Summary
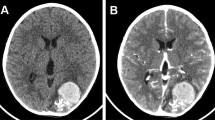
The authors investigated the validity of noncontrast computerized tomography (NCCT) to predict the presence of arteriovenous malformations (AVM) as a cause of intracerebral haemorrhage (ICH) in the acute stage. They found a small iso- or slightly hyperdense nodular or tubular defect devoid of haematoma in its periphery on NCCT in 8 of the 13 AVM cases that underwent both NCCT and contrast CT. This CT finding was named “nidus sparing sign” (NSS). This haematoma-free notch was enhanced on contrast infusion and confirmed to correspond to the AVM nidus surgically and pathologically. In one case with negative angiograms, a small AVM was verified histologically within the tissue corresponding to the NSS.
The NSS noted on the NCCT could be of great value in case emergency surgery is needed for comatose patients with ICH, particularly lobar ICH, without enough time left to undergo angiography and/or magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosurgeons are able to safely perform an evacuation of the haematoma keeping in mind the possibility of a ruptured AVM and if so, the spatial relationship between the AVM nidus and the haematoma. This might also be a valuable CT sign in deciding whether or not angiography should be undertaken in ICH cases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell BA, Kendall BE, Symon L (1978) Angiographically occult arteriovenous malformations of the brain. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 41: 1057–1064
Bradley WG, Waluch V, Yadley RA, Wycoff RR (1984) Comparison of CT and MR in 400 patients with suspected disease of the brain and cervical spinal cord. Radiology 152: 695–702
Brant-Zawadzki M, Davis PL, Crocks LE, Mills CM, Norman D, Newton TH, Sheldon P, Kaufmann L (1983) NMR demonstration of cerebral abnormalities: comparison with CT. AJR 140: 847–854
Brunelle FOS, Harwood-Nash DCF, Fritz CR, Chuang SH (1983) Intracranial vascular malformations in children: CT and angiographic evaluation. Radiology 149: 455–461
Butzer JF, Cancilla PA, Cornell SH (1976) Computerized axial tomography of intracerebral hematoma. A clinical and neuropathological study. Arch Neurol 33: 206–214
Chen MN, Nakazawa S, Ikeda Y, Murayama K (1985) CT findings of intracranial AVM. CT Kenkyu 7: 671–675 (Jpn)
Crowell RM, Ojemann RG (1981) Surgery for brain hemorrhage. In: Moossy J, Reinmuth OM (eds) Cerebrovascular diseases: twelfth research (Princeton) conference. Raven Press, New York, pp 233–254
Crowell RM (1985) Comments on Ref. 30. Neurosurgery 17: 556
DeLaPaz RL, New PFJ, Buouanno FS, Kistler JP, Oot RF, Rosen BR, Taveras JM, Brady TJ (1984) NMR imaging of intracranial hemorrhage. J Comput Assist Tomogr 8: 599–607
Fujita K, Shirakuni T, Masumura M, Matsumoto S (1986) MRI in arteriovenous malformation. CT Kenkyu 6: 653–659 (Jpn)
Gomori JM, Grossman RI, Goldberg HI, Zimmerman RA, Bilaniuk LT (1985) Intracranial hematomas: Imaging by high field MR. Radiology 157: 87–93
Gomori JM, Grossman RI, Goldberg HI, Hackery DB, Zimmerman RA, Bilaniuk LT (1986) Occult cerebral vascular malformations: high-field MR imaging. Radiology 158: 707–713
Hayman LA, Fox AJ, Evans RA (1981) Effectiveness of contrast regimens in CT detection of vascular malformations of the brain. AJNR 2: 421–425
Hayward RD, O'Reilly GVA (1976) Intracerebral haemorrhage. Accuracy of computerized transverse axial scanning in predicting the underlying aetiology. Lancet 1: 1–4
Hayward RD (1976) Intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Observations after experience with computerized tomography. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 39: 1027–1033
Kendall BE, Claveria LE (1976) The use of computerized axial tomography (CAT) for the diagnosis and management of intracranial angiomas. Neuroradiology 12: 141–160
Kramer RA, Wing SD (1977) Computed tomography of angiographically occult vascular malformations. Radiology 123: 649–652
Kucharczyk W, Lemme-Pleghos L, Uske A, Brant-Zawadzki M, Dooms G, Norman D (1985) Intracranial vascular malformations: MR and CT imaging. Radiology 156: 383–389
Kumar AJ, Fox AJ, Vinuela F, Rosenbaum AE (1984) Revisited old and new CT findings in unruptured larger arteriovenous malformations of the brain. J Comput Assist Tomogr 8: 648–655
Leblanc R, Ethier R, Little JR (1979) Computerized tomography findings in arteriovenous malformations of the brain. J Neurosurg 51: 765–772
Leblanc R, Levesque M, Comair Y, Ethier R (1987) Magnetic resonance imaging of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 21: 15–20
Lee BCP, Herzberg L, Zimmerman RD, Deck MDF (1985) MR imaging of cerebral vascular malformations. AJNR 6: 863–870
Lemme-Plaghos L, Kucharczyk W, Brant-Zawadzki M, Uske A, Edwards M, Norman D, Newton TH (1986) MRI of angiographically occult vascular malformations. AJR 146: 1223–1228
Masdeu JC, Rubino FA (1984) Management of lobar intracerebral hemorrhage: Medical or surgical. Neurology (Cleve) 34: 381–383
Nemoto Y, Inoue Y, Fukuda T, Shakudo M, Hashimoto H, Matsumura Y, Takemoto K, Kida A, Fukuda H, Onoyama Y, Hakuba A, Nishimura S (1987) MRI of cerebral vascular malformations. Jpn J Clin Radiol 32: 373–378 (Jpn)
New PFJ, Ojemann RG, Davis KR, Rosen BR, Heros R, Kjellberg RN, Adams RD, Richardson EP (1986) MRI and CT of occult vascular malformations of brain. AJNR 7: 771–779
Schorner W, Bradac GB, Treisch J, Bender A, Felix R (1986) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the diagnosis of cerebral arteriovenous angiomas. Neuroradiology 28: 313–318
Terao H, Hori T, Matsutani M, Okeda R (1979) Detection of cryptic vascular malformations by computerized tomography. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg 51: 546–551
Terbrugge K, Scotti G, Ethier R, Melancon D, Tchang S, Milner C (1977) Computed tomography in intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Radiology 122: 703–705
Wakai S, Ueda Y, Inoh S, Nagai M (1985) Angiographically occult angiomas: A report of thirteen cases with analysis of the cases documented in the literature. Neurosurgery 17: 549–556
Weisberg LA (1979) Computed tomography in the diagnosis of intracranial vascular malformations. Comput-Tomogr 3: 125–132
Young IR, Bydder GM, Hall AS, Steiner RE, Worthington BS, Hawkes RC, Holland GN, Moore WS (1983) NMR imaging in the diagnosis and management of intracranial angiomas. AJNR 4: 837–838
Zimmerman RA, Bilaniuk LT, Grossman RI, Levine RS, Lynchi R, Goldberg HI, Samuel L (1985) Resistive NMR of intracranial hematomas. Neuroradiology 27: 16–20
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wakai, S., Nagai, M. “Nidus sparing sign” on computerized tomography in intracerebral haemorrhage due to a rupture of arteriovenous malformation. Acta neurochir 95, 102–108 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01790769
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01790769