Summary
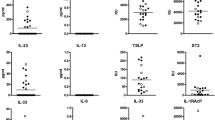
In 36 HIV seropositive patients with the clinical manifestation of AIDS and a suspectedPneumocystis carinii infection, lymphocyte subpopulations were analzyed in the peripheral blood (PBL) and compared with the results of the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL).
Of those 36 patients, 29 showed a highly abnormal CD4/CD8 ratio in both the PBL and the BAL. The clinical course of these 29 patients was unpredictable. In seven patients, however, the CD4/CD8 ratio in the BAL was normal or only slightly altered, despite a highly abnormal CD4/CD8 ratio in the PBL. Five of these seven patients improved greatly during the clinical course.
The positive outcome of the clinical course was even more strongly correlated with the number of macrophages in the BAL. Twelve of the 36 patients showed normal or only slightly changed numbers of macrophages in the BAL. Eleven of these twelve patients (92%) improved rapidly during antibiotic therapy, while the clinical course was unpredictable in patients with markedly reduced macrophage counts in the BAL.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FITC:
-
Fluorescein-isothiocyanat
- PE:
-
Phycoerythrin
- CD:
-
Clusters of Differentiation (Nomenklatur für monoklonale Antikörper nach den Vereinbarungen der Internationalen Workshops)
Literatur
Broaddus C, Dake MD, Stulbarg MS, Blumenfeld W, Hadley WK, Golden JA, Hopewell PC (1985) Bronchoalveolar lavage and transbronchial biopsy for the diagnosis of pulmonary infections in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med 102:747–752
Costabel U, Bross KJ, Matthys H (1985) Bronchoalveoläre Lavage: Klinische Bedeutung zytologischer und immunzytologischer Befunde. Prax Klin Pneumol 39:343–355
Costabel U, Bross KJ, Matthys H (1983) Pulmonary sarcoidosis: assessment of disease activity by lung lymphocyte subpopulations. Klin Wochenschr 61:349–356
Costabel U, Bross KJ, Marxen J, Matthys H (1984) T-Lymphocytosis in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of hypersensitivity pneumonitis: changes in profile of T-cell subsets during the course of disease. Chest 85:514–518
Costabel U, Bross KJ, Rühle KH, Löhr GW, Matthys H (1985) 1a-like antigens on T cells and their subpopulations in pulmonary sarcoidosis and in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Analysis of bronchoalveolar and blood lymphocytes. Am Rev Respir Dis 131:337–342
Costabel U, Matthys H, Barth J, Bauer KH, Dierkesmann R, König G, Konietzko N, Loddenkemper R, Loos U, Petermann W, Rust M, Steppling H, Worth H (1988) Ergebnisse einer Umfrage zum methodischen Vorgehen bei der bronchoalveolären Lavage (BAL). Prax Klin Pneumol 42:79–82
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Pneumologie und Tuberkulose (1988) Empfehlungen zur diagnostischen bronchoalveolären Lavage. Prax Klin Pneumol 42:119–122
Dörfler H, Hehlmann R, Zoller WG, Goebel F-D (1987) Bronchoskopischer Nachweis der Pneumocystis-carinii-Pneumonie. Med Klin 82:515–517
Hartmann B, Koss M, Hui A, Baumann W, Athos L, Boylen T (1985) Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Diagnosis with bronchial brushings, biopsy and bronchoalveolar lavage. Chest 87:603–607
Masur H, Michelis MA, Greene JB, Onarato J, van de Stouwe RA, Holzmann RS, Wormser G, Brettmann L, Lange M, Murray HW, Cunningham-Rundles S (1981) An outbreak of community — acquired pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: Initial manifestation of cellular immune dysfunction. New Engl J Med 305:1431–1438
Müller-Quernheim J (1987) Kompartimentalisierte T-Zellaktivierung bei der akuten Sarkoidose. Prax Klin Pneumol 41:118–128
Plata F, Autran B, Martins LP, Wain-Hobson S, Raphal M, Mayaud C, Denis M, Guillon JM, Debr P (1987) AIDS virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in lung discorders. Nature 328:348–351
Redfield RR, Wright DC, Tramont EC (1986) Special Report. The Walter Reed Staging Classification for HTLV-III/LAV Infection. New Engl J Med 314:131–132
Reynolds HY (1987) Bronchoalveolar lavage: state of art. Am Rev Respir Dis 135:250–263
Turner-Warwick M, Haslam PL (1986) Clinical applications of bronchoalveolar lavage: an interim view. Br J Dis Chest 80:105–121
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huhn, C., Nerl, C., Siebert, A. et al. Die prognostische Bedeutung von Lymphozytensubpopulationen und Makrophagen im peripheren Blut und in der bronchoalveolären Lavage bei AIDS-Patienten mit Verdacht auf Pneumocystis-carinii-Pneumonie. Klin Wochenschr 68, 853–856 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01662781
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01662781