Summary
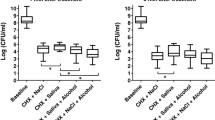
Bacampicillin was given as tablets or syrup in doses of 400 mg three times per day for seven days to twelve subjects. Saliva, throat and faecal specimens were taken during fourteen days for cultivation of aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. No changes in the oral, throat and faecal flora were seen in the subjects receiving tablets while there was a decrease in the number of aerobic and anaerobic bacteria in those subjects receiving syrup. No increased resistance to ampicillin were found in the isolated bacterial strains. Bacampicillin was well-tolerated and no gastro-intestinal disturbances were experienced.
Zusammenfassung
Bacampicillin wurde in Tabletten- oder Sirupform in Dosen von 400 mg dreimal täglich für sieben Tage an zwölf Personen verabreicht. Speichel-Rachensekret-und Stuhlproben wurden über einen Zeitraum von vierzehn Tagen abgenommen und kulturell auf aerobe und anaerobe Bakterien untersucht. Bei den Personen, die Tabletten erhielten, waren keine Veränderungen der Mund-, Rachen- und Darmflora zu sehen. Hingegen fand sich bei den Personen, die Sirup erhielten, eine Erniedrigung der Anzahl aerober und anaerober Bakterien. Eine erhöhte Resistenz gegen Ampicillin bei den isolierten Bakterienstämmen wurde nicht festgestellt. Bacampicillin wurde gut vertragen, gastrointestinale Störungen traten nicht auf.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Bodin, N. O., Ekström, B., Forsgren, U., Jalar, L. P., Magni, L., Ramsay, C. H., Sjöberg, B. Bacampicillin: A new orally well-absorbed derivate of ampicillin. Antimicrob. Ag. Chemother. 8 (1975) 518–525.
Clayton, J. P., Cole, M., Elson, S. W., Ferres, H. BRL 8988 (talampicillin), a well-absorbed oral form of ampicillin. Antimicrob. Ag. Chemother. 5 (1974) 670–671.
Shiobara, Y., Tachibana, A., Sasaki, H., Watanabe, T., Sado, T. Phthalidyl D-α-aminobenzyl-penicillinate hydrochloride (PC-183), a new orally active ampicillin ester. J. Antibiot. 27 (1974) 665–673.
Knudsen, E. T., Harding, J. W. A multicentre comparative trial of talampicillin and ampicillin in general practice. Brit. J. Clin. Pract. 10 (1975) 255–264.
EkstrÖm, B., Forsgren, U., Magni, L., Sjöberg, B., Sjöwall, J., Tolf, R. Bacampicillin, a well-absorbed prodrug of ampicillin — a report on properties and clinical experience. J. Drug Res. 2 (1977) 39–44.
Willcox, J. B., Brogden, R. N., Avery, G. S. Pivampicillin: A preliminary report of its pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic efficacy. Drugs 6 (1973) 94–103.
Jalling, B., Malmborg, A. S., Lindman, A., Boreus, L. O. Evaluation of a micromethod for determination of antibiotic concentrations in plasma. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 4 (1972) 150–157.
Holdeman, L. V., Cato, E. C., Moore, W. E. C. Anaerobe Laboratory Manual, 4th ed. Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg/Virginia, 1977.
Nord, C. E., Lindberg, A. A., Dahlbäck, A. Evaluation of five test kits — API, Auxotab, Enterotube, Pathotec and R/B — for identification ofEnterobacteriaceae. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 159 (1974) 211–220.
Nord, C. E., Wretlind, B., Dahlbäck, A. Evaluation of two test-kits — API and OxiFerm tube — for identification of oxidative-fermentative Gram-negative rods. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 163 (1977) 93–97.
Dornbusch, K., Nord, C. E., Olsson, B., Wadström, T. Some properties of coagulase-negative deoxyribonuclease-producing strains of staphylococci from human infections. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 162 (1976) 143–152.
Facklam, R. R., Padala, J. P., Thaeker, L. G., Wortham, E. C., Sconyers, B. J. Presumptive identification of A, B and D streptococci. Appl. Microbiol. 27 (1974) 107–113.
Wadström, T., Nord, C. E., Lindberg, A. A., Möllby, R. Rapid grouping of streptococci by immunoelectroosmophoresis. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 159 (1974) 191–200.
Nord, C. E., Dahlbäck, A., Wadström, T. Evaluation of a test-kit for identification of anaerobic bacteria. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 161 (1975) 239–242.
Dornbusch, K., Nord, C. E., Wadström, T. Biochemical characterization and in vitro determination of antibiotic susceptibility of clinical isolates ofBacteroides fragilis. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 6 (1974) 253–257.
Eriksson, H. M., Sherris, J. Antibiotic sensitivity testing. Report of an international collaborative study. Acta Path. Microbiol. Scand. Suppl. 217 (1971) 35–37.
Sutter, V. L., Finegold, S. M. The effect of antimicrobial agents on human faecal flora; studies with cephalexin, cyclacillin and clindamycin. In: Skinner, F. A., Carr, J. G. (ed): Normal microbial flora of man. Academic Press, London 1974, p. 229.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heimdahl, A., Nord, C.E. & Weilander, K. Effect of bacampicillin on human mouth, throat and colon flora. Infection 7 (Suppl 5), S446–S451 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01659768
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01659768