Summary
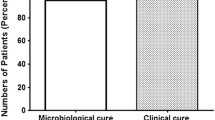
The clinical efficacy and the safety of ciprofloxacin was studied in 92 patients (aged 26 to 83 years; mean 57.5 years) affected by urinary tract infections (UTI) and respiratory tract infections (RTI) suffering also with various liver diseases. Ciprofloxacin was given orally at different dose regimens: 500 mg b.i.d. (22 cases), 250 mg b.i.d. (20 cases), 500 mg s.i.d. (20 cases) for the treatment of UTIs; 500 mg b.i.d. (ten cases) and 250 mg b.i.d. (20 cases) for the treatment of RTIs. The doses were not correlated to the severity of the infections. Patients were treated for five to 15 days. All the bacteria isolated from sputum or urine before treatment were sensitive to ciprofloxacin (MIC range ≤ 0.015 mg/1 to 8 mg/1). The clinical and bacteriological responses were favourable in a high percentage of patients both for RTIs and UTIs, irrespective of the dose. Side effects were infrequent (7%) and mild (nausea, gastralgia, oral candidosis), never requiring the interruption of the treatment. No change in the blood chemistry tests was observed at any dose.
Zusammenfassung
Die klinische Wirksamkeit und Sicherheit von Ciprofloxacin wurde bei 92 Patienten (Alter 26 bis 83 Jahre, im Mittel 57,5 Jahre), die an verschiedenen Leberkrankheiten litten, bei interkurrent aufgetretenen Harnwegs- und Atemwegsinfektionen geprüft. Ciprofloxacin wurde in verschiedenen Dosierungen oral verabreicht. Zur Behandlung von Harnwegsinfektionen wurden Dosierungen von 500 mg zweimal täglich (22 Fälle), 250 mg zweimal täglich (20 Fälle) oder 500 mg in einer täglichen Einzeldosis (20 Fälle) verabreicht. Atemwegsinfektionen wurden mit zweimal täglich 500 mg (10 Fälle) oder mit zweimal täglich 250 mg (20 Fälle) behandelt. Die Dosen wurden nicht nach dem Schweregrad der Erkrankung gewählt. Die Behandlungsdauer betrug fünf bis 15 Tage. Alle aus Sputum oder Urin vor der Therapie isolierten Bakterien waren für Ciprofloxacin empfindlich (MHK-Werte ≤ 0,015 mg/l bis 8 mg/l). Bei einem hohen Prozentsatz der Patienten mit Atemwegs- und Harnwegsinfektionen wurden unabhängig von der Dosierung günstige klinische und bakteriologische Ergebnisse erzielt. Nebenwirkungen traten selten auf (7%) und waren leicht (Übelkeit, Magenschmerzen, orale Candidiasis). Ein Therapieabbruch war in keinem Fall nötig. Bei keiner der angewandten Dosierungen waren Änderungen in den klinisch-chemischen Parametern festzustellen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Galante, D., Pennucci, C., Esposito, S., Barba, D. Comparative activity of ciprofloxacin and five other quinolone derivatives against gram-negative isolates. Drugs Exptl. Clin. Res. 11 (1985) 331–334.
King, A., Shannon, K., Phillips, I. Thein vitro activity of ciprofloxacin compared with that of norfloxacin and nalidixic acid. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 13 (1984) 325–331.
Felmingham, D., O'Hare, M. D., Robbins, M. J., Wall, R. A., Williams, A. H., Cremer, A. W., Grüneberg, R. N. Comparativein vitro studies with 4-quinolone antimicrobials. Drugs Exptl. Clin. Res. 11 (1985) 317–320.
Smith, S. M., Eng, R. H. K. Activity of ciprofloxacin against methicillin resistantStaphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 27 (1985) 688–691.
Fass, R. J. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin (Bay o 9867). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 24 (1983) 568–574.
Husson, M. O., Izard, D., Bouillet, L., Leclerc, H. Comparativein vitro activity of ciprofloxacin against non-fermenters. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 15 (1985) 457–462.
Chin, N. X., Neu, H. C. Ciprofloxacin, a quinolone carboxylic acid compound active against aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 25 (1984) 319–326.
Smith, J. T. Mutational resistance to 4-quinolone antibacterial agents. Eur. J. Clin. Microb. 3 (1984) 347–350.
Barba, D., Pennucci, C., Esposito, S., Galante, D. Cross resistance of quinolone derivatives in gram-negative bacteria. Chemioterapia 2 (1985) 192–196.
Van Caekeberghe, D. L., Pattyn, S. R. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin compound with those of other new fluorinated piperazinyl substituted quinoline derivatives. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 25 (1984) 518–521.
Crump, B., Wise, R., Dent, J. Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 24 (1983) 784–786.
Davis, R. L., Koup, J. R., Williams-Warren, J., Weber, A., Smith, A. Pharmacokinetics of three oral formulations of ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 28 (1985) 74–77.
Hoeffken, G., Lode, H., Prinzing, C., Borner, K., Koeppe, P. Pharmacokinetics of ciprofloxacin after oral and parenteral administration. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 27 (1985) 375–379.
Bauer, A. W., Kirby, W. M. M., Sherris, J. C., Turck, M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by standardized single disk method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 45 (1966) 493–496.
Barbare, J. C., Poupon, R. E., Jaillon, P., Prod'home, S., Darnis, F., Poupon, R. Y. Intrinsic hepatic clearance and Child-Turcotte classification for assessment of liver function in cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 1 (1985) 253–259.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esposito, S., Galante, D., Barba, D. et al. Efficacy and safety of ciprofloxacin in the treatment of UTIs and RTIs in patients affected by liver diseases. Infection 16 (Suppl 1), S57–S61 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01650510
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01650510