Summary
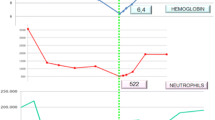
Data on the efficacy and safety of pentavalent antimony in the treatment of visceral leishmaniasis during pregnancy are scanty. A case of visceral leishmaniasis in a 39-year-old woman in the second trimester of pregnancy is reported here. The patient was hospitalized in poor condition with high fever and pancytopenia which had lasted for 6 weeks. A bone marrow aspirate revealed numerous amastigotes and serodiagnosis forLeishmania was positive at a high titer. The patient was successfully treated with meglumine anti-moniate at a daily dose of 850 mg of antimony for 20 days. She delivered at term a healthy female baby who remains in good condition at 18 months of age. Thus a dose of 850 mg of antimony, which is lower than that presently recommended, seems to be effective and non toxic to the fetus when administered at the second trimester of pregnancy.
Zusammenfassung
Zur Behandlung der Leishmaniasis mit pentavalenten Antimon in der Schwangerschaft liegen nur spärliche Daten vor. Bei einer 39 Jahre alten Frau trat im zweiten Schwangerschaftstrimester eine viszerale Leishmaniasis auf. Die Patientin wurde in schlechtem Zustand mit hohem Fieber und Panzytopenie, die schon über 6 Wochen bestanden hatten, stationär aufgenommen. Im Knochenmarkpunktat fanden sich zahlreiche Amastigoten, die Serodiagnose war hochtitrig-positiv fürLeishmania. Die Patientin wurde erfolgreich mit Meglumin Antimonat mit einer täglichen Dosis von 850 mg Antimon behandelt. Diese Dosis liegt unterhalb der derzeit empfohlenen Dosis, doch scheint sie wirksam und nicht fetotoxisch zu sein, wenn sie im zweiten Schwangerschaftstrimester verabreicht wird.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berman, J. D. Chemotherapy for leishmaniasis: biochemical mechanisms, clinical efficacy, and future strategies. Rev. Infect. Dis. 10 (1988) 560–586.
Rosenblatt, J. E. Symposium on antimicrobial agents. Antiparasitic agents. Mayo Clin. Proc. 67 (1992) 276–287.
Olliaro, P. L., Bryceson, A. D. M. Practical progress and new drugs for changing patterns of leishmaniasis. Parasitology Today 9 (1993) 323–328.
Massip, P., Goutner, Ch., Dupic, Y., Navarrot, P. Kala-Azar chez la femme enceinte. Presse Méd. 20 (1986) 95.
Nyakundi, P. M., Muigai, R., Were, J. B. O., Oster, C. N., Gachihi, G. S., Kirigi, G. Congenital visceral leishmaniasis: case report. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 82 (1988) 564.
Yadav, T. P., Gupta, H., Satteya, U., Kumar, R., Mittal, V. Congenital kala-azar. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 83 (1989) 535–537.
Kaplanski, G., Farnarier, C., Durand, J., Soubeyrand, J., Bongrand, P., Kaplanski, S. Leishmaniasis acquired in Belgium. Lancet 338 (1991) 885.
Eltoum, I. A., Zijlstra, E. E., Ali, M. S., Ghalib, H. W., Satti, M. M. H., Eltoum, B., El-Assan, A. M. Congenital kala-azar and leishmaniasis in the placenta. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 46 (1992) 57–62.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Utili, R., Rambaldi, A., Tripodi, M.F. et al. Visceral leishmaniasis during pregnancy treated with meglumine antimoniate. Infection 23, 182–183 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01793862
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01793862