Abstract
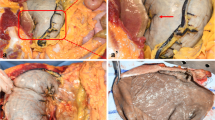
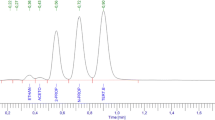
After ingestion of an unknown amount of formalin with suicidal intent, a 55-year-old female and a 34-year-old male were admitted to the hospital with extensive gastrointestinal corrosive damage, circulatory shock, metabolic acidosis, respiratory insufficiency and impairment of renal function, which rapidly progressed to acute renal failure. Metabolic acidosis was in part due to high plasma levels of formic acid, the main metabolite of formaldehyde, and hyperlactatemia. Both patients underwent hemodialysis and hemofiltration treatment. In the male patient, a gastrectomy had to be performed. The further clinical course in the patients was characterized by sepsis and protracted pulmonary complications. Both patients died after developing adult respiratory distress syndrome and global cardiac insufficiency. In vitro experiiments on formaldehyde reactivity to proteins yielded evidence for almost complete but reversible binding to plasma and blood. Formaldehyde probably exerts systemic toxicity in the form of its labile Schiff's base with proteins, but not as free formaldehyde.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jacobsen D, McMartin KE (1986) Methanol and ethylene glycol poisonings. Mechanisms of toxicity, clinical course diagnosis and treatment. Med Toxicol 1:309–319
Baselt RC (1981) Disposition of drugs and chemicals in man. Biomedical Publications. Davis, CA, pp 345–347
Kochhar R, Nanda V, Nagi B, Mehta SK (1986) Formaldehyde-induced corrosive gastric cicatrization: case report. Hum Toxicol 5:381–382
Roy M, Calonje MA, Mouten R (1962) Corrosive gastritis after formaldehyde ingestion. N Engl J Med 266:1248–1249
Powner DJ, Grenvik A (1981) Ventilatory management of life-threatening bronchopleural fistulae. A summary. Crit Care Med 9:54–56
Köppel C, Tenczer J (1983) Identification and quantitation of drugs on an emergency basis with EI, CI and NCI gas chromatography/mass spectrometry in a toxicological laboratory. Int J Mass Spectrom Ion Phys 48:213–216
Henschler D (ed) (1983) Analytische Methoden zur Prüfung gesundheitschädlicher Arbeitsstoffe, Bd I. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim
Weiss JS, Gautam A, John J, Lauf MS et al (1983) The clinical importance of a protein-bound fraction of serum bilirubin in patients with hyperbilirubinemia. N Engl J Med 309:147–150
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Prof. Adebahr on the occasion of his 65th birthday
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Köppel, C., Baudisch, H., Schneider, V. et al. Suicidal ingestion of formalin with fatal complications. Intensive Care Med 16, 212–214 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01724806
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01724806