Summary
Wistar rats from the same litter were randomly divided into four groups and received subcutaneously from the 6th to 28th daypost partum one of the following drugs:l-proline, methylmalonate,l-phenylalanine plus α-methylphenylalanine, or equivalent volumes of 0.9% (w/v) saline (controls). On day 30, the animals were killed, the brain was removed and the cerebral cortex and cerebellum was immediately dissected.
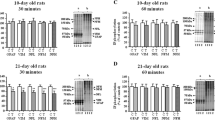
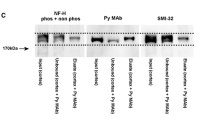
Total intermediate filament fraction (IF) was obtained from cerebral cortex and cerebellum by using a high-salt phosphate-buffered solution supplemented by 1% Triton X-100. The pellet contained the bulk of the IF proteins. Following SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, these proteins were identified as the 200, 150 and 68 kD subunits of neurofilaments (NF-H, NF-M and NF-L, respectively), the 66 kDa associated protein, the 57 kDa intermediate filament-like protein and the 52 kDa glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). They were further scanned through densitometry from enriched fractions of controls and of animals treated with the various drugs in order to determine the effects of the treatments on their concentration. Our results showed that the concentration of IF protein in cerebellum was not affected by the treatments, whereas chronic administration of all drugs significantly decreased NF-H subunit concentration in rat cerebral cortex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benson PF, Fensom AH (1985) Disorders of proline and hydroxyproline metabolism. In Benson PF, Fensom AH eds.Genetic Biochemical Disorders. New York: Oxford University Press, 243–245
Bulfield G (1980) Inherited metabolic disease in laboratory animals: a review.J Inher Metab Dis 3: 133–143
Chiu F-C, Norton W (1982) Bulk preparation of CNS cytoskeleton and the separation of individual neurofilament proteins by gel filtration: dye-binding characteristics and amino acid composition.J Neurochem 39: 1252–1260
Chiu F-C, Bornes EA, Das K et al (1989) Characterization of a novel 66 kD subunit of mammalian neurofilaments.Neuron 2: 1435–1445
Davis JL, Cherkin A (1977) Intraventricularl-proline induces retrograde amnesia in mice.IRCS Med Sci 5: 88–94
Dutra JC, Wajner M, Wannmacher CF, Dutra-Filho CS, Wannmacher CMD (1991a) Effects of methylmalonate and propionate on uptake of glucose and ketone bodies in vitro by brain of developing rats.Biochem Med Metab Biol 45: 56–64
Dutra JC, Wajner M, Wannmacher CMD, Wannmacher LE, Pires RF, Rosa A Jr (1991b) Effect of postnatal methylmalonate administration on adult rat behavior.Brazil J Med Biol Res 24: 595–605
Greengard O, Yoss MS, Delvalle JR (1976) Alpha-methylphenylalanine, a new inducer of chronic hyperphenylalaninemia in suckling rats.Science 192: 1007–1008
Keller E, Davis JL, Tachiki KH, Cummins J, Baxter CF (1981)l-proline inhibition of glutamate release: possible involvement in memory formation.J Neurochem 37: 1335–1337
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of the bacteriophage T4.Nature 277: 680–685
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent.J Biol Chem 193: 265–267
Mollica F, Pavone L (1976) Hyperprolinemia: a disease which does not need treatment?Acta Paediatr Scand 65: 206–208
Moreira JCF, Wannmacher CMD, Costa SM, Wajner M (1989) Effect of proline administration on rat behaviour in aversive and nonaversive tasks.Pharmacol Biochem Behav 32: 885–890
O'Farrell PH (1975) High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins.J Biol Chem 250: 4007–4021
Parysek LM, Goldman RD (1988) Distribution of a novel 57 kD intermediate filament protein in the nervous system.J Neurosci 8: 555–563
Paz MM, Valente GB, Tasca CI, de Mattos AG, Pessoa-Pureur R (1991) Malnutrition induces an increase in intermediate filament protein content of rat cerebral cortex.J Nutr 121: 1349–1354
Pureur RP, Coffe G, Soyer-Gobillard M-O, de Billy F, Pudles J (1986) A network of 2–4 nm filaments found in sea urchin smooth muscle.Exp Cell Res 162: 63–76
Scriver CR, Kaufman S, Woo SLC (1989) The hyperphenylalaninemias. In Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D eds.The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease, 6th edn. New York: McGraw-Hill, 495–546
Shaw G, Weber K (1982) Differential expression of neurofilament triplet proteins in brain development.Nature 298: 277–279
Shea TB, Clarke JF, Weelock TR, Paskevich PR, Nixon RA (1989) Aluminium salts induce the accumulation of neurofilaments in perikarya of NB2 a/dI neuroblastoma.Brain Res 492: 53–64
Sihag RK, Nixon RA (1989) In vivo phosphorylation of distinct domains of the 70-kilodaltons neurofilament subunit involves different protein kinases.J Biol Chem 264: 457–464
Strupp BJ, Cevitsry DR, Blumstein L (1984) PKU, learning and models of mental retardation.Dev Psychobiol 17: 109–120
Wajner M, Brites EC, Dutra JC et al (1988) Diminished concentration of ganglioside N-acetylneuraminic acid (G-NeuRc) in cerebellum of young rats receiving chronic administration of methylmalonic acid.J Neurol Sci 85: 233–238
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rubin, M.A., Wannmacher, C.M.D., Valente, G.B. et al. Diminished concentration of the NF-H subunit of neurofilaments in cerebral cortex of rats chronically treated with proline, methylmalonate and phenylalanine plus α-methylphenylalanine. J Inherit Metab Dis 15, 252–260 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01799639
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01799639