Abstract
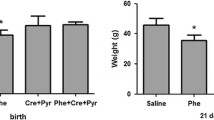
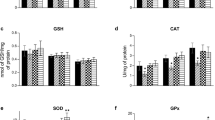
The influence of α-methylphenylalanine-induced hyperphenylalaninaemia (HYP) on the lysosomal protein degradation system in brain and liver of suckling rats was investigated. In both tissues cathepsind andl activities, measured at 5, 10 and 15 days post partum (p.p.), exhibited no differences between experimental and control animals.N-Acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase (NAGase) activity in brain, measured at 10 and 15 days p.p., was not affected by HYP either. The release of valine and lysine from liver and brain homogenates respectively, serving as a measure for the lysosomal content of degradable proteins, was not influenced by HYP. Lysosomal integrity during incubation of homogenate was monitored by the recovery of NAGase activity in the cytosolic supernatant, and by the relative NAGase activity in total homogenates in the absence of the lysosome disrupting detergent Triton X-100. In conclusion, experimental HYP appears unlikely to influence the lysosomal protein degradation system in brain and liver of suckling rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrett, A. J. Cathepsin D and other carboxyl proteinases. In Barrett, A. J. (ed.)Proteinases in Mammalian Cells and Tissues, North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1977, pp. 209–248
Binek, P. A., Johnson, T. C. and Kelly, C. J. Effect of α-methylphenylalanine and phenylalanine on brain polyribosome and protein synthesis.J. Neurochem. 36 (1981) 1476–1484
Carroll, M. Characterization of proteins structurally related to humanN-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase.Biochem. J. 173 (1978) 191–196
Hughes, J. V. and Johnson, T. C. The effects of phenylalanine on amino acid metabolism and protein synthesis in brain cellsin vitro.J. Neurochem. 26 (1976) 1105–1113
Huether, G., Schott, K., Sprotte, U., Thoemke, F. and Neuhoff, V. Regulation of the amino acid availability in developing brain. No physiological significance of amino acid competition in experimental hyperphenylalaninaemia.Int. J. Devel. Neuroscience 1 (1983) 305–318
Kelly, C. H. and Johnson T. C. Effects ofp-chlorophenylalanine and α-methylphenylalanine on amino acid uptake and protein synthesis in mouse neuroblastoma cells.Biochem. J. 174 (1978) 931–938
Kirscke, H., Langner, J., Riemann, S., Wiederanders, B., Ansorge, S. and Bohley, P. Lysosomal cystein proteinases. InProtein Degradation in Health and Diseases, Ciba Foundation Symp. 75, Excerpta Medica, 1980, pp. 15–31
Lane, J. D., Schöne, B., Langenbeck, U and Neuhoff, V. Characterization of experimental phenylketonuria: augmentation of hyperphenylalaninemia with α-methylphenylalanine andp-chlorophenylalanine.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 627 (1980) 144–156
Langner, J., Wakil, A., Zimmermann, M., Ansorge, S., Bohley, P., Kirschke, H. and Wiederanders, B. Aktivitätsbestimmung proteolytischer Enzyme mit Azocasein als Substrat.Acta Biol. Med. Germ. 31 (1973) 1–18
Lowry, O. N., Rosenbrough, N. J., Farr, A. L. and Randall, R. L. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent.J. Biol. Chem. 193 (1951) 265–275
Mortimore, G. E. Mechanisms of cellular protein catabolism.Nutr. Rev. 40 (1982) 1–12
Mortimore, G. E. and Ward, W. F. Internalization of cytoplasmatic protein by hepatic lysosomes in basal and deprivation-induced proteolytic states.J. Biol. Chem. 256 (1981) 7650–7665
Neuhoff, V. Selected micromethods for use in neurochemistry. In Lajtha, A (ed.)Handbook of Neurochemistry, Vol. 2, 2nd edn., Plenum, New York, 1982, pp. 349–396
Peters, T. J., Müller, M. and DeDuve, C. Lysosomes of the arterial wall.J. Exp. Med. 136 (1972) 1117–1139
Schmidt-Glenewinkel, T., Nomura, Y. and Giacobini, E. The conversion of lysine into piperidine, cadaverine, and pipecolic acid in the brain and other organs of the mouse.Neurochem. Res. 2 (1977) 619–637
Schworer, C. M., Shiffer, A. and Mortimore, G. E. Quantitative relationship between autophagy and proteolysis during graded amino acid deprivation in perfused rat liver.J. Biol. Chem. 256 (1981) 7652–7658
Seglen, P. O., Gordon, P. B. and Poli, A. Amino acid inhibition of the autophagic lysosomal pathway of protein degradation in isolated rat hepatocytes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 630 (1980) 103–118
Taylor, E. H. and Hommes, F. A. Effect of experimental hyperphenylalaninemia on myeline metabolism at later stages of brain development.Int. J. Neuroscience 20 (1983) 217–228
Vahvelainen, M.-L. and Oja, S. S. Kinetic analysis of phenylalanine-induced inhibition in the saturable influx of tyrosine, tryptophan, leucine and histidine into brain cortex slices from adult and 7 day-old ratsJ. Neurochem. 24 (1975) 885–892
Ward, W. F., Chua, B. L., Li, J. B., Morgan, H. E. and Mortimore, G. E. Inhibition of basal and deprivation-induced proteolysis by leupeptin and pepstatin in perfused rat liver and heartBiochem.Biophys. Res. Comm. 87 (1979) 92–98
Žanić-Grubišić, T., Lipovac, K. and Juretić, D. Lysosomal enzyme activities in rats with experimental hyperphenylalaninemiaJ. Inher. Metab. Dis. 5 Suppl. 1 (1982) 43–44
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schröter, J., Schott, K.J., Purtill, M.A. et al. Lysosomal protein degradation in experimental hyperphenylalaninaemia. J Inherit Metab Dis 9, 273–282 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01799660
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01799660