Summary
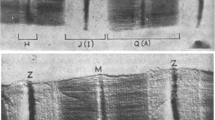
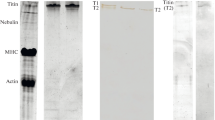
A simplified procedure to isolateα-connectin (titin 1, TI), a gigantic elastic protein, from rabbit skeletal muscle is described. A rapid column chromatography step to concentrateα-connectin is introduced. Separation ofα-connectin fromβ-connectin is introduced. Separation ofα-connectin fromβ-connectin (titin 2, TII) in the presence of 4 M urea at pH 7.0 did not cause any change in the secondary structure ofα-connectin as judged by circular dichroic spectra. Ultraviolet absorption spectra and the amino acid composition ofα-connectin (MW, approximately 3×106) were similar to those of its proteolytic product,β-connectin (MW, approximately 2×106). Circular dichroic spectra suggested that bothα- andβ-connectin consist of 60%β-sheet and 30%β-turn. It thus appears that the whole elastic filament of connectin has a foldedβ-strand structure. Proteolysis ofα-connectin by calpain resulted in formation ofβ-connectin and smaller peptides. Theα-connectin interacted with both myosin and actin filaments similarly toβ-connectin. Polyclonal antibodies raised against 1200 kDa peptides obtained from aged rabbit skeletal myofibrils reacted withα-connectin (titin 1, TI) but only weakly withβ-connectin (titin 2, TII) in rabbit skeletal muscle. Immunoelectron microscopy and indirect immunofluorescence microscopy revealed that the antibodies bound at the Z-line and at the epitope regions in the I-band near the binding site of a monoclonal antibody SMI whose position depends on sarcomere length. It thus appears thatβ-connectin extends from the edge of M-line to the above epitope region in the I-band.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benian, G. M., Kiff, J. E., Neckelmann, N., Moerman, D. G. &Waterston, R. H. (1989) Sequence of an unusually large protein implicated in regulation of myosin activity inC. elegans.Nature 342, 45–50.
Campbell, D. G., Williams, A. F., Bayley, P. M. &Reid, K. B. M. (1979) Structural similarities between Thy-1 antigen from rat brain and immunoglobulin.Nature 282, 341–42.
Funatsu, T., Higuchi, H. &Ishiwata, S. (1990) Elastic filaments in skeletal muscle revealed by selective removal of thin filaments with plasma gelsolin.J. Cell Biol. 110, 53–62.
Fürst, D. O., Osborn, M., Nave, R. &Weber, K. (1988) The organization of titin filaments in the half-sarcomere revealed by monoclonal antibodies in immunoelectron microscopy: a map of ten non-repetitive epitopes starting at the Z-line extends close to the M-line.J. Cell Biol. 106, 1563–72.
Fürst, D. O., Nave, R., Osborn, M. &Weber, K. (1989) Repetitive titin epitopes with a 42 nm spacing coincide in relative position with known A-band striations also identified by major myosin-associated proteins: an immunoelectron microscopical study on myofibrils.J. Cell Sci. 94, 119–25.
Horowits, R. &Podolsky, R. J. (1987) The positional stability of thick filaments in activated skeletal muscle depends on sarcomere length: evidence for the role of titin filaments.J. Cell Biol. 105, 2217–23.
Horowits, R., Maruyama, K. &Podolsky, R. J. (1989) Elastic behavior of connectin filaments during thick filament movement in activated skeletal muscle.J. Cell Biol. 109, 2169–76.
Hu, D. H., Kimura, S. &Maruyama, K. (1989a) Myosin oligomers as the molecular mass standard in the estimation of molecular mass of nebulin (800 kDa) by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.Biomed. Res. 10, 165–8.
Hu, D. H., Kimura, S., Kawashima, S. &Maruyama, K. (1989) Calcium activated neutral protease quickly convertsα-connectin toβ-connectin.Zool. Sci. 6, 797–800.
Itoh, Y., Suzuki, T., Kimura, S., Ohashi, K., Higuchi, H., Sawada, H., Shimizu, T., Shibata, M. &Maruyama, K. (1988) Extensible and less-extensible domains of connectin filaments in stretched vertebrate skeletal muscle sarcomere as detected by immunofluorescence and immunoelectron microscopy using monoclonal antibodies.J. Biochem. 104, 504–8.
Kimura, S. &Maruyama, K. (1983a) Preparation of native connectin from chicken breast muscle.J. Biochem. 94, 2083–5.
Kimura, S. &Maruyama, K. (1983) Interaction of native connectin with myosin and actin.Biomed. Res. 4, 607–10.
Kimura, S. &Maruyama, K. (1989) Isolation ofα-connectin, an elastic protein, from rabbit skeletal muscle.J. Biochem. 106, 952–4.
Kimura, S., Yoshidomi, H. &Maruyama, K. (1984) Proteolytic fragments of connectin cause aggregation of myosin filaments but not of actin filaments.J. Biochem. 96, 1947–50.
Kurzban, G. P. &Wang, K. (1988) Giant polypeptides of skeletal muscle titin: sedimentation equilibrium in guanidine hydrochloride.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 150, 1155–61.
Labeit, S., Barlow, D. P., Gautel, M., Gibson, T., Holt, J., Hsieh, C. L., Francke, U., Leonard, K., Wardale, J., Whiting, A. &Trinick, J. (1990) A regular pattern of two types of 100-residue motif in the sequence of titin.Nature 345, 273–6.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage-T4.Nature 227, 680–5.
Maruyama, K. (1986) Connectin, an elastic filamentous protein of striated muscle.Int. Rev. Cytol. 104, 81–114.
Maruyama, K., Kimura, S., Yoshidomi, H., Sawada, H. &Kikuchi, M. (1984) Molecular size and shape ofβ-connectin, an elastic protein of striated muscle.J. Biochem. 95, 1423–33.
Maruyama, K., Yoshioka, T., Higuchi, H., Ohashi, K., Kimura, S. &Natori, R. (1985) Connectin filaments link thick filaments and Z-lines in frog skeletal muscle as revealed by immunoelectron mycroscopy.J. Cell Biol. 101, 2167–72.
Maruyama, K., Itoh, Y. &Arisaka, F. (1986) Circular dichroism spectra show abundance ofβ-sheet structure in connectin, a muscle elastic protein.FEBS Lett. 202, 353–5.
Maruyama, K., Hu, D. H., Suzuki, T. &Kimura, S. (1987) Binding of actin filaments to connectin.J. Biochem. 101, 1339–46.
Maruyama, K., Matsuno, A., Higuchi, H., Shimaoka, S., Kimura, S. &Shimizu, T. (1989) Behaviour of connectin (titin) and nebulin in skinned muscle fibres released after extreme stretch as revealed by immunoelectron microscopy.J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 10, 350–9.
Murayama, T., Nakauchi, Y., Kimura, S. &Maruyama, K. (1989) Binding of connectin to myosin filaments.J. Biochem. 105, 323–6.
Matsuno, A., Takano-Ohmuro, H, Itoh, Y., Matsuura, T., Shibata, M., Nakae, H., Kaminuma, T. &Maruyama, K. (1989) Anti-connectin monoclonal antibodies that react with unc-22 gene product bind dense bodies ofCaenorhabditis (nematode) bodywall muscle cells.Tissue & Cell 21, 537–44.
Nave, R., Fürst, D. O. &Weber, K. (1989) Visualization of the polarity of isolated titin molecules: a single globular head on a long thin rod as the M band anchoring domain?J. Cell Biol. 109, 2177–87.
Perry, S. V. (1953) Preparation of myosin.Methods Enzymol.2, 582–8.
Pierobon-Bormioli, S., Betto, R. &Salviati, G. (1989) The organization of titin (connectin) and nebulin in the sarcomeres: an immunocytolocalization study.J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 10, 446–56.
Provencher, S. W. &Glöckner, J. (1981) Estimation of globular protein secondary structure from circular dichroism.Biochemistry 20,33–7.
Salviati, G., Betto, R., Ceoldo, S. &Pierobon-Bormioli (1990) Morphological and functional characterization of the endosarcomeric elastic filament.Am. J. Physiol. 259 (Cell Physiol. 28), C144-C149.
Sonoda, M., Kimura, S., Moriya, H., Shimada, Y. &Maruyama, K. (1990) Molecular shape ofα-connectin, an elastic filamentous protein of skeletal muscle.Proc. Jap. Acad. 66B, 213–16.
Spudich, J. A. &Watt, S. J. (1971) The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin.J. Biol. Chem. 246, 4866–71.
Takahashi, K. &Takai, H. (1988) Transformation ofα-connectin toβ-connectin in rabbit skeletal muscle stored at 5°C.Abstract of the 80th Jap. Soc. Zootech. Sci. p. 102 (in Japanese).
Takeda, K. &Moriyama, Y. (1989) Secondary structural changes in the intact and the disulfide bridges cleavedβ-lactoglobulin A and B in solutions of urea, guanidine hydrochloride, and sodium dodecyl sulfate.J. Protein Chem. 8, 487–94.
Trinick, J. (1981) End-filaments: a new structural element of vertebrate skeletal muscle thick filaments.J. Mol. Biol. 151, 309–14.
Trinick, J., Knight, P. &Whiting, A. (1984) Purification and properties of native titin.J. Mol. Biol. 180, 331–56.
Wang, K., Ramirez-Mitchell, R. &Palter, D. (1984) Titin is an extraordinarily long, flexible, and slender myofibrillar protein.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA) 81, 3685–9.
Weber, K. &Osborn, M. (1969) The reliability of molecular weight determination by dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.J. Biol. Chem. 244, 4406–12.
Whiting, A., Wardale, J. &Trinick, J. (1989) Does titin regulate the length of muscle thick filaments?J. Mol. Biol. 205, 263–8.
Williams, A. F. (1987) A year in the life of the immunoglobulin superfamily.Immunology Today 8, 299–303.
Wu, C. S. C., Hasegawa, J., Smith, A. P., Loh, H. H., Lee, N. M. &Yang, J. T. (1990) Opioid-binding protein (OBCAM) is rich inβ-sheets.J. Protein Chem. 9, 3–7.
Yoshioka, T., Higuchi, H., Kimura, S., Ohashi, K., Umazume, Y. &Maruyama, K. (1986) Effects of mild trypsin treatment on the passive tension generation and connectin splitting in stretched skinned fibers from frog skeletal muscle.Biomed. Res. 7, 181–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kimura, S., Matsuura, T., Ohtsuka, S. et al. Characterization and localization of α-connectin (titin 1): An elastic protein isolated from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 13, 39–47 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01738426
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01738426