Summary
Prospectively, 43 patients with Crohn's disease (41 clinically active, 2 clinically inactive) and 7 patients with irritable bowel syndrome were examined by111In-oxine-labelled leukocytes (‘mixed’ leukocyte preparations,n=8; ‘pure’ granulocyte preparations,n=42).
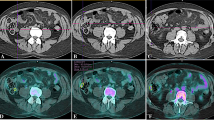
The number of scintigraphically diagnosed inflamed bowel segments correlated significantly (r=0,95,p<0.001) with the number of radiologically and endoscopically diagnosed segments. The exact localization of the diseased ileum may be difficult by scintigraphy. One complicating abscess and two fistulas were correctly diagnosed.
The percentage of fecal excretion of radiolabelled leukocytes is highly specific for intestinal inflammations. It correlates significantly with the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (r=+0.69,p<0.001), serum albumin (r=−0.54,p<0.001), orosomucoid (r=+0.65,p<0.001), and with the A.I. (van Hees) (r=+0.67,p<0.001).
In the follow-up of 9 patients, the percentage of fecal excretion decreased or increased more rapidly, but in correlation with the CDAI, A.I., or ESR.
The authors conclude that this method is an alternative to common methods and that it is superior in primary diagnosis in patients with severe disease, bowel stenosis, abscesses, and after surgery. After clinical and biopsy-proven diagnosis of Crohn's disease, the special value of the leukocyte scan lies in the noninvasive follow-up of patients and its potential of localizing inflamed bowel segments and assessing disease activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A.I.:
-
activity index (van Hees)=Dutch index
- CADI:
-
Crohn's disease activity index
- ESR:
-
erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- IBS:
-
irritable bowel syndrome
- MBq:
-
Mega Bequerel
- SEM:
-
standard error of the mean
- μCi:
-
micro-Curie
References
André C, Descos L, Landais P, Fermanian J (1981) Assessment of appropriate laboratory measurements to supplement the Crohn's disease activity index. Gut 22:571–574
Becker W, Fischbach W, Reiners Ch, Koch W, Börner W (1984) Autologe111In-markierte Leukozyten bei entzündlichen Darmerkrankungen. Z Gastroenterol 9:343 (abstract)
Becker W, Fischbach W, Reiners Ch, Börner W (1985)111In-oxin markierte Granulozyten bei Morbus Crohn und Colitis ulzerosa — Markierungs- und Untersuchungstechnik. Fortschr Röntgenstr 142:320–325
Becker W, Fischbach W, Börner W (1985) Autologous111In-oxin-labeled granulocytes in Yersinia infections. Europ J Nucl Med 10:377–378
Ten Berge RJM, Natarajan AT, Hardeman MR, van Royen EA, Schellekens PThA (1983) Labeling with Indium-111 has detrimental effects on human lymphocytes: concise communications. J Nucl Med 24:615–620
Best WR, Becktel JM, Singleton JW, Kern F Jr (1976) Development of a Crohn's disease activity index. National Cooperative Crohn's Disease Study. Gastroenterology 70:439–444
Burke JET, Roath S, Ackery D, Wyeth P (1982) The comparison of 8-hydroxyquinoline, tropolone, acetylacetone as mediators in the labelling of polymorphonuclear leukocytes with Indium-111. A functional study. Eur J Nucl Med 7:73–76
Dombrowski H, Bürkle G (1981) Röntgentechnik und Röntgenbefunde bei chronisch entzündlichen Darmerkrankungen. Internist 22:385–400
Fischer MF, Rudd TG (1983)111In-labelled-leukocyte imaging: false-positive study due to acute gastrointestinal bleeding. J Nucl Med 24:803–804
Goodwin DA, Finston RA, Smith SI (1980) The distribution and dosimetry of In-111-labelled leukocytes and platelets in humans. Proc. of the 3rd Intern. Radiopharm. Dos. Symp Oak Ridge Tennessee. Food and Drug Administration:88–101
van Hees PAM, van Elteren PH, van Lier HJJ, van Togeren JHM (1980) An index of inflammatory activity in patients with Crohn's disease. Gut 21:279–286
Hidell J, Lindstrom C, Wenckert A (1980) Radiographic patterns of Crohn's disease IV. Radiographic appearance of the new distal ileum after surgery. Acta Radiol (Diagn) (Stockh) 21:221–229
Jenss H, Klott KH, Malchow H (1980) Sonographie: Darstellung von Fisteln und Abszessen bei Morbus Crohn. Leber-Magen-Darm 10:317
Kruis W, Thieme Ch, Weinzierl M, Schüssler P, Holl J, Paulus W (1984) A diagnostic score for the irritable bowel syndrome. Its value in the exclusion of organic disease. Gastroenterology 87:1–7
Maier K, Frühmorgen P, Bode JCh, Heller Th, Gaisberg UV, Klotz U (1985) Erfolgreiche Akutbehandlung chronisch-entzündlicher Darmerkrankungen mit oraler 5-Aminosalicylsäure. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 110:363–368
Malchow H, Daiss W (1984) Therapie des Morbus Crohn. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 109:1811–1816
Malchow H, Daiss W (1984) Diagnostik des Morbus Crohn. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 109:1770–1775
Malchow H, Ewe K, Brandes W, Goebell H, Ehms H, Sommer H, Jeschinsky H (1984) European Cooperative Crohn's disease Study (ECCDS) Results of drug treatment. Gastroenterology 86:249–266
Oehlert W (1978) Klinische Pathologie des Magen-Darm-Trakts. Schattauer, Stuttgart New York
Peters AM, Saverymuttu SH, Reavy HJ, Danpure HJ, Osman S, Lavender P (1983) Imaging of inflammation with indium-111 tropolonate labeled leukocytes. J Nucl Med 24:39–44
Saverymuttu SH, Peters AM, Hodgson HJF, Chadwick VS, Lavender JP (1982)111Indium autologous leukocyte scanning: comparison with radiology for imaging the colon in inflammatory bowel disease. Brit Med J 285:255–257
Saverymuttu SH, Peters AM, Lavender JP, Pepys MB, Hodgson HJF, Chadwick VS (1983) Quantitative fecal indium-111-labeled leukocytes excretion in the assessment of disease in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology 85:1333–1339
Schmitz-Moormann P, Malchow H, Miller B, Brandes JW (1979) Häufigkeit und Vorkommen der epithelzelligen Granulome in Rektum- und Kolonbiopsien bei Morbus Crohn. Ein Beitrag zur formalen Pathogenese. Z Gastroenterol 17:287–292
Segal AW, Ensell J, Munro JM, Sarner M (1981) Indium-111-tagged leukocytes in the diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease. Lancet II:230–232
Stein DT, Paldi JH, Goodwin DA (1983)111In-leukocyte scan in ‘diversion’ colitis. Clin Nucl Med 18:1012–1019
Stein DT, Gray GM, Gregory PB, Anderson M, Goodwin DA, McDougall IJ (1983) Location and activity of ulcerative and Crohn's colitis by Indium-111-leukocyte scan. A prospektive comparison study. Gastroenterology 84:388–393
Thakur M, Lavender JP, Arnot RN, Silvester DJ, Segal AW (1977) Indium-111-labelled autologous leukocytes in man. J Nucl Med 18:1012–1019
Thakur M, Segal AW, Ouis L, Welch MJ, Hopkins J, Peters TJ (1977) Indium-111-labelled cellular blood components: mechanism of labelling and intracellular location in human neutrophils. J Nucl Med 18:1020–1024
Touya JJ, Anselmi OE, Riley RE, Bennett LR (1975) Metabolism of111Indium transferrin as a measure of bone marrow activity. In: Dynamic studies with radioisotopes in medicine. Vol. 1, IAEA, Vienna, pp 413–427
Weiblen BJ, Forstrom L, McCullough J (1979) Studies of the kinetics of Indium-111-labelled granulocytes. J Lab Clin Med 94:246
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Becker, W., Fischbach, W., Jenett, M. et al. 111In-oxine-labelled white blood cells in the diagnosis and follow-up of crohn's disease. Klin Wochenschr 64, 141–148 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01732640
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01732640