Summary
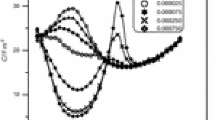
A method was devised to obtain a correct surface tension vs. equilibrium concentration curve for a very dilute solution of surface active substance, such as sodium dodecyl sulfate dissolved in an aqueous solution of saturated ammonium sulfate, where the decrease of the bulk concentration due to the adsorption is not negligible. Adsorption isotherm was obtained by applyingGibbs adsorption equation to the curve, and the pressure vs. area curve was plotted. The latter plot is in agreement with that directly measured for the spread film on saturated ammonium sulfate solution, the surface pressure of which was obtained by the extrapolation to time zero of the plot of log surface pressure vs. square root of time. The amount of calculated saturation value is in agreement with that directly measured by the radiotracer method. These agreements show the validity of the present method of obtaining surface tension and adsorption isotherms, together with the method of extrapolation to obtain the surface pressure vs. area curve for soluble film.
Zusammenfassung
Es wurde eine Methode entwickelt, die adsorbierte Menge aus hochverdünnten Lösungen von oberflächen-aktiven Substanzen — Natriumdodecylsulfat in gesättigter Ammoniumsulfatlösung-aus Oberflächenspannungs-Konzentrationskurven zu berechnen. Ferner wurde aus diesen Daten die Oberflfichendruck(F)-Fläche pro Molekül(A)-Kurve konstruiert. Sie stimmt mit derjenigen über-ein, die unmittelbar an Natriumdodecylsulfatfilmen auf der Oberflache gesattigter Ammoniumsulfatlösungen gemessen wurde. Die berechnete Menge im Sattigungswert stimmt gut mit derjenigen dberein, die nach radioaktiver Methode gemessen wurde.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cassie, A. B. D. andR. C. Palmer, Trans. Faraday Soc.37, 156 (1941). —Matijevic, E. andB. A. Pethica, Trans. Faraday Soc.54, 1382 (1958). —Lange, H., Kolloid Z.152, 155 (1957). —Tajima, K., Bull. Chem. Soc. Japan43, 3063 (1970). —Tajima, K., M. Muramatsu, andT. Sasaki, Bull. Chem. Soc. Japan43, 1991(1970).
Ter Minassian-Saraga, L., J. Colloid Sci.11, 398 (1956). —Rosano, H. L. andG. Karg, J. Phys. Chem.63, 1695 (1959). —Brady, A. P., J. Colloid S'ci.4, 417 (1949). —Seimiya, T., K. Ohbu, A. Nakamura, andT. Sasaki, Bull. Chem. Soc. Japan44, 2918 (1971).
Bull, H. B., J. Amer. Chem. Soc.67, 10 (1945).
Seimiya, T., H. Kozai, andT. Sasaki, Bull. Chem. Soc. Japan42, 2794 (1969).
Tajima, K., See ref. (1).
Tajima, K., M. Muramatsu, andT. Sasaki, See ref. (1).
Sasaki, J., T. Tajima, andT. Sasaki, Bull. Chem. Soc. Japan45, 348 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With 6 figures
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sasaki, J., Koyama, M., Seimiya, T. et al. Strong adsorption from highly dilute solution: adsorption of sodium dodecyl sulfate from saturated ammonium sulfate solution. Colloid & Polymer Sci 253, 127–131 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01775677
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01775677