Abstract
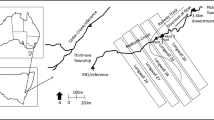
A reclamation project at the abandoned Blackhawk Mine site near Terre Haute, Indiana, lasted about four months and involved the burial of coarse mine refuse in shallow (less than 9 m) pits excavated into loess and till in an area of about 16 ha. An abandoned flooded underground coal mine underlies the reclamation site at a depth of about 38 m; the total area underlain by the mine is about 10 km2. The potentiometric levels associated with the mine indicate a significant (2.7 m) and prolonged perturbation of the deeper confined groundwater system; 14 months after completing reclamation, the levels began to rise linearly (at an average rate of 0.85 cm/d) for 11 months, then fell exponentially for 25 months, and are now nearly stable. Prominent subsidence features exist near the reclamation site. Subsidence-related fractures were observed in cores from the site, and such fractures may have provided a connection between the shallower and deeper groundwater systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Aldous, P. J., and P. L. Smart, 1988, Tracing ground-water movement in abandoned coal-mined aquifers using fluorescent dyes: Ground Water, v. 26, no. 2, p. 172–178.
Aldous, P. J., P. L. Smart, and J. A. Black, 1986, Groundwater management problems in abandoned coal-mined aquifers: a case study of the Forest of Dean, England: Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology, London, v. 19, p. 375–388.
Bauer, R. A., 1984, Subsidence of bedrock above abandoned coal mines in Illinois produces few fractures: Society of Mining Engineers of AIME Preprint 84-400, 8 p.
Bradbury, K. R., and E. R. Rothschild, 1985, A computerized technique for estimating the hydraulic conductivity of aquifers from specific capacity data: Ground Water, v. 23, no. 2, p. 240–246.
Cartwright, K., and C. S. Hunt, 1978, Hydrogeology of underground coal mines in Illinois: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Water in Mining and Underground Works, September 17–22, Granada, Spain.
Cifelli, R. C., and H. W. Rauch, 1986, Preliminary results of research on aquifer dewatering effects by underground coal mining in north-central West Virginia: Abstracts for 2nd Workshop on Surface Subsidence due to Underground Mining, June 9–11, Morgantown, West Virginia, sponsored by U.S. Office of Surface Mining Reclamation and Enforcement and West Virginia University, p. 92–93.
Cocroft, J. E., 1984, Hydrogeochemical study of a mined region in the Carbondale Group (Pennsylvanian), southwestern Indiana: MA thesis, Bloomington, Indiana University, 198 p.
Funkhouser, R. V., 1983, Hydrogeological study of the French Lake area, Vigo County, Indiana: MA thesis, Bloomington, Indiana University, 171 p.
Hobba, W. A., Jr., 1981, Effects of underground mining and mine collapse on the hydrology of selected basins in West Virginia: West Virginia Geological and Economic Survey Report of Investigation RI-33, 77 p.
Smith, C. R., 1983, Hydrology of the Carbondale and Raccoon Creek Groups, Pennsylvanian System, Vigo, Clay, and Sullivan Counties, Indiana: MA thesis, Bloomington, Indiana University, 93 p.
Thompson, D. B., 1987, A microcomputer program for interpreting time-lag permeability tests: Ground Water, v. 25, no. 2, p. 212–218.
Wangsness, D. J., R. L. Miller, Z. C. Bailey, and C. G. Crawford, 1981, Hydrology of area 32, eastern region, interior coal province, Indiana: U.S. Geological Survey Water Resources Investigation Open-File Report 81-498, 76 p.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harper, D., Olyphant, G.A. & Hartke, E.J. Unexpected hydrologic perturbation in an abandoned underground coal mine: Response to surface reclamation?. Environ. Geol. Water Sci 15, 179–187 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01706409
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01706409