Summary
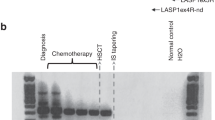
A modified two-step polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was used for the amplification of BCR/ABL mRNA in 16 patients with Philadelphia chromosomepositive (Ph+) chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation (BMT). At different intervals after BMT, patient cells were assessed for the presence of BCR/ABL mRNA by two subsequent rounds of PCR amplification; this procedure increased the sensitivity for the detection of one Ph+ cell in 104–5 to one cell in 105–6. Eight of 16 patients were negative by two-step PCR 1–39 months after BMT, suggesting an elimination of Ph-positive cells or a decrease below the threshold of detection. Although five patients showed negative results by the one-step PCR only, they were tested positive when nested primers were used, indicating a substantial decrease in the amount of BCR/ABL target mRNA compared with earlier pre- or post-transplant analyses. One patient who was still PCR positive 27 months after BMT became negative 12 months later. Persistence of BCR/ABL mRNA-expressing cells correlated with subsequent clinical relapse only when the transplantation was performed during blast crisis. All patients who underwent transplantation in chronic phase, including those with BCR rearrangement by PCR, are in clinical and hematological remission between 24 and 95 months after BMT. We conclude that aggressive chemotherapy combined with total body irradiation is unable to completely eradicate the malignant clone in all CML patients, and it might be speculated that other mechanisms (e.g., graft versus host reaction [GVHD] or graft versus leukemia effect [GVL]) may effectively eliminate residual leukemic cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chelly J, Kaplan J-C, Maire P, Gautron S, Kahn A (1988) Transcription of the dystrophin gene in human muscle and non-muscle tissues. Nature 333: 858–860
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162: 156–159
Cooperative Study Group on Chromosomes in Transplanted Patients (1988) Cytogenetic follow-up of 100 patients submitted to bone marrow transplantation for Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia. Eur J Haematol 40: 50–57
Delfau M-H, Kerckaert, J-P, d'Hooghe MC, Fenaux P, Lai J-L, Jouet J-P, Grandchamp B (1990) Detection of minimal residual disease in chronic myeloid leukemia patients after bone marrow transplantation by polymerase chain reaction. Leukemia 4: 1–5
Dobrovic A, Trainor KJ, Morley AA (1988) Detection of the molecular abnormality in chronic myeloid leukemia by use of the polymerase chain reaction. Blood 72: 2063–2065
Gabert J, Lafage M, Maraninchi D, Thuret I, Carcassonne Y, Mannoni P (1989) Detection of residual BCR/ABL translocation by polymerase chain reaction in chronic myeloid leukaemia after bone marrow transplantation. Lancet 2: 1125–1128
Grosveld G, Verwoerd T, van Agthoven T, de Klein A, Ramachandran KL, Heisterkamp N, Stam K, Groffen J (1986) The chronic myelocytic cell line K 562 contains a breakpoint in bcr and produces a chimeric bcr/c-abl transcript. Mol Cell Biol 6: 607–616
Heisterkamp N, Stam K, Groffen J, de Klein A, Grosveld G (1985) Structural organization of the bcr gene and its role in the Ph′-translocation. Nature 315: 758–761
Hughes T, Jansen JWG, Morgan G, Martiat P, Saglio G, Pignon JM, Pignatti FP, Mills K, Keating A, Gluckman E, Bartram CR, Goldman JM (1990) False-positive results with PCR to detect leukaemia-specific transcript. Lancet 1: 1037–1038
Hughes TP, Morgan GJ, Martiat P, Goldman JM (1991) Detection of residual leukemia after bone marrow transplant for chronic myeloid leukemia: role of polymerase chain reaction in predicting relapse. Blood 77: 874–878
Kawasaki ES, Clark SS, Coyne MY, Smith SD, Champlin R, Witte ON, McCormick FP (1988) Diagnosis of chronic myeloid and acute lymphocytic leukemias by detection of leukemia-specific mRNA sequences amplified in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 5698–5702
Kohler S, Galili N, Sklar JL, Donlon TA, Blume KG, Cleary ML (1990) Expression of bcr-abl fusion transcripts following bone marrow transplantation for Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemia. Leukemia 4: 541–547
Lange W, Snyder DS, Castro R, Rossi JJ, Blume KG (1989) Detection by enzymatic amplification of BCR/ABL mRNA in peripheral blood and bone marrow cells of patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood 73: 1735–1741
Lee M-S, LeMaistre A, Kantarjian HM, Talpaz M, Freireich EJ, Trujillo JM, Stass SA (1989) Detection of two alternative BCR/ABL mRNA junctions and minimal residual disease in Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia by polymerase chain reaction. Blood 73: 2165–2170
Martiat P, Maisin D, Philippe M, Ferrant A, Michaux JL, Cassiman JJ, Van Den Berghe H, Sokal G (1990) Detection of residual BCR/ABL transcripts in chronic myeloid leukemia patients in complete remission using the polymerase chain reaction and nested primers. Br J Haematol 75: 355–358
Morgan GJ, Janssen JWG, Guo A-P, Wiedemann LM, Hughes T, Gow J, Goldman JM, Bartram CR (1989) Polymerase chain reaction for detection of residual leukemia. Lancet 1: 928–929
Pignon JM, Henni T, Anselem S, Vidaud M, Duquesnoy P, Vernant JP, Kuentz M, Cordonnier C, Rochant H, Goossens M (1990) Frequent detection of minimal residual disease by use of the polymerase chain reaction in long-term survivors after bone marrow transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 4: 83–86
Roth MS, Antin JH, Bingham EL, Ginsburg D (1989) Detection of Philadelphia chromosome-positive cells by the polymerase chain reaction following bone marrow transplant for chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood 74: 882–885
Rowley JD (1980) Ph1-positive leukemia including chronic myelogenous leukemia. Clin Hematol 9: 55–86
Sawyers CL, Timson L, Kawasaki ES, Clark SS, Witte ON, Champlin R (1990) Molecular relapse in chronic myelogenous leukemia patients after bone marrow transplantation detected by polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 563–567
Shtivelman E, Lifshitz B, Gale RP, Roe BA, Canaani E (1986) Alternative splicing of RNAs transcribed from the human ABL gene and from the BCR/ABL fused gene. Cell 47: 277–284
Thomas ED, Clift RA (1989) Indications for marrow transplantation in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood 73: 861–864
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The studies were supported by grant Do 176/5-1 from theDeutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lange, W., Herkert, R., Finke, J. et al. Apparent decrease and elimination of BCR/ABL mRNA-expressing residual cells in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Ann Hematol 63, 189–194 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01703441
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01703441