Summary
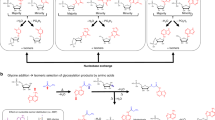
The fact that proteins contain onlya-amino acids and that protein structure is determined by 3′ → 5′ linked ribonucleotides is postulated to be the result of the copolymerization of these molecules in the prebiotic environment. Ribonucleotides therefore represent partial degradation products and proteins represent a side reaction developing from copolymerization. The basic structural unit of copolymerization is a nucleotide substituted with an amino acid at the 2′ position. Characteristics of modern amino and ribonucleic acid structure are all consistent with and necessary for this hypothesis. The characteristics and individual base assignments of the code also provide strong support for origin from the postulated copolymers. All characteristics of the code can be accounted for by this single hypothesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crick, F. H. C. (1966) J. Mol. Biol.19, 548–555
Crick, F. H. C. (1968) J. Mol. Biol.38, 367–379
Dunnill, P. (1966) Nature210, 1267–1268
Eigen, M. (1971) Naturwissenschaften58, 465–523
Jukes, T. H. (1977) Science198, 319–320
Lehninger, A. L. (1970) Biochemistry, New York: Worth Publishers
Miller, S. L., Orgel, L. E. (1974) The Origins of Life on the Earth, Concept of Modern Biology Series, ed. McElroy, W.D., and Swanson, C. P. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Prentice - Hall, Inc.
Oparin, A. I. (1962) Life: Its Nature, Origin and Development, New York: Academic Press
Pelc, S. R., Welton, G. E. (1966) Nature209, 868–870
Sonneborn, T. M. (1965) in Bryson, V. and Vogel, H. J., eds. Evolving Genes and Proteins. p. 377–397. New York: Academic Press
Sulston, J., Lohrmann, R., Orgel, L. E., Miles, H. T. (1968) Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.60, 409–415
T'so, P. O. P. (1974) in Basic Principles in Nucleic Acid Chemistry (T'so, P. O. P., ed.), Vol. 1, pp. 1–92. New York: Academic Press
Woese, C. R. (1970) Bioscience20, 471–485
Woese, C. R., Dugre, D. H., Dugre, S. A., Kondo, M., Saxinger, W. C. (1966) J. Mol. Biol.56, 723–736
Wong, J. T.-F. (1975) Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.72, 1909–1912
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
An Established Investigator of the American Heart Association
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nelsestuen, G.L. Amino acid-directed nucleic acid synthesis. J Mol Evol 11, 109–120 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01733887
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01733887