Summary
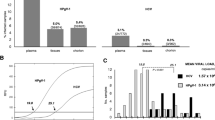
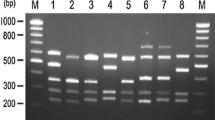
We evaluated the validity of DNA enzymatic amplification (PCR) in a population at risk for HIV-1 infection, consisting of hemophiliacs and children born to seropositive mothers. All but one of the seropositive hemophiliacs and controls were found positive with the three sets of primers. All the seronegative patients and controls were found negative in PCR. No correlation with the anti-nef serology was found, one seropositive being anti-nef negative and three seronegative anti-nef positive. The results obtained with PCR are in good agreement with classical serology, and this would suggest that the possible period of latency may not be as long as suspected. No seroconversion has been described in hemophiliacs since solvent-detergent inactivated blood products have been in use, and seronegative hemophiliacs no longer constitute a population at risk. Studies on seronegative sexual partners of seropositive patients would be of great interest. For newborns from seropositive mothers, PCR is the only possible technique in early age before seronegativation of the healthy children. Further studies will be required to determine the fiability and sensitivity of the test.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott MA, Poiesz BJ, Byrne BC, Kwok S, Sninsky JJ, Ehrlich GD (1988) Enzymatic gene amplification: qualitative and quantitative methods for detecting proviral DNA amplified in vitro. J Infect Dis 158: 1158–1169
Ahmad N, Venkatesam S (1988)NEF protein of HIV-1 is a transcriptional repressor of HIV-1 LTR. Science 241: 1481–1485
Ameisen JC, Guy B, Chamaret S, Loche M, Mouton Y, Neyrinck JL, Khalife J, Leprevost C, Beaucaire G, Boutillon C, Gras-Masse H, Maniez M, Kieny MP, Laustriat D, Berthier A, Mach B, Montagnier L, Lecocq JP, Capron A (1989) Antibodies to the protein and toNEF peptides in HIV-1-infected seronegative individuals. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 5: 279–291
de la Salle C, Baas MJ, Grunebaum L, Wiesel ML, Bianco A, Gialeraki R, Mandalaki T, Cazenave JP (1989) Carrier detection in hemophilia using pedigree analysis coagulation tests and DNA probes. Nouv Rev Fr Hématol 31: 193–202
Gibbons J, Cory J, Hewlett I, Epstein J, Eyster E (1990) Silent infections with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 are highly unlikely in multitransfused seronegative hemophiliacs. Blood 76: 1924–1926
Guy B, Kieny MP, Rivière Y, Le Peuch C, Dott K, Girard M, Montagnier L, Lecocq JP (1987) HIV F/3′ Orf encodes a phosphorylated GTP binding protein resembling an oncogene product. Nature 330: 266–269
Hammes SR, Dixon EP, Malim MH, Cullen BR, Greene WC (1989)nef Protein of human immunodeficiency virus type A: evidence against its role as a transcriptional inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 9549–9553
Hewlett IK, Gregg RA, Ou CY, Hawthorne CA, Mayner RE, Schumacher RT, Schochetman G, Epstein JC (1988) Detection in plasma of HIV-1-specific DNA and RNA by polymerase chain reaction before and after seroconversion. J Clin Immunoassay 11: 161–164
Hewlett IK, Laurian Y, Epstein J, Hawthorne CA, Ruta M, Allain JP (1990) Assessment by gene amplification and serological markers of transmission of HIV-1 from hemophiliacs to their sexual partners and secondarily to their children. AIDS 3: 714–720
Imagawa DT, Lee MH, Wolinsky SM, Sano K, Morales F, Kwok S, Sninsky JJ, Nishanian PG, Giorgi J, Fahey JL, Dudley J, Visscher B, Detels R (1989) Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in homosexual men who remain seronegative for prolonged periods. N Engl J Med 320: 1458–1462
Jackson JB, Kwok SY, Hopsicker JS, Sannerud KJ, Sninsky JJ, Edson JR, Balfour HH (1989) Absence of HIV-1 infection in antibody-negative sexual partners of HIV-1 infected hemophiliacs. Transfusion 29: 265–267
Kogan SC, Doherty ABM, Gitschier J (1987) An improved method for prenatal diagnosis of genetic diseases by analysis of amplified DNA sequences. N Engl J Med 317: 985–990
Kwok SY, Kellogg DE, Mc Kinney N, Spasic D, Goda L, Levenson C, Sninksy JJ (1990) Effect of primer-template mismatches on the polymerase chain reaction: human immunodeficiency virus type I model studies. Nucleic Acids Res 18: 999–1005
Larzul D, Guigne F, Sninsky JJ, Mack DM, Brechot C, Guesdon JL (1988) Detection of hepatitis B virus sequences in serum by using in vitro enzymatic amplification. J Virol Method 20: 227–237
Laure F, Rouzioux C, Veber F, Jacomet C, Courgnaud V, Blanche S, Burgard M, Griscelli C, Brechot C (1988) Detection of HIV-1 DNA in infants and children by means of the polymerase chain reaction. Lancet 2: 538–540
Lefrère JJ, Mariotti M, Rouger Ph, Salmon C (1989) Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) et infection par le virus de l'immunodeficience humaine (VIH). Rev Fr Transfus Hémobiol 32: 431–449
Lefrère JJ, Mariotti M, Ferrer-le-Coeur F, Rouger P, Noël B, Bosser C (1990) PCR testing in HIV-1 seronegative haemophilia. Lancet 2: 1386
Loche M, Mach B (1988) Identification of HIV-infected seronegative individuals by a direct diagnostic test based on hybridisation to amplified viral DNA. Lancet 2: 418–421
Mariotti M, Lefrère JJ, Noël B, Ferrer-le-Coeur F, Vittecoq D, Girot R, Bosser C, Couroucé AM, Salmon C, Rouger P (1990) DNA amplification of HIV-1 in seropositive individuals and in seronegative at-risk individuals. AIDS 4: 633–637
Ou CY, Kwok S, Mitchell S, Mack DH, Sninsky JJ, Krebs JW, Feorino P, Warfield D, Schochetman G (1988) DNA amplification for direct detection of HIV-1 in DNA of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Science 239: 295–297
Prince AM, Horowitz B, Brotman B (1986) Sterilisation of hepatitis and HTLV-III viruses by exposure to tri (n-butyl) phosphate and sodium cholate. Lancet 1: 706–710
Rogers MF, Ou CY, Rayfield M, Thomas PA, Schoenbaum EE, Abrams E, Krasinski K, Selwyn PA, Moore J, Kaul A, Grimm KT, Bamji M, Schochetman G (1989) Use of the polymerase chain reaction for early detection of the proviral sequences of human immunodeficiency virus in infants born to seropositive mothers. N Engl J Med 320: 1649–1654
Saiki RK, Scharf S, Faloona F, Mullis KB, Ho GT, Erlich HA, Arnheim N (1985) Enzymatic amplification of β globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science 230: 1350–1354
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The study was supported by a grant from CNAMTS-INSERM (Biologie moléculaire des maladies hémorragiques et thrombotiques héréditaires).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de la Salle, C., Baas, M.J., Laustriat, D. et al. DNA amplification of HIV genome in hemophiliacs and in newborns from seropositive mothers. Ann Hematol 62, 165–168 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01703142
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01703142