Summary
Many OCC are at present current constituents of the global ecosystem. Their biological effects are of great interest to ecologists and environmental toxicologists.
This paper deals with the interrelationship between OCC (p,p′-DDT, Dieldrin and Arochlor 1221) and the serum level of protein fractions in rabbits receiving the above-mentioned compounds.
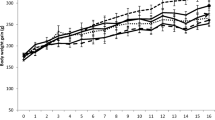
Sixty rabbits were divided into 6 groups given respectively no OCC, 200 ppm p,p′-DDT, 50 ppm Dieldrin, 200 ppm Arochlor-1221, 100 ppm p,p′-DDT and 100 ppm Arochlor-1221, 25 ppm Dieldrin and 100 ppm Arochlor in their drinking water which contained 6‰ ethyl alcohol in all groups.
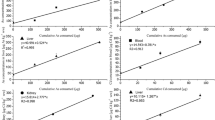
After p,p′-DDT administration the increased plasma levels of DDT were accompanied by increased levels of Dieldrin,γ-BHC and PCBs, although the animals did not receive extra dosage of these OCC, except the amounts currently present in food and water. Dieldrin administration led to a concomitant increase in total DDT plasma level. A moderate increase in total DDT plasma level occurred also after the administration of PCBs. When administered concomitantly, in half doses, the same results were obtained at a lower level.
Variations in plasma level of different OCC as a result of feeding a given compound may explain differences in the degree of toxicity based on the resultant of metabolic interrelationships of OCC in the animal body.
The serum level of gamma globulin fractions (IgG and IgM) shows a tendency to decrease in rabbits given OCC. The serum albumin level rose in rabbits receiving OCI and fell in those receiving PCBs. In regard to the biological effects of OCC these facts point to a moderation of the activity of the immunological system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ANDERSON, D.W., J.J. HICKEY, R.W. RISEBROUGH, D.F. HUGHES and R.E. CHRISTENSEN: Canadian Field-Naturalist83, 91 (1969).
ARMOUR, A. JUDITH and J.A. BRUKE: J. of the AOAC53, 761 (1970).
BAGLEY, G.E., W.L. REICHEL and E. CROMARTIE: J. of Ass. of Official Analytical Chemists53, 251 (1970).
BIROS, FRANCIS J., AMITA C. WALKER and ANGELA MEDBERY: Bull. Env. Cont. and Toxic.5, 317 (1970).
DRINKER, C.K., W.F. WARREN and G.A. BENNELL: J. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol.19, 283 (1937).
Dustman, E.M., L.F. Stickel, L.J. Blus, W.L. Reichel and S.N. Wiemeyer: Transactions of the Thirty-Sixth North American Wildlife and Natural Resources Conference, March 17–20, 1971.
FAHEY, Y.L. and E.M. McKELVEY: J. Immun.94, 98 (1965).
HOLMES, D.C., J.H. SIMMONS and J.O.G. TATLON: Nature216, 227 (1967).
HOWELL, D.E.: Proc. Oklahoma Acad. Sci.29, 31 (1948).
IRISH, O.D.: Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology. Vol. 2. New York: F.A. Patty Ed. 1963.
JENSEN, S.: New Sci.32, 612 (1966).
Jensen, S.: PCB Conference, Uppsala, September 29,1970.
KOEMAN, J.H., TEN NOEVER, M.D. DE BRAUW and R.H. DE VOS: Nature221, 1126 (1969).
Lichtenstein, E.P., K.R. Schultz, T.W. Fuhremann and T.T. Liang: J. of Econ. Entomol. p. 761 (1969).
MILLER, J.W.: U.S. Public Health Rec.59, 1085 (1944).
MULHERN, B.M., W.L. REICHEL, L.N. LOCKE, T.G. LAMONT, A. DELISLE, E. CROMARTIE, G.E. BAGLEY and R.M. PROUTY: Pesticides Monitoring J.4, 141 (1970).
PEAKAL, D.B. and J.L. LINCER: BioScience20, 958 (1970).
PREOTT, JAN, D.Y. JEFFERES and N.W. MOORE: Environmental Pollution1, 3 (1970).
REICHEL, W.L., E. CROMARTIE, THAIR G. LAMONT, BERNARD M. MULHERN and R.M. PROUTY: Pesticides Monitoring J.3, 142 (1969).
RISEBROUGH, R.W., P. REICHE, D.B. PEAKALL, S.G. HEIMAN and M.N. KINVEN: Nature220, 1098 (1968).
VOS, J.G. and R.B. BEEMS: Toxic. Appl. Pharmacol.19, 617 (1971).
WASSERMANN, M., DORA WASSERMANN, ZIPORA GERSHON and L. ZELLER-MAYER: Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.160, 393 (1969).
VOS, J.G. and TH. DE ROIJ: Toxic. Appl. Pharmacol.21, 549 (1972)
WASSERMANN, M., DORA WASSERMANN, E. KEDAR and M. DJAVAHERIAN: Bull. Env. Cont. and Toxicol.6, 426 (1971).
WASSERMANN, M., DORA WASSERMANN, E. KEDAR, M. DJAVAHERIAN and SIMI CUCOS: Bull. Environ, Cont. and Toxicol. 8, 177 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wassermann, M., Wassermann, D., Kedar, E. et al. Effect of organochlorine compounds on serum proteins. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 10, 42–50 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01684753
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01684753