Abstract
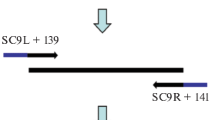
A polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay was applied for the selective amplification of a characteristic sequence within aSalmonella-specific chromosomal fragment. A two-temperature PCR cycle enhanced both the speed and overall sensitivity of the amplification procedure. Twenty-one well-characterizedSalmonella strains and a number of non-Salmonella strains were tested. With the exception of the rarely isolatedSalmonella arizonae strain, the PCR-based approach enabled the specific identification ofSalmonella with a detection limit of 103 organisms. In combination with a nested PCR assay, as few as ten organisms were detectable. Specificity was demonstrated as no distinct amplification products were detectable with any of the testednon-Salmonella strains. With a pre-enrichment step using paramagnetic antiSalmonella beads, an increase in sensitivity was observed in the case of clinical samples while the amplification process was not influenced.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baird-Parker AC: Foodborne illness: foodborne salmonellosis. Lancet 1990, 336: 1231–1236.
Kühn H, Rabsch W, Liesegang A: Gegenwärtige epidemiologische Situation bei der Salmonellose in Deutschland. Immunität und Infektion 1994, 22: 69–71.
Roszak DB, Colwell PRR: Survival strategies of bacteria in the natural environment. Microbiological Reviews 1987, 51: 365–379.
Blackburn C: Detection ofSalmonella using impedance. European Food and Drink Review 1991, 15: 35–40.
Lund A, Helleman AL, Vartdal F: Rapid isolation of K88+Escherichia coli by using immunomagnetic particles. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1988, 26: 2572–2575.
Fluit AC, Torensma R, Visser MJC, Aarsmann CJM, Poppelier MJJG, Keller BHI, Klapwijk R Verhoef J: Detection ofListeria monocytogenes in cheese with the magnetic immuno-polymerase chain reaction assay. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 1993, 59: 1289–1293.
Skjerve E, Rørvik LM, Ølsvik O: Detection ofListeria monocytogenes in food by immunomagnetic separation. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 1990, 56: 3478–3481.
Ølsvik O, Popovic T, Skjerve E, Kudjoe KS, Homes E, Ugelstad J, Uhlen M: Magnetic separation techniques in diagnostic microbiology. Clinical Microbiology Reviews 1994, 7: 43–54.
Widjojoatmodjo MN, Fluit AC, Toresma R, Keller BHI, Verhoef J: Evaluation of the magnetic immuno PCR assay for rapid detection ofSalmonella. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases 1991, 10: 935–938.
Aabo S, Rasmussen OF, Rossen L, Sorensen PD, Olsen JE:Salmonella identification by polymerase chain reaction. Molecular and Cellular Probes 1993, 7: 171–178.
Olsen JE, Aabo S, Nielsen FO, Nielsen RB: Isolation of aSalmonella specific DNA hybridization probe. Acta Pathologica Microbiologie, et Immunologica Scandinavica 1991, 99: 114–120.
Hall ML, Rowe B:Salmonella arizonae in the United Kingdom from 1966 to 1990. Epidemiology and Infection 1992, 108: 59–65.
Widjojoatmodjo MN, Fluit AC, Torensma R, Verdonk GPHT, Verhoef J: The magnetic immuno polymerase chain reaction for direct detection ofSalmonellae in fecal samples. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1992, 30: 3195–3199.
Fluit AC, Widjojoatmodjo MN, Box ATA, Torensma R, Verhoef J: Rapid detection ofSalmonellae in poultry with the magnetic immuno polymerase chain reaction. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 1993, 59: 1342–1346.
Vermunt AEM, Franken AAJM, Beumer RR: Isolation of salmonellas by immunomagnetic separation. Journal of Applied Bacteriology 1992, 72: 112–118.
Way JS, Josephson KL, Pillai SD, Abbaszadegan M, Gerba CG, Pepper IL: Specific detection ofSalmonella spp. by multiplex polymerase chain reaction. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 1993, 59: 1473–1479.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haedicke, W., Wolf, H., Ehret, W. et al. Specific and sensitive two-step polymerase chain reaction assay for the detection ofSalmonella species. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 15, 603–607 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01709372
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01709372