Summary
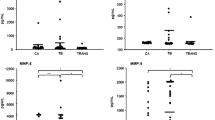
Polymorphonuclear (PMN) granulocyte derived neutrophil elastase (NE) is rapidly antagonized by α1-proteinase inhibitor (α1 PI) in vivo. To determine the clinical value of elastase α1-proteinase inhibitor complexes (E-α1 PI) in pleural effusions, fluid samples of 99 patients were examined. Fifty-six had malignant effusions, 30 had nonmalignant exudates (pleural protein above 3 g/dl) mainly of inflammatory origin, and 13 patients had low protein transudates (below 3 g/dl) due to congestive heart failure. Nonmalignant exudates showed significantly higher (P<0.001) concentrations of E-α1 PI compared with malignant effusions or low protein transudates (P<0.001). Malignant exudates secondary to lung cancer were characterized by higher (P<0.001) median pleural E-α1 PI concentrations compared to malignant exudates due to primarily extrathoracic malignancies. Total pleural leukocyte counts and pleural neutrophil counts were performed in 68 effusions. By this means no clear-cut differentiation between malignant and nonmalignant exudates seems possible except for marked empyema. In conclusion, E-α1 PI complexes in pleural fluid may better reflect the stage of inflammation of pleural effusions rather than mere pleural leukocyte counts. Low levels of E-α1 PI complexes (<75 ng/ml) in pleural exudates with protein values above 3 g/dl are characteristic of malignant exudates. Determination of E-α1 PI in pleural exudates may serve as a sensitive marker of inflammation and useful adjunct to pleural cytology in aspects of differential diagnosis of pleural effusions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- E-α1 PI:
-
elastase α1 proteinase inhibitor complexes
- NE:
-
neutrophil elastase
- PMN:
-
polymorphonuclear
References
Brown BW, Hollander M (1977) Statistics: A biomedical introduction. Wiley, New York
Chretien J, Hirsch A, Maillard JM (1983) Definition and classification of pleural disorders. In: Chretien J, Hirsch A (eds) Diseases of the pleura. Masson, New York, pp 148–151
Cohen AB, Rossi M (1983) Neutrophils in normal lung. Am Rev Respir Dis 127:3–9
Cohen G, Fehr K, Wagenhaeuser FJ (1983) Leucocyte elastase and free collagenase activity in synovial effusions: Relation to numbers of polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Rheumatol Int 3:89–95
Conover WJ (1980) Practical nonparametric statistics. 2nd ed, Wiley, New York
Dines DE, Pierre RV, Franzen SJ (1974) The value of cells in the pleural fluid in the differential diagnosis. Mayo Clinic Proc 50:571–572
Egbring R, Schmidt W, Fuchs G, Havemann K (1977) Demonstration of granulocytic proteases in plasma of patients with acute leukemia and septicemia with coagulation defects. Blood 49:219–231
Hirsch A, Ruffie P, Nabut M, Bignon J, Chretien J (1979) Pleural effusion: Laboratory tests in 300 cases. Thorax 34:106–112
Israel L, Breau JL (1983) Effusions due to pleural metastases. In: Chretien J, Hirsch J (eds) Diseases of the pleura. Masson, New York, pp 261–268
Jochum M, Fritz H, Duswald KH, Haller E (1983) Plasma levels of human granulocyte elastase-α1 proteinase inhibitor complex (E-α1 PI) in patients with septicemia and acute leucemia. In: Goldberg D, Werner M (eds) Selected topics in clinical enzymology. Gruyter, Berlin New York, pp 34–38
Jochum M, Pelletier A, Bondier Chr, Pauli G, Bieth JG (1985) The concentrations of leucocyte elastase-α1-proteinase inhibitor complex in bronchoalveolar lavage fluids from healthy human subjects. Am Rev Respir Dis 132:913–914
Klebanoff SJ, Clark RA (1978) Degranulation: extracellular enzyme release. In: The neutrophil: function and clinical disorders. North-Holland, Amsterdam New York Oxford, pp 225–262
Klech H, Rona G, Bayer PM, Kummer F (1985) Malignant pleural exudates are characterized by low concentrations of neutrophil elastase alpha-1 protein inhibitor complexes. Am Rev Respir Dis 131:4, A83 (abstract)
Klech H, Rona G, Knoth E, Kummer F, Bayer PM (1986) Value of neutrophile elastase α1 proteinase inhibitor complexes and leucocyte counts in differential diagnosis of pleural effusions. Bericht OEKC 8:97–103
Kleesiek K, Neumann S, Greiling H (1982) Determination of the elastase α1 proteinase inhibitor complex, elastase activity and proteinase inhibitors in the synovial fluid. Fresenius Z Anal Chem 311:434–436
Leuallen EC, Carr DT (1955) Pleural effusions, statistical study of 436 patients. N Engl J Med 25:79
Light RW, Erozan YS, Ball WC (1973) Cells in pleural fluid. Arch Intern Med 824:1322
Lonky SA, McCarren J (1983) Neutrophil enzymes in the lung: regulation of neutrophil elastase. Am Rev Respir Dis 127:9–15
Lowell RJ (1977) Pleural effusions. A comprehensive review. University Park Press, Baltimore, p 57
Neumann S, Gunzer G, Hennrich N, Lang H (1984) Enzyme linked immunoassay for human granulocyte elastase in complex with proteinase inhibitor. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 22:375
Neumann S, Gunzer G, Hennrich N, Lang H (1985) Enzymimmunoassay für Granulozyten-Elastase in Komplex mit α1-Proteinaseinhibitor. In: Jochum M, Gabl F, Greiling H, Fritz H (eds) Neue Wege in der Entzündungsdiagnostik. GIT Verlag, Darmstadt, pp 9–16
Petterson T, Riska H (1981) Diagnostic value of total and differential leucocyte counts in pleural effusion. Acta Med Scand 210:129–135
Petterson T, Klockars M, Hellstions PE (1982) Chemical and immunological features of pleural effusions: comparison between rheumatoid arthritis and other diseases. Thorax 37:354–361
Poe RH, Israel RH, Utell MJ, Hall WJ, Greenblatt DW, Kallay MC (1984) Sensitivity, specificity and predictive value of closed pleural biopsy. Arch Intern Med 144:325–328
Reynolds HY (1983) Lung inflammation: Role of endogenous chemotactic factors in attracting polymorphonuclear granulocytes. Am Rev Respir Dis 127:16–25
Storey DD, Dines DE, Coles DT (1976) Pleural effusion. A diagnostic dilemma. JAMA 236:2183
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klech, H., Rona, G., Knoth, E. et al. Neutrophil elastase α1-proteinase inhibitor complexes in pleural effusions. Klin Wochenschr 66, 346–350 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01735792
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01735792