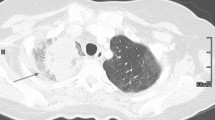
Summary
Invasive fungal infections have become an increasing problem in severely immunocompromised hosts. We here report a case of septicemia, caused byTrichosporon beigelii, an unusual pathogen of systemic infections. This infection was acquired during a period of severe neutropenia after chemotherapy for relapsed acute myelogenous leukemia following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. The patient recovered from a life-threateningT. beigelii septicemia due to early intensified treatment with amphotericin B and a rapid neutrophil recovery, enhanced by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF). According to the current literature, amphotericin B is the treatment of choice for systemicT. beigelii infections. In patients with severe granulocytopenia, the rapid recovery of neutrophils remains the most important factor for the outcome of this infection.
Zusammenfassung
Systemische Mykosen stellen ein zunehmendes Problem bei immunsupprimierten Patienten dar. Wir schildern hier den Fall eines Patienten mit einerT.-beigelii-Sepsis, ein für systemische Infektionen ungewöhnlichen Erreger, der in einer Phase ausgeprägter Neutropenie nach Chemotherapie eines Rezidives einer akuten myeloischen Leukämie nach allogener Knochenmarktransplantation erworben wurde. Dieser Patient überlebte die lebensbedrohliche Infektion aufgrund einer frühzeitig initiierten, hochdosierten Therapie mit Amphotericin B und eines raschen Anstiegs der neutrophilen Granulozyten, induziert durch den Granulozyten-Kolonien stimulierenden Wachstumsfaktor (G-CSF). Therapie der Wahl für systemischeT. beigelii-Infektionen ist Amphotericin B. Bei Patienten mit ausgeprägter Neutropenie ist der rasche Anstieg der Granulozyten ein entscheidendes Kriterium für den Verlauf der Infektion mitT. beigelii.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meunier, F. Infections in patients with acute leukemia and lymhoma. In:Mandell, G. L., Douglas R. G., Bennett J. E. (eds.): Principles and practice of infectious diseases. Churchill Livingstone, New York 1990, pp. 2265–2275.
Brown, A. E. Overview of fungal infections in cancer patients. Semin. Oncol. 17 (1990) 2–5.
Maschmeyer, G., Link, H., Meyer, P., Helmerking, M., Schmitt, J., Adam, D.: Treatment of lung infiltrates in patients with severe neutropenia — results in 269 patients from a multicenter trial. Ann. Hematol. 65 (1992) A251.
Meyer, P., Adam, D., Hiddemann, W., Link, H., Maschmeyer, G., Helmerking, M. Interventionstherapie von Infektionen und Fieber unklarer Genese bei neutropenischen Patienten mit malignen hämatologischen Grunderkrankungen. Z.A.C. 10 (1992) 1–27.
Crawford, J., Ozer, H., Stoller, R. Reduction by granulocyte colonystimulating factor of fever and neutropenia induced by chemotherapy in patients with small cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 325 (1991) 959–967.
Lieschke, G. J., Burgess, A. W. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. N. Engl. J. Med. 327 (1992) 28–35, 99–106.
Morace, G., Manzara, S., Dettoni, G. In vitro susceptibility of 119 yeast isolates to fluconazole, 5-fluorocytosine, amphotericin B and ketoconazole. Chemotherapy 91 (1991) 23–31.
Lowenthal, R. M., Atkinson, K., Challis, D. R., Tucker, R. G., Biggs, J. C. InvasiveTrichosporon cutaneum infection: an increasing problem in immunosuppressed patients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2 (1987) 321–327.
Walsh, T. J., Melcher, G. P., Rinaldi, M. G., Lecciones, J., McGouth, D. A., Kelly, P., Lee, J., Callender, D., Rubin, M., Pizzo, P. A. Trichosporon beigelii, an emerging pathogen resistant to amphotericin. Br. J. Clin. Microbiol. 28 (1990) 1616–1622.
Siegert, W., Henze, G., Wagner, J., Rodloff, A., Zimmermenn, R., Malchus, R., Schwerdtfeger, R., Reichelt, A., Graef, K., Huhn, D. InvasiveTrichosporon cutaneum (beigelii) infection in a patient with relapsed acute myeloid leukemia undergoing bone marrow transplantation. Transplantation 46 (1988) 151–153.
Ogata, K., Tanabe, Y., Iwakiri, K., Ito, T., Yamada, T., Dan, K., Nomura, T. Two cases of disseminatedTrichosporon beigelii infection treated with combination antifungal therapy. Cancer 65 (1990) 2793–2795.
Marin, J., Chiner, E., Franco, J., Borras, R. Trichosporon beigelii pneumonia in a neutropenic patient. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 8 (1989) 631–633.
Parsonnet, J. Trichosporon beigelii peritonitis. South. Med. J. 82 (1989) 1062–1063.
Reinhart, H. H., Urbanski D. M., Harrington, S. D., Sobel J. D. Prosthetic valve endocarditis caused byTrichosporon beigelii. Am. J. Med. 84 (1988) 355–358.
Ness, M. J., Markin, R. S., Wood, R. P., Shaw, B. W., Woods, G. L. DisseminatedTrichosporon beigelii infection after orthotopic liver transplantation. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 92 (1989) 119–123.
Anaissie, E., Bodey, G. P., Kantarjian, H., Ro, J., Vartivarian, S. E., Hopfer, R., Hoy, J., Rolston, K. New spectrum of fungal infections in patients with cancer. Rev. Infect. Dis. 11 (1989) 369–378.
Anaissie, E., Gokaslan, A., Hachem, R., Rubin, R., Grittin, G., Robinson, R., Sobel, J., Bodey, G. Azole therapy for trichosporonosis: clinical evaluation of eight patients, experimental therapy for murine infection, and review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 15 (1992) 781–787.
Lipp, H. P., Schuler, U., Saal, I., Schaaf, D. Amphotericin B in Fettemulsionen. Arzneimitteltherapie 11 (1993) 319–326.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grauer, M.E., Bokemeyer, C., Bautsch, W. et al. Successful treatment of aTrichosporon beigelii septicemia in a granulocytopenic patient with amphotericin B and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Infection 22, 283–286 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01739918
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01739918