Summary
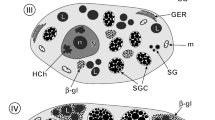
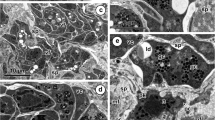
The enzyme-gold cytochemical technique was used to label RNA in the nucleolus and rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) of the hepatocytes of normal, male American bullfrogs (Rana catesbeiana) and in bullfrogs eight days following treatment with estradiol-17β. Concurrently, stereology was applied to quantitate: (1) the density of RNA labelling, and (2) changes in the size of the nucleus and nucleolus in response to estrogen treatment. In the hepatocytes from untreated frogs, specific labelling for RNA was present over the fibrillar and, to a greater extent, the granular portions of the nucleolus, and, to the greatest extent, over the RER. Following estrogen treatment, the density of RNA labelling increased over both parts of the nucleolus but was unchanged over the RER. The size of the nucleolus enlarged in response to estrogen: in combination with the increase in its RNA labelling, this suggested an increase of about 80% in the total amount of RNA in the nucleolus. Previous data on enlargement of the RER compartment, along with the present data on RNA labelling of RER, suggested that the total amount of this nucleic acid increased about 430% in this entity, in response to estrogen. However, the density of RNA labelling over the RER appears to be constant in spite of changes in the amount of RER.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ALBERTS, B., BRAY, D., LEWIS, J., RAFF, M., ROBERTS, K., & WATSON, J. D. (1983)Molecular Biology of the Cell. New York: Garland.
BENDAYAN, M. (1981) Ultrastructural localization of nucleic acids by the use of enzyme-gold complexes.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 29, 531–41.
BENDAYAN, M. (1984) Enzyme-gold electron microscopic cytochemistry: A new affinity approach for the ultrastructural localization of macromoleculesJ. Elect. Micro. Tech. 1, 349–72.
BENDAYAN, M., BRUNEAU, A. & MORISSET, J. (1985) Morphometrical and immunocytochemical studies of rat pancreatic acinar cells under control and experimental conditions.Biol. Cell 54, 227–34.
BLOBEL, G. (1987) How proteins move across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane.Hepatology 7, 26S–29S.
FARMER, S. R., HENSHAW, E. C., BERRIDGE, M. V., & TATA, J. R. (1978) Translation ofXenopus vitellogenin mRNA during primary and secondary induction.Nature 273, 401–3.
GREEN, C. D. & TATA, J. R. (1976) Direct induction by estradiol of vitellogenin synthesis in organ cultures of maleXenopus laevis liver.Cell 7, 131–9.
HAYWARD, M. A., BROCK, M. L. & SHAPIRO, D. J. (1982) The role of estrogen receptor inXenopus laevis vitellogenin gene expression.Amer. J. Physiol. 243, C1-C6.
HERBENER, G. H., FELDHOFF, R. C. & FONDA, M. L. (1983) A correlated morphometric and biochemical study of estrogen-induced vitellogenesis in maleRana pipiens.J. Ultrastructure Res. 83, 28–42.
HERBENER, G. H., BENDAYAN, M. & FELDHOFF, R. C. (1985) Immunocytochemical localization of a non-vitellogenin, estrogen-induced plasma protein in the hepatocyte of the American bullfrog,Rana catesbeiana.Eur. J. Cell Biol. 39, 142–6.
HERBENER, G. H., BENDAYAN, M. & FELDHOFF, R. C. (1986) Albumin localization in the frog hepatocyte during vitellogenesis as revealed by protein A-gold immunocytochemistry.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 34, 665–71.
HESS, P. P. (1981) The regulation of vitellogenin in the American bullfrog. M. S. Thesis, University of Louisville.
RIEGEL, A. T., MATIN, M. B. & SCHOENBERG, D. R. (1986) Transcriptional and post-transcriptional inhibition of albumin gene expression by estrogen inXenopus liver.Molec. Cell. Endocr. 44, 201–9.
SHAPIRO, D. J., BAKER, H. J. & STITT, D. T. (1976)In vitro translation and estradiol-17β induction ofXenopus laevis vitellogenin messenger RNA.J. Biol. Chem. 251, 3105–11.
SHAPIRO, D. J. & BAKER, H. J. (1977) Purification and characterization ofXenopus laevis vitellogenin messenger RNA.J. Biol Chem. 257, 5244–5250.
TATA, J. R. (1979) Control by oestrogen of reversible gene expression: The vitellogenin model.J. Steroid Biochem. 11, 361–71.
WALLACE, R. A. (1985) Vitellogenesis and oocyte growth in nonmammalian vertebrates. InDevelopmental Biology. Volume 1 (edited by L. W. BROWDER) pp 127–7. New York: Plenum.
WALTER, P. & BLOBEL, G. (1981) Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum, III. Signal recognition protein (SRP) causes signal sequence-dependent and site-specific arrest of chain elongation that is released by microsomal membranes.J. Cell Biol. 91, 557–61.
WEIBEL, E. R. (1979) Stereological Methods 1: Practical Methods for Biological Morphometry. New York: Academic Press.
WOLFFE, A. P., GLOVER, J. F., MARTIN, S. C., TENNIS-WOOD, M. R. P., WILLIAMS, J. L., & TATA, J. R. (1985) Deinduction of transcription ofXenopus 74—kDa albumin genes and destabilization of mRNA by estrogenin vivo and in hepatocyte cultures.Eur. J. Biochem. 146, 489–96.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herbener, G.H., Bendayan, M. A correlated morphometric and cytochemical study on hepatocyte nucleolar size and RNA distribution during vitellogenesis. Histochem J 20, 194–200 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01747463
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01747463