Summary
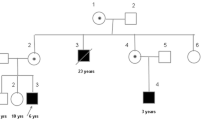
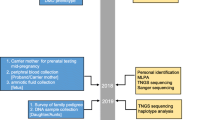
Application of molecular genetic techniques has greatly increased diagnostic possibilities of hereditary disorders. In 1983 the first linkage of Duchenne muscular dystrophy with flanking DNA probes was described, which made carrier detection possible in a limited number of cases. The first published prenatal diagnosis for Duchenne muscular dystrophy dates from 1985. DNA-analysis for Duchenne muscular dystrophy and Becker muscular dystrophy has become increasingly informative, firstly by the development of more flanking markers, followed by intragenic probes detecting deletions and, more recently, by the use of cDNA probes detecting a deletion or duplication mutation in over 60% of the Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy patients. Although these developments allow a highly reliable (>99%) carrier detection and prenatal diagnosis in over 90% of cases, the continuing introduction of new probes and/or technologies has necessitated constant reappraisal of many families to derive maximum information. During the past 3 years we applied prenatal diagnosis for Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies with DNA-analysis on 53 male fetuses in 47 families. Twenty-two healthy male babies were born, after being diagnosed to have a low Duchenne muscular dystrophy risk. Two pregnancies also diagnosed as low risk have not yet come to term. In the other cases a high risk for Duchenne muscular dystrophy was found and the parents chose abortion. Our studies also revealed a number of important diagnostic pitfalls, such as non-paternity, karyotypic anomalies and gonadal mosaicism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakker, E., Hofker, M. H., Goor, N., Mandel, J. L., Davies, K. E., Kunkel, L. M., Willard, H. F., Fenton, W. A., Sandkuyl, L. Majoor-Krakauer, D. van Essen, A. J., Jahoda, M., Sachs, E. S., van Ommen, G. J. B. and Pearson, P. L. Prenatal diagnosis and carrier detection of Duchenne muscular dystrophy with closely linked RFLP's.Lancet 1 (1985) 655–658
Bakker, E., Bonten, E. J., de Lange, L. F., Veenema, H., Majoor-Krakauer, Hofker, M. H., van Ommen, G. J. B., Pearson, P. L. DNA probe analysis for carrier detection and prenatal diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy: A standard diagnostic procedure.J. Med. Genet. 23 (1986) 573–580
Bakker, E., Van Broeckhoven, Ch., Bonten, E. J., Van de Vooren, M. J., Veenema, H., Van Hul, W., Van Ommen, G. J. B., Vandenberghe, A. and Pearson, P. L. Germline mosaicism and Duchenne muscular dystrophy mutations.Nature, 328 (1987) 554–556
Bakker, C., Veenema, H., den Dunnen, J. T., Van Breechhoven, C., Grootschalten, P. M., Bouten, E. J., van Ommen, G. J. B. and Pearson, P. L. Germinal mosaicism increases the recurrence risk for “new” DMD mutations.J. Med. Genet. (1989) in press
Boyd, Y., Buckle, V., Holt, S., Munro, E., Hunter, D., and Graig, I. Muscular dystrophy in girls with X:autosome translocations.J. Med. Genet. 23 (1986) 484–490
Bullock, D. G., McSweeney, F. M., Whitehead, T. P. and Edwards, J. H. Serum creatine kinase activity and carrier status for Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Lancet 2 (1979) 1151
Burghes, A. H. M., Logan, C., Hu, X., Belfall, B., Worton, R. G., and Ray, P. N. A cDNA clone from the Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy gene.Nature 328 (1987) 434–437
Burmeister, M., Monaco, A. P., Gillard, E. F., van Ommen, G. J. B., Affara, N. A., Ferguson-Smith, M. A., Kunkel, L. M. and Lehrach, H. A 10-megabase physical map of human Xp21, including the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene.Genomics 2 (1988) 189–202
Chelly, J., Kaplan, J. C., Maire, P., Gautron, S. and Kahn, A. Transcription of the dystrophin gene in human muscle and non-muscle tissues.Nature 333 (1988) 858–860
Darras, B. T., Harper, J. F., and Francke, U. Prenatal diagnosis and carriers with DNA probes in Duchenne's muscular dystrophy.N. Engl. J. Med. 316 (1987) 985–992
Darras, B. T. and Francke, U. A partial deletion of the muscular dystrophy gene transmitted twice by an unaffected male.Nature 329 (1987) 556–558
Darras, B. T., Koenig, M., Kunkel, L. M. and Francke, U. Direct method for prenatal diagnosis and carrier detection in Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy using the entire dystrophin cDNA.Am. J. Med. Genet. 29 (1988) 713–726
Davies, K. E., Pearson, P. L., Harper, P. S.et al. Linkage analysis of two cloned DNA sequences flanking the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus on the short arm of the human X-chromosome.Nucl. Acids Res. 11 (1983) 2303–2312
Dunnen, J. T. den, Bakker, E., Klein Breteler, E. G., Pearson, P. L., and van Ommen, G. J. B. Direct detection of more than 50% of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy mutations by field inversion gels.Nature 329 (1987) 640–642
Emery, A. E. H. Duchenne muscular dystrophy. In: Motulski, A. G., Harper, P. S., Bobrow, M. and Scriver, C. (Eds.)Oxford Monographs on Medical Genetics, No. 15, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1987
Francke, U., Ochs, H. D., de Martinville, B.et al. Minor Xp21 chromosome deletion in a male associated with expression of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, chronic granulomatous disease, retinitis pigmentosa and McLeod syndrome.Am. J. Hum. Genet. 37 (1985) 250–267
Forrest, S. M., Cross, G. S., Thomas, N. S. T., Harper, P. S., Smith, T. J., Read, A. P., Mountford, R. C., Geirsson, R. T. and Davies, K. E. Effective strategy for prenatal prediction of Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy.Lancet 1 (1987) 1294–1296
Greenberg, C. R., Rohringer, M., Jacobs, H. K., Averill, N., Nylen, E., van Ommen, G. J. B., and Wrogemann, K. Gene studies in newborn males with Duchenne muscular dystrophy detected by neonatal screening.Lancet 2 (1988) 425–427
Hoffman, E. P., Monaco, A. P., Feener, C. C., and Kunkel, L. M. Conservation of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene in mice and humans.Science 238 (1987a) 347–350
Hoffman, E. P., Brown, R. H., Kunkel, L. Dystrophin: The protein product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus.Cell 51 (1987b) 919–928
Jeffreys, A. J., Wilson, V., and Thein, S. L. Individual-specific ‘fingerprints’ of human DNA.Nature 316 (1985) 76–79
Kedes, L. H. The Duchenne dystrophy gene: A great leap forward on the long march.Trends Genet. 1 (1985) 205–209
Kingston, H. M., Harper, P. S., Peason, P. L., Davies, K. E., Williamson, R., and Page, D. Localization of the gene for Becker muscular dystrophy.Lancet 2 (1983) 1200
Koenig, M., Hoffman, E. P., Bertelson, C. J., Monaco, A. P., Feener, C. and Kunkel, L. M. Complete cloning of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) cDNA and preliminary genomic organization of the DMD gene in normal and affected individuals.Cell 50 (1987) 509–517
Koenig, M., Monaco, A. P., and Kunkel, L. M. The complete sequence of dystrophin predicts a rod-shaped cytoskeletal protein.Cell 53 (1988) 219–228
Kunkel, L. M., Monaco, A. P., Middlesworth, W.et al. Specific cloning of DNA fragments from the DNA from a patient with an X-chromosome deletion.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82 (1985) 82 4778–4782
Kunkel, L. M. and co-authors. Analysis of deletions in DNA from patients with Becker and Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Nature 322 (1986) 73–77
Monaco, A. P., Bertelson, C. J., Middlesworth, W.et al. Detection of deletions spanning the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus using a tightly linked DNA segment.Nature 316 (1985) 845–848
Monaco, A. P., Neve, R. L., Colletti-Feener, C. A., Bertelson, C. A., Kurnit, D. M. and Kunkel, L. M. Isolation of candidate cDNAs for portions of the Duchenn muscular dystrophine gene.Nature 323 (1986) 646–650
Monaco, A. P., Bertelson, C. J., Liechti-Gallati, S., Moser, H. and Kunkel, L. M. An explanation for the phenotypic differences between patients bearing partial deletions of the DMD locus.Genomics 2 (1988) 90–95
van Ommen, G. J. B., Bertelson, C., Ginjaar, H. B., Den Dunnen, J. T., Bakker, E., Chelly, J., Matton, M., Van Essen, A. J., Bartley, J., Kunkel, L. M. and Pearson, P. L. Long-range genomic map of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) gene: Isolation and use of J66 (DXS268), a distal intragenic marker.Genomics 1 (1987) 329–336
Ray, P. N., Belfall, B., Duff, C.et al. Cloning of the breakpoint of an X;21 translocation associated with Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Nature 318 (1985) 672
Verellen-Dumoulin, C. H., Freund, M., de Meyer, R.et al. Expression of an X-linked muscular dystrophy in a female due to translocation involving Xp21 and non-random inactivation of the normal X-chromosome.Hum. Genet. 67 (1984) 115–119
Wapenaar, M. C., Kievits, T., Hart, K. A., Abbs, S., Blonden, L. A. J., Den Dunnen, J. T., Grootscholten, P. M., Baaker, E., Verellen-Dumoulin, C., Bobrow, M., van Ommen, G. J. B. and Pearson, P. L. A deletion hot spot in the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene.Genomics 2 (1988) 101–108
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bakker, E., Bonten, E.J., Veenema, H. et al. Prenatal diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy: A three-year experience in a rapidly evolving field. J Inherit Metab Dis 12 (Suppl 1), 174–190 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01799293
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01799293