Summary
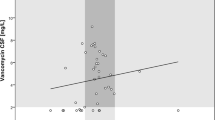
In patients with different neurological diseases with blood-brain barrier dysfunction subjected to diagnostic CSF-tap, simultaneous determinations of ofloxacin concentrations in serum and in CSF were carried out. The results show that ofloxacin penetrates well into the CSF achieving adequate bactericidal concentrations against most of the common causative pathogens of meningitis.
Zusammenfassung
Bei Patienten mit verschiedenen neurologischen Erkrankungen und Störungen der Blutliquorschranke, wurde im Rahmen diagnostisch erforderlicher Liquorpunktionen eine simultane Bestimmung der Ofloxacinkonzentrationen im Serum und Liquor vorgenommen. Die Ergebnisse lassen auf eine gute Liquorgängigkeit schließen, wobei Ofloxacin-Liquorspiegel erreicht werden, die für eine bakterizide Wirkung gegen die meisten gängigen Meningitiserreger ausreichen dürften.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Bruch, K. Clinical results with ofloxacin. FAC 3–5 (1984) 741–748.
Dagrosa, E., Seeger, K., Malerczyk, V., Lameire, N. Pharmacokinetics of ofloxacin (Hoe 280). FAC 3–5 (1984) 665–671.
Naber, K. In vitro activity and pharmacokinetics of ofloxacin urology patients with complicated urinary tract infections. RAC 1–2 (1985) 59–62.
Naber, K., Bartosik-Wich, B. Serum and urinary concentrations of norfloxacin, ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin in elderly urology patients. FAC 3–5 (1984) 701–709.
Stille, W. Progress in the development of newer gyrase inhibitors. RAC 1–2 (1985) 31–34.
Bauernfeind, A., Ullmann, U. In vitro activity of enoxacin, ofloxacin, norfloxacin and nalidixic acid. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 14 Suppl. c (1984) 33.
Knothe, H., Shah, P. M. Antibacterial activities of gyrase inhibitors. RAC 1–2 (1985) 37–41.
Seibert, G., Limbert, M., Klesel, N. Comparison of the antibacterialin vitro andin vivo activity of ofloxacin (Hoe 280 DL-8280) and nalidixic acid analogues. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2 (1983) 548–553.
Reiber, H. The discrimination between different blood-CSF barrier dysfunctions and inflammatory reactions of the CNS by a recent evaluation graph for the protein profile of CSF. J. Neurol. 224 (1980) 89–99.
Friedrich, H., Hänsel-Friedrich, G., Dietz, H., Potel, J. Penetration of antimicrobial drugs into the cerebrospinal fluid. Its relevance in postoperative CNS infections. Modern Neurosurgery 1 (1982) 81–90.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stübner, G., Weinrich, W. & Brands, U. Study of the cerebrospinal fluid penetrability of ofloxacin. Infection 14 (Suppl 4), S250–S253 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01661285
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01661285