Abstract
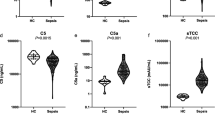
Previously we studied levels of the cytokine IL-6 and activation of the complement and contact system and of neutrophils in a group of 48 patients with sepsis. Some of these inflammatory parameters appeared to be associated with a poor prognosis. Here we report on the relationships of C4a and C3a (complement activation products), of factor XII and prekallikrein (contact system proteins), of elastase (a protease released by activated neutrophils) and of the cytokine IL-6 to hemodynamic and biochemical parameters measured in those 48 patients at the time of admission to the Intensive Care Unit. No significant correlations between any inflammatory parameter and either systemic vascular resistance or cardiac index were found. Mean arterial pressure significantly correlated with both factor XII and prekallikrein levels. Lactate correlated with C3a and C4a, with elastase, and in particular, with IL-6, whereas it did not correlate with either factor XII or prekallikrein. Platelet numbers inversely correlated with both C3a and C4a, as well as with elastase and IL-6, whereas they positively correlated with factor XII and prekallikrein. Based on these findings we propose a model for the interplay of these fnflammatory mediators in the pathogenesis of sepsis. This model takes into consideration the occurrence of capillary leakage, shock, disseminated intravascular coagulation, thrombocytopenia and of acute phase reactions in sepsis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harris RL, Musher DM, Bloom K, Gathe J, Rice L, Sugarman B, Williams TW, Young EJ (1987) Manifestations of sepsis. Arch Intern Med 147:1895–1906
Kreger BEW, Craven DE, McCabe WR (1980) Gram-negative bacteremia: IV. Re-evaluation of clinical features and treatment in 612 patients. Am J Med 68:344–355
Morrison DC, Ulevitch RJ (1978) The effects of bacterial endotoxins in host mediation systems. Am J Pathol 93:527–617
Beutler B, Cerami A (1987) Cachectin: more than a tumor necrosis factor. N Engl J Med 316:379–385
Girardin E, Grau GE, Dayer JM, Roux-Lambard P, the J5 Study Group, Lambert P-H (1988) Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 in the serum of children with severe infectious purpura. N Engl J Med 319:397–400
Beutler B, Milsark IW, Cerami A (1985) Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect endotoxin. Science 229:869–871
Mathison JC, Wolfson E, Ulevitch RJ (1988) Participation of tumor necrosis factor in the mediation of Gram negative bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced injury in rabbits. J Clin Invest 81:1925–1937
Okusawa S, Gelfand JA, Ikejima T, Conolly RJ, Dinarello CA (1988) Interleukin 1 induces a shock-like state in rabbits. Synergism with tumor necrosis factor and the effect of cycloxygenase inhibition. J Clin Invest 81:1162–1172
Egbring R, Schmidt W, Fuchs G, Havermann K (1977) Demonstration of granulocytic proteases in plasma of patients with acute leukemia and septicemia with coagulation defects. Blood 49:219–231
McCabe WR (1973) Serum complement levels in bacteremia due to gram-negative organisms. N Engl J Med 288:21–23
Fearon DT, Ruddy S, Schur PH, McCabe WR (1975) Activation of the properdin pathway of complement in patients with gram-negative bacteremia. N Engl J Med 292:937–940
Mason JW, Kleeberg U, Dolan P, Colman RW (1970) Plasma kallikrein and Hageman factor in gram-negative bacteremia. Ann Intern Med 73:545–551
Nies AS, Forsyth RP, Williams HE, Melmon KL (1968) Contribution of kinins to endotoxin shock in unanesthetized Rhesus monkeys. Circ Res 22:155–164
Colman RW (1989) The role of plasma proteases in septic shock. N Engl J Med 320:1207–1209
Suffredini AF, Harpel PC, Parillo JE (1989) Promotion and subsequent inhibition of plasminogen activation after administration of intravenous endotoxin to normal subjects. N Engl J Med 320:1165–1172
Hack CE, Nuijens JH, Felt-Bersma RJF, Schreuder WO, Eerenberg-Belmer AJM, Paardekooper J, Bronsveld W, Thijs LG (1989) Elevated plasma levels of the anaphylatoxins C3a and C4a are associated with a fatal outcome in sepsis. Am J Med 86:20–26
Nuijens JH, Huijbregts CCM, Eerenberg-Belmer AJM, Abbink JJ, Strack van Schijndel RJM, Felt-Bersma RJF, Thijs LG, Hack CE (1988) Quantification of plasma factor XIIa-C1-inhibitor and kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complexes in sepsis. Blood 72:1842–1848
Hack CE, de Groot ER, Felt-Bersma RJF, Nuijens JH, Strack van Schijndel RJM, Eerenberg-Belmer AJM, Thijs LG, Aarden LA (1989) Increased plasma levels of Interleukin-6 in sepsis. Blood 74:1704–1710
Nuijens JH, Eerenberg-Belmer AJM, Huijbregts CCM, Schreuder WO, Felt-Bersma RJF, Abbink JJ, Thijs LG, Hack CE (1989) Proteolytic inactivation of plasma C1-inhibitor in sepsis. J Clin Invest 84:443–450
Groeneveld ABJ, Bronsveld W, Thijs LG (1986) Haemodynamic determinants of mortality in human septic shock. Surgery 99:140–152
Groeneveld ABJ, Nauta JJP, Thijs LG (1988) Peripheral vascular resistance in septic shock: its relation to clinical outcome. Intensive Care Med 72:487–497
Nuijens JH, Huijbregts CCM, Cohen M Navis GO, de Vries A, Eerenberg AJM, Bakker JC, Hack CE (1987) Detection of activation of the contact system of coagulation in vitro and in vivo: quantification of activated hageman factor-C1-inhibitor and kallikrein-C1-inhibitor complexes by specific radioimmunoassays. Thromb Haemostas 58:778–785
Hack CE, Paardekooper J, Eerenberg AJM, Navis GO, Nijsten MWN, Thijs LG, Nuijens JH (1988) A modified competitive radioimmunoassay for the detection of C3a. Use of 125I-C3 instead of 125I-C3a. J Immunol Methods 108:77–84
Aarden LA, de Groot ER, Schaap OL, Lansdorp PM (1987) Production of HGF by human monocytes. Eur J Immunol 17:1411–1416
Thijs LG, Hack CE, Nuijens JH, Groeneveld ABJ (1989) Peripheral circulation in septic shock. In: Schalg G, Redl H (ed) Second Vienna Shock Forum. Liss, New York, pp 163–174
Pralong G, Calandra T, Glauser MP, Schellekens J, Verhoef J, Bachmann F, Kruithof EKO (1989) Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1: A new prognostic marker in septic shock. Thromb Haemostas 61:459–462
Berrettini M, Schleef RR, Espana F, Loskutoff DJ, Griffin JH (1989) Interaction of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor with the enzymes of the contact activation system. J Biol Chem 264:11738–11743
Mason DT, Melmon KL (1965) Effects of bradykinin on fore-arm venous tone and vascular resistance in man. Circ Res 17:106–113
Groeneveld ABJ, Thijs LG (1987) Increased systemim microvascular permeability in septic shock. In: Schlag G, Redl H (ed) First Vienna Shock Forum Part A. Liss, New York, pp 487–494
Fey GH, Gauldie J (1988) The acute phase response of the liver in inflammation. In: Popper H, Schaffner F (ed) Progress in liver disease. Saunders, Philadelphia
Hugli TE (1984) Structure and function of the anaphylatoxins. Springer Semin Immunopathol 7:193–219
Vogt W (1986) Anaphylatoxins: possible roles in disease. Complement 3:177–188
Tannesen MG, Smedly LA, Henson PM (1984) Neutrophil-endothelial cell interactions. Modulation of neutrophil adhesiveness induced by complement fragments C5a and C5a-desarg and formylmethianyl-leucyl-phenylalanine in vitro. J Clin Invest 74:1581–1592
Mantovani A, Dejana E (1989) Cytokines as communication signals between leukocytes and endothelial cells. Immunol Today 10:370–375
Smedly LA, Tannesen MG, Sandhaus RA, Haslett C, Guthrie LA, Johnston Jr RB, Henson PM, Worthen GS (1986) Neutrophil-mediated injury to endothelial cells. Enhancement by endotoxin and an essential role of neutrophil elastase. J Clin Inves 77:1233–1243
Bevilacqua MP, Pober JS, Majeau GR, Cotran RS, Gimbrone Jr MA (1984) Interleukin 1 (IL-1) induces biosynthesis and cell surface expression of procoagulant activity in human vascular endothelial cells. J Exp Med 160:618–623
Bevilacqua MP, Pober JS, Majeau GR, Fiers W, Cotran RS, Gimbrone Jr MA (1986) Recombinant tumor necrosis factor induces procoagulant activity in cultured human vascular endothelium: characterization and comparison with the actions of interleukin. 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:4533–4537
Nawroth PP, Stern DM (1986) Modulation of endothelial cell hemostatic properties by tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med 163:740–745
Osterud B, Olsen JO, Benjaminsen AW (1984) The role of complement in the induction of thromboplastin synthesis. Haemostasis 14:386–392
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hack, C.E., Nuijens, J.H., Strack van Schijndel, R.J.M. et al. A model for the interplay of inflammatory mediators in sepsis —a study in 48 patients. Intensive Care Med 16 (Suppl 3), S187–S191 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01709698
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01709698