Summary
-
1.
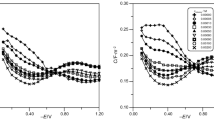
A comparative study of the effect of some macromolecules such as invertase, insulin, and albumin on the one hand and the simple molecules like isobutyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol on the other, on the dropping mercury electrode capacity has been investigated. Effect of shift of the electro-capillary zero on the magnitude of the desorption peaks have been examined taking some typical cases.
-
2.
It is found that the positive desorption peaks are enhanced by the lowering of p4. This indicates that the electro-capillary zero is shifted towards cathodio potentials at lower p4.
-
3.
At lower p4 values (1.0 and 5.0) the increase in concentration of the alcohol elevates all the desorption peaks, whereas at p4 12.3 the positive desorption peaks get progressively depressed by the increase in the concentration of the alcohols studied. These effects have been discussed.
-
4.
There is a shift of the desorption potentials to values away from the electro-capillary zero, as the concentration of the surface active substance increases.
-
5.
At p4 1.0 isobutyl alcohol gives a small intermediate peak, in addition to the usual two peaks. The magnitude of this peak increases with rise in concentration of the alcohol.
-
6.
It is to be seen that the colloids in general, though they may show sufficiently high depression of capacity due to adsorption, the desorption peaks are either small or non-existent. This is attributed to the highly sluggish movements of the macro-molecules.
Zusammenfassung
-
1.
Die Wirkungen verschiedener makromolekularer Substanzen, wie Invertase, Insulin und Albumin, einerseits und kleiner Moleküle, wie Isobutyl- und Isopropylalkohol, andererseits auf die Kapazität der Quecksilbertropfelektrode wurden verglichen. In einigen typischen Fällen ließ sich die Verlagerung des elektrokapillaren Nullpunktes in Abhängigkeit von der Höhe der Desorptionsspitzen prüfen.
-
2.
Positive Desorptionsspitzen werden bei Erniedrigung des p4-Wertes erhöht. Daher verschiebt sich mit kleineren p4-Werten der elektrokapillare Nullpunkt zu negativen Werten.
-
3.
Bei niedrigen p4-Werten zwischen 1 und 5 vergrößert steigende Alkoholkonzentration alle Desorptionsspitzen, während bei p4 12,3 die positiven Desorptionsspitzen mit wachsender Alkoholkonzentration laufend erniedrigt werden. Diese Effekte werden diskutiert.
-
4.
Wächst die Konzentration an oberflächenaktiver Substanz, so entfernen sich die Desorptionspotentiale vom elektrokapillaren Nullpunkt.
-
5.
Für p4 1 ergibt Isobutylalkohol zusätzlich zu den zwei normalen Spitzen ein kleines zwischenliegendes Maximum, dessen Höhe mit steigender Konzentration im Alkohol steigt.
-
6.
Es zeigt sich im allgemeinen, daß die Desorptionsspitzen für Kolloide entweder klein sind oder nicht existieren, obwohl die Kapazität der Elektroden entsprechend der Adsorption abnimmt. Dies ist der relativ hohen Trägheit der Makromoleküle zuzuschreiben.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kalyansundaram and Tandon, still unpublished.
Randles, Faraday Soc. Disc.1, 11 (1947).
Keilin, J. Amer. Chem. Soc,70, 1984 (1948).
Breyer and Gutman, Faraday Soc. Disc.,1, 25 (1947).
Ershler, Faraday Soc. Disc.,1, 48 (1947).
Bowden and Grew, Faraday Soc. Disc.,1, 49 (1947).
Proskurnin and Frumkin. Trans. Far. Soc.31, 110 (1935).
Grahame, Amer. Chem. Soc.68, 301 (1946).
Doss and Kalyansundaram, Proc. Indian Acad. Sc.35, 27 (1952).
Breyer and Hacobian, Austr. J. Scien. Res., Series A,5, 500 (1952).
Doss and Gupta, Proc. Indian Acad. Sc.36, 493 (1952).
Gupta, J. Sci. Ind. Res.12B, 84 (1953).
Doss and Gupta, Under Publication.
Doss and Kalyansundaram, Curr. Sci.20, 199 (1951).
Doss and Kalyansundaram, Proc. Ind. Acad. Sc.35, 173 (1952).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, S.L. Comparative study of the effect of some macro-molecules and some simple molecules on dropping mercury electrode capacity. Kolloid-Zeitschrift 137, 86–93 (1954). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01781995
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01781995