suppl] 28: 556–560
Scanarini M, Zuccarello M, Andrioli GC, Testa G (1980) Partial complex seizures: a corticographic and ultrastructure study. Zbl Neurochirurgie 41: 91–98
Senoo K, Asakura T, Awa H (1092) A case report of cerebral angioma: An epileptogenic lesion detected by CT scan and surgically treated. Acta Med Univ Kagoshima 24: 93–103
Wyllie E, Luders H, Morris III HH, Lesser RP, Dinner DS, Hahn J, Estes ML, Rothner AD, Erenberg G, Cruse R, Friedmann D (1987) Clinical outcome after complete or partial cortical resection for intractable epilepsy. Neurology 37: 1634–1641
Yeh HS, Kashiwagi S, Tew Jr Jm, Berger TS (1990) Surgical management of epilepsy associated with cerebral arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 72: 216–223
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamada, K., Isu, T., Takahashi, T. et al. Remote epileptogenic focus detected by electrocorticogram in a case of cavernous angioma. Acta neurochir 127, 236–239 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01808773
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01808773