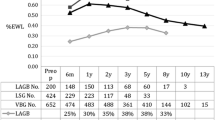
Abstract
Sixty-nine (13M, 56F), severely obese patients (body mass index 47 kg/m2) have had vertical banded gastroplasty (GP) with 5-cm polypropylene mesh (n=39) or fascia (n=30) bands since 1981. Of these 69 patients, 30 also had truncal vagotomy (TVG) without drainage. Total office follow-up rate is 94%. During follow-up of 1 year or more (mean 60 months), 25 patients with vagotomy plus gastroplasty lost 33±3 kg, corresponding to 51% of excess weight, compared to 21±3 kg (34% Excess weight) in the 34 patients having gastroplasty alone (p<0.01). In patients followed ≥ 5 years (mean 83 months) 10 patients with TVG lost 40±5 kg (61% of excess) compared to 17±4 kg (28% of excess) in 22 patients with GP alone (p<0.001). Frequency and severity of complications were similar in both groups, but there were seven reoperations after GP and three after TVG (p<0.05). Studies of gastric emptying of a solid meal in 14 of the patients with GP and 14 with TVG demonstrated greater weight loss in those with prolonged emptying and gastroesophageal pooling, though the emptying rates of patients with GP and those with TVG showed no statistically significant difference. Our earlier studies, which showed reduced liquid consumption after vagotomy, imply that this mechanism (rather than delayed emptying) explains why vagotomy potentiates weight loss after gastroplasty.
Résumé
Soixante-neuf patients sévèrement obèses (13 hommes: index de masse corporelle = 47 kg/m2) ont eu une gastroplastie verticale (GV) au moyen d'une plaque de polypropylène (n= 39) ou d'une aponévrose (n=30) depuis 1981. Parmi ceux-ci, 30 ont eu une vagotomie tronculaire (VT) sans drainage. Quatrevingt quatorze pourcent de ces patients ont été suivis. Parmi les patients suivis pendant plus d'un an (moyenne = 60 mois), 25 patients ayant en une GV + VT ont perdu 33±3 Kg (51% du surpoids), comparés à 21±3 Kg (34% du surpoids) pour les 34 patients qui ont eu une GV seule (p<0.01). Chez les patients suivis pendant plus de 5 ans (moyenne = 83 mois), les 10 patients ayant eu une GV + VT ont perdu 40±5 Kg (61% du surpoids) comparés à 17±4 Kg (28% du surpoids) chez les 22 patients qui ont eu une GV seule (p<0.001). La fréquence des complications et leur séverité ont été similaires dans les deux groupes. Cependant, il y a eu 7 réinterventions après GV comparées à 3 après GV + VT (p<0.05). L'étude de la vidange gastrique, après un repas solide, chez 14 patients de chaque groupe a démontré que la perte de poids était proportionnelle au temps de vidange et au “pooling” gastrooesophagien, mais qu'il n'y avait aucune différence significative entre les deux groupes. Dans une étude antérieure, nous avons démontré que la consommation liquidienne était réduite après vagotomie, ce qui implique que ce soit ce mécanisme, plutÔt que le retard de vidange qui explique l'effet potentialisateur de la VT dans la perte de poids après GV + VT.
Resumen
Sesenta y nueve (13 hombres) pacientes con obesidad severa (Indice de Masa Corporal = 47 kg/m2) fueron sometidos a gastroplastia de banda vertical (GP) con malla de polipropileno de 5 cm (n=39) o con fascia (n=30) a partir de 1981; en 30 se practicó vagotomía troncular (VGT) sin drenaje. La tasa de seguimiento es de 94%. En el seguimiento a≥1 año (media:60 meses), 25 pacientes con VGT y GP perdieron 33±3 kg, equivalente al 51% del exceso de peso, en comparacion con una pérdida de 21±3 kg (34% del exceso) en los 34 pacientes con GP solamente (p<0.01). En los pacientes seguidos por ≥ 5 años (media:83 meses), 10 con VGT perdieron 40±5 kg (61% del exceso), contra 17±4 kg (28% del exceso) en 22 pacientes con GP solamente (p<0.001). La frecuencia y la severidad de las complicaciones fueron similares en los dos grupos; sin embargo, se realizaron 7 reoperaciones después de GP y 3 después de VGT (p<0.05). Los estudios de vaciamiento gástrico de una comida sólida en 14 de los pacientes con GP y en 14 con VGT demostraron mayor pérdida de peso en los pacientes con vaciamiento prolongado y estancamiento gastroesofágico, aunque no se halló diferencia estadísticamente significativa en las tasas de vaciamiento entres los pacientes con GP y con VGT. Nuestros estudios previos que mostraron una reducción en el consumo de líquidos después de vagotomía implican que este mecanismo, más que un vaciamiento retardado, puede explicar el por qué la vagotomía potencia la pérdida de peso consecuente a la gastroplastía.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
NIH Consensus Development Conference: Gastrointestinal surgery for severe obesity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 55(Suppl. 2):487S, 1992
Kral, J.G.: Surgical treatment of obesity. In Obesity. P. Bjorntorp, B.N. Brodoff, editors. Philadelphia, Lippincott, 1992, pp. 731–741
Sclafani, A., Kramer, T.H.: Aversive effects of vagotomy: a conditioned taste aversion analysis. Physiol. Behav.34:721, 1985
Kraly, F.S., Gibbs, J., Smith, G.P.: Disordered drinking after abdominal vagotomy in rats. Nature258:226, 1975
Kral, J.G.: Vagotomy as a treatment for severe obesity. Lancet1:307, 1978
Görtz, L., Wallin, G., Kral, J.G.: Vertical banded gastroplasty with and without vagotomy. Clin. Nutr.5(Suppl.):79, 1986
Mason, E.E., Maher, J.W., Scott, D.H., Rodriguez, E.M., Doherty, C.: Ten years of vertical banded gastroplasty for severe obesity. Probl. Gen. Surg.9:280, 1992
Eckhout, G.V., Willbanks, O.L., Moore, J.T.: Vertical ring gastroplasty for morbid obesity: five year experience with 1,463 patients. Am. J. Surg.152:713, 1986
MacLean, L.D., Rhode, B.M., Forse, R.A.: Late results of vertical banded gastroplasty for morbid and super obesity. Surgery107:20, 1990
Drane, W.E., Marks, D.S., Simms, S.M., Saylor, J.G., Haas, P.A., Kambouris, A.A.: Work in progress: radioisotopic evaluation of gastroplasty patients. Radiology147:215, 1983
Villar, H.V., Wangensteen, S.L., Burks, T.F., Patton, D.D.: Mechanisms of satiety and gastric emptying after gastric partitioning and bypass. Surgery90:229, 1981
Horowitz, M., Collins, P.J., Chatterton, B.E., Harding, P.E., Watts, J.McK., Shearman, D.J.C.: Gastric emptying after gastroplasty for morbid obesity. Br. J. Surg.71:435, 1984
Behrns, K.E., Soper, N.J., Sarr, M.G., Kelly, K.A., Hughes, R.W.: Anatomic, motor and clinical assessment of vertical banded gastroplasty. Gastroenterology97:91, 1989
Christian, P.E., Datz, F.L., Moore, J.G.: Gastric emptying studies in the morbidly obese before and after gastroplasty. J. Nucl. Med.27:1686, 1986
Wilbur, B.G., Kelly, K.A.: Effect of proximal gastric, complete gastric, and truncal vagotomy on canine gastric electric activity, motility, and emptying. Ann. Surg.178:295, 1973
Powers, M.A., Pappas, T.N.: Physiologic approaches to the control of obesity. Ann. Surg.209:255, 1989
Gastrointestinal surgery for severe obesity: National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference Statement. Ann. Intern. Med.115:956, 1991
Sugerman, H.J., Starkey, J.V., Birkenhauer, R.: A randomized prospective trial of gastric bypass versus vertical banded gastroplasty for morbid obesity and their effects on sweets versus non-sweets eaters. Ann. Surg.205:613, 1987
Görtz, L., Björkman, A-C., Andersson, H., Kral, J.G.: Truncal vagotomy reduces food and liquid intake in man. Physiol. Behav.48:779, 1990
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kral, J.G., Görtz, L., Hermansson, G. et al. Gastroplasty for obesity: Long-term weight loss improved by vagotomy. World J. Surg. 17, 75–78 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01655710
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01655710