Abstract
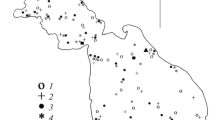
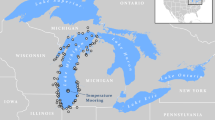
Recent studies of potential climatic change on Great Lakes fisheries (e.g. Meisner , 1987; Magnuson , 1990; Regieret al., 1990) and our general ignorance of the natural variability of the basic physical properties of the Great Lakes (McCormick, 1990) have demonstrated the need for a long-term observation program which is representative of the lake-wide environment. In April 1990 a site was established in Lake Michigan to continuously monitor the offshore thermal structure and vertical velocity profile. The site is located near the center of the lake's southern basin in 160 m of water. Temperature is measured at 16 depths (winter) to 28 depths (summer), and the horizontal velocity components are measured at 5 levels which allows us to characterize the offshore environment with high temporal resolution. The goals of this effort are to provide basic physical measurements to better describe the flow of energy through the lake ecosystem and to provide a basis against which future change can be better gauged.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Assel, R. A.: 1991, ‘Implications of CO2 Warming on Great Lakes Ice Cover’,Clim. Change 18, 377–395.
Assel, R. A. and Quinn, F. H.: 1979, ‘A Historical Perspective of the 1976–77 Lake Michigan Ice Cover’,Mon. Wea. Rev. 107, 336–341.
Ayers, J. C.: 1965, ‘The Climatology of Lake Michigan’,Univ. Michig., Great Lakes Res. Div. Publication12, 73 pp.
Blumberg, A. F. and DiToro, D. M.: 1990, ‘Effects of Climate Warming on Dissolved Oxygen Concentrations in Lake Erie’,Transact. Amer. Fish. Soc. 119, 210–223.
Church, P. E.: 1945, ‘The Annual Temperature Cycle of Lake Michigan. II. (Spring Warming and Summer Stratification Period 1942)’,Depart. Meteorol., Univ. Chicago MR18, 100 pp.
Croley, T. E., II: 1990, ‘Laurentian Great Lakes Double-CO2 Climatic Change Hydrological Impacts’,Clim. Change 17, 27–47.
Hill, D. K. and Magnuson, J. J.: 1990, ‘Potential Effects of Global Climate Warming on the Growth and Prey Consumption of Great Lakes Fish’,Transact. Amer. Fish. Soc. 119, 265–275.
Johnson, T. B. and Evans, D. O.: 1990, ‘Size-Dependent Winter Mortality of Young-of-the-Year White Perch: Climate Warming and Invasion of the Laurentian Great Lakes’,Transact. Amer. Fish. Soc. 119, 301–313.
Lesht, B. M. and Brandner, D. J.: 1992, ‘Functional Representation of Great Lakes Surface Temperatures’,J. Great Lakes Res. 18, 98–107.
Magnuson, J. J., Crowder, L. B., and Medvick, P. A.: 1979, ‘Temperature as an Ecological Resource’,Amer. Zoologist 19, 331–343.
Magnuson, J. J., Meisner, J. D., and Hill, D. K.: 1990, ‘Potential Changes in the Thermal Habitat of Great Lakes Fish after Global Climate Warming’,Transact. Amer. Fish. Soc. 119, 254–264.
Mandrak, N. E.: 1989, ‘Potential Invasion of the Great lakes by Fish Species Associated with Climatic Warming’,J. Great Lakes Res. 15, 306–316.
McCormick, M. J.: 1990, ‘Potential Changes in Thermal Structure and Cycle of Lake Michigan Due to Global Warming’,Transact. Amer. Fish. Soc. 119, 183–194.
McCormick, M. J. and Meadows, G. A.: 1988, ‘An Intercomparison of Four Mixed Layer Models in a Shallow Inland Sea’,J. Geophys. Res. 93 (C6, 6774–6788.
Meisner, J. D., Goodier, J. L., Regier, H. A., Shuter, B. J., and Christie, W. J.: 1987, ‘An Assessment of the Effects of Climate Warming on Great Lakes Basin Fishes’,J. Great Lakes Res. 13, 340–352.
Pollard, R. T., Rhines, P. B., and Thompson, R. O. R. Y.: 1973, ‘The Deepening of the Wind-Mixed Layer’,Geophys. Fluid Dynam. 3, 381–404.
Regier, H. A., Holmes, J. A., and Pauly, D.: 1990, ‘Influence of Temperature Changes on Aquatic Ecosystems: An Interpretation of Empirical Data’,Transact. Amer. Fish. Soc. 119, 374–389.
Saylor, J. H., Huang, J. C. K., and Reid, R. O.: 1980, ‘Vortex Modes in Southern Lake Michigan’,J. Phys. Oceanogr. 10, 1814–1823.
Smith, J. B.: 1991, ‘The Potential Impacts of Climate Change on the Great Lakes’,Bull. Amer. Meteorol. Soc. 72 (1, 21–28.
Thompson, R. O. R. Y.: 1976, ‘Climatological Numerical Models of the Surface Mixed Layer of the Ocean’,J. Phys. Oceanogr. 6, 496–503.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCormick, M.J., Pazdalski, J.D. Monitoring midlake water temperature in southern Lake Michigan for climate change studies. Climatic Change 25, 119–125 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01661201
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01661201