Summary
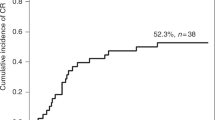
In essential thrombocythemia patients α-IFN rapidly reduces platelet count, and it is also able to maintain a low count during long-term treatment. In order to verify if long-term IFN treatment can produce sustained remission in selected patients, we decided to suspend IFN treatment in two subsets of 21 patients on long-term α-IFN treatment: (a) all six patients who had shown a platelet count below 450×109/l for at least 2 months with 3 MU once a week; (b) three patients who had shown the same platelet count for at least 2 months with 3 MU three times a week. After withdrawal of α-IFN treatment, a rapid increase in the platelet count was observed in all three patients requiring 3 MU three times a week. Three of the six patients treated with 3 MU once a week are still free of symptoms and have been in complete hematological remission (platelet count below 450×109/l) for 9+, 13+, and 14+ months, respectively. As far as the three remaining cases are concerned, one was not assessable because of loss to follow-up, while the other two relapsed after 1 and 2 months. We believe that the three cases of sustained remission might be the result of a long-term tumor load reduction produced by the α-IFN treatment. Finally, the factor best able to predict sustained, unmaintained remission seems to be the clinical response to a low dose of α-IFN during the maintenance phase, rather than disease features prior to treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abegg-Werter MJBP, Raemaekers JMM, de Pauw BE, Haanen C (1990) Recombinant interferon-alpha, but not interferongamma, is effective therapy for essential thrombocythemia. Blut 60: 37–40
Chott A, Gisslinger H, Thiele J, Fritz E, Linkesch W, Radaszkiewicz T, Ludwig H (1990) Interferon-alpha induced morphological changes of megakaryocytes: a histomorphometrical study on bone marrow biopsies in chronic myeloproliferative disorders with excessive thrombocytosis. Br J Haematol 74: 10–16
Giles FJ (1991) Maintenance therapy in the myeloproliferative disorders: the current options. Br J Haematol 79 [Suppl 1]: 92–95
Gisslinger H, Chott A, Scheithauer W, Gilly B, Linkesch W, Ludwig H (1991) Interferon in essential thrombocythaemia. Br J Haematol 79 [Suppl 1]: 42–47
Kasparu H, Bernhart M, Krieger O, Lutz D (1992) Remission may continue after termination of rIFNα-2b treatment for essential thrombocythemia. Eur J Haematol 48: 33–36
Lazzarino M, Vitale A, Morra E, Gagliardi A, Bernasconi P, Torromeo C, Inverardi D, Burgio VL, Castello A, Bernasconi C, Mandelli F (1990) Therapy of essential thrombocythemia with alpha-interferon: results and prospects. Eur J Haematol 45 [Suppl 52]: 15–21
Middelhoff G, Boll I (1992) A long-term clinical trial of interferon-alpha therapy in essential thrombocythemia. Ann Hematol 64: 207–209
Sacchi S, Tabilio A, Leoni P, Riccardi A, Vecchi A, Messora C, Falzetti F, Rupoli S, Ucci G, Martelli MF (1991) Interferon alpha-2b in the long-term treatment of essential thrombocythemia. Ann Hematol 63: 206–209
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sacchi, S., Tabilio, A., Leoni, P. et al. Sustained complete hematological remission in essential thrombocythemia after discontinuation of long-term α-IFN treatment. Ann Hematol 66, 245–246 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01738473
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01738473