Summary
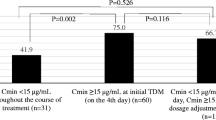
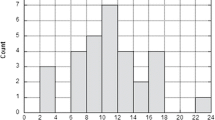
In order to establish guidelines for the dosage of teicoplanin, a new glycopeptide antibiotic, in patients with end stage renal failure, 40 cases of suspected or proven gram-positive infections were treated with teicoplanin. Three different dosage regimens were used and peak/trough serum levels measured. Thirty-one patients were cured and six patients died. Teicoplanin was well tolerated. For severe cases of septicemia with staphylococci in patients undergoing hemodialysis a teicoplanin therapy consisting of 800 mg on day 1 followed by administrations of 400 mg on days 2, 3, 5, 12, and 19 is recommended. Minor infections are treated initially with 800 mg followed by administration of 400 mg at weekly intervals.
Zusammenfassung
Mit dem Ziel, Richtlinien für die Dosierung von Teicoplanin, einem neuen Glykopeptidantibiotikum, bei chronischer Niereninsuffizienz aufzustellen, wurden 40 Fälle von vermuteter oder nachgewiesener Infektion mit grampositiven Erregern mit Teicoplanin behandelt. Drei verschiedene Dosierungen wurden untersucht und die Spitzen- und Talserumspiegel gemessen. 31 Patienten wurden geheilt und sechs Patienten verstarben. Die Substanz wurde gut vertragen. In schweren Fällen von Sepsis verursacht durch Staphylokokken wird eine initiale Behandlung mit 800 mg gefolgt von 400 mg am 2., 3., 5., 12. und 19. Tag empfohlen. Mildere Verläufe werden initial mit 800 mg gefolgt von 400 mg in wöchentlichen Abständen behandelt.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Faßbinder, W. Langzeitergebnisse bei Dialysepatienten. In:Franz, H. E. (ed.): Blutreinigungsverfahren. Technik und Klinik. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart, New York 1990, pp. 494–499.
Brodersen, H. P., Beckers, B., Hoyme, H., Larbig, D. Bakteriämien bei Patienten mit verschiedenen Formen des Nierenversagens. Nieren-und Hochdruckkrankh. 17 (1988) 315–320.
Keane, W. F., Raij, L. R. Host defenses and infectious complications in maintenance hemodialysis patients. In:Drukker, W., Parsons, F. M., Maher, J. F. (eds.): Replacement of renal function by dialysis. Martinus Nijhoff, Boston 1983, pp. 646–658.
Brumfitt, W., Hamilton, J. M., Miller, T. The world wide problem of methicillin-resistance. Drugs Exp. Clin. Res. 15 (1990) 205–214.
Brodersen, H. P., Beckers, B., Stolpmann, R. M., Willkomm, F. J., Jansen, G., Larbig, D. Grampositive Septikämie bei Patienten mit terminaler Niereninsuffizienz und ihre Behandlung mit Teicoplanin. Intensivmed. 28 (1991) 356–359.
Brodersen, H. P., Beckers, B., Stolpmann, R. M., Larbig, D., Jansen, G. Calculated teicoplanin therapy in hemodialysis patients and dosage recommendations for repeated doses. Zeitschr. Antimikrob. Antineopl. Chemother. 8 (1990) 39–42.
Höffler, D. Dialyse und Medikamente. In:Franz, H. E. (ed.): Blutreinigungsverfahren. Technik und Klinik. Georg Thieme-Verlag Stuttgart, New York 1990, pp. 331–346.
Höffler, D., Koeppe, P., Naumann, E., Lang, E., Sörgel, F. Pharmacokinetics of teicoplanin in hemodialysis patients. Infection 19 (1991) 324–327.
Bowley, J., Pickering, S. J., Scantlebury, A. J., Ackrill, P., Jones, D. M. Intraperitoneal teicoplanin in the treatment of peritonitis associated with continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 21 (Suppl. A) (1988) 133–139.
Lewis, P., Garand, J. J., Parenti, F. A multicentre open clinical trial of teicoplanin in infections caused by gram-positive bacteria. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 21 (Suppl. A) (1988) 61–79.
Simon, C., Stille, W. Antibiotikatherapie in Klinik und Praxis. Schattauer Verlag, Stuttgart, New York 1989, p. 202.
Stille, W., Sietzen, W., Dietrich, H. A., Tell, J. J. Clinical efficacy and safety of teicoplanin. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 21 (Suppl. A) (1988) 69–79.
Kureishi, A., Jewesson, P. J., Cole, C. D., Reece, D. E., Phillips, G. L.: The nephrotoxic potential of teicoplanin vs. vancomycin in the empiric treatment of febrile neutropenic patients. 29th Intersc. Conf. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., Houston, Texas, USA, 1989. Abstract no. 0597.
Sahai, J., Healy, D. P., Shelton, M. J., Miller, J. S., Ruberg, S. J., Polk, R. Comparison of vancomycin- and teicoplanin-induced histamine release and “Red Man Syndrome.” Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 34 (1990) 765–769.
Buniva, G., Del Favero, A., Bernareggi, A., Patoia, L., Palumbo, R. Pharmacokinetics of14C-teicoplanin in healthy volunteers. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 21 (Suppl. A) (1988) 23–28.
Domart, Y., Pierre, C., Claire, B., Garand, J. J., Regnier, B. Pharmacokinetics of teicoplanin in critically ill patients with various degrees of renal impairment. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 31 (1987) 1600–1604.
Traina, G. L., Bonati, M. Pharmacokinetics of teicoplanin in man after intravenous administration. J. Pharmacokinet. and Biopharm. 12 (1984) 119–128.
Verbist, L., Tjandramaga, B., Hendrickx, B., van Hecken, A. N., van Meile, P. In vitro activity and human pharmacokinetics of teicoplanin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 26 (1984) 881–886.
Traina, G. L., Gentile, M. G., Fellin, G., Rosina, R., Cavenaghi, L. Pharmacokinetics of teicoplanin in patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 31 (1986) 501–504.
Bonati, M., Traina, G. L., Rosina, R., Buniva, G. Pharmacokinetics of a single intravenous dose of teicoplanin in subjects with various degrees of renal impairment. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 21 (Suppl. A) (1988) 29–37.
Falcoz, C., Ferry, N., Pozet, N., Cuisinand, G., Zech, P. Y. Pharmacokinetics of teicoplanin in renal failure. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 31 (1987) 1255–1262.
Wopperer, J., Pilgrim, R., Stolpmann, R., Muth, P., Sörgel, F.: Pharmacokinetics of teicoplanin in renal failure patients. Dosing by experience: Inter. Congr. Chemother., Berlin, June 24–27, 1991. Abstract no. 451.
Jehl, F., Monteil, B., Tarral, A. HPLC quantitation of the six main components of teicoplanin in biological fluids. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 21 (Suppl. A) (1988) 53–59.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beckers, B., Jansen, G., Brodersen, H.P. et al. Efficacy and pharmacokinetics of teicoplanin in hemodialysis patients. Infection 21, 71–74 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01739321
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01739321