Summary
By auramine and modified Ziehl-Neelsen staining, cryptosporidial oocysts were found in the stools of 31 (1.36%) out of 2,367 patients with diarrhoea. All specimens were also tested for Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter, Yersinia, and Rotavirus. Among these patients, 432 were children and 24 (5.5%) of them were positive for cryptosporidia. All children infected with cryptosporidia were immunocompetent. Watery diarrhoea, vomiting and abdominal pain were the most frequent symptoms. The survey showed that in patients with gastroenteritis, cryptosporidial oocysts were found more commonly in the stools of children than in those of adults, and the prevalence of infection was the highest in August and September (16 cases). The epidemiological aspects and clinical significance are discussed.
Zusammenfassung
Mit Hilfe einer Auramin- und einer modifizierten Ziehl-Neelsen-Färbung wurden Kryptosporidien-Oozysten in den Stühlen von 31 (1,36%) der 2367 untersuchten Patienten mit Durchfall gefunden. Alle Proben wurden daneben auf Salmonellen, Shigellen, Campylobacter, Yersinien und Rotaviren untersucht. Unter den Patienten befanden sich 432 Kinder, von denen 24 (5,5%) einen positiven Kryptosporidien-Nachweis aufwiesen. Alle mit Kryptosporidien infizierten Kinder waren immunkompetent. Die häufigsten mit einer Kryptosporidien-Infektion einhergehenden Symptome waren wäßrige Diarrhoe, Erbrechen und Abdominalschmerzen. Bei Gastroenteritis wurden Kryptosporidien-Oozysten häufiger im Stuhl von Kindern als im Stuhl von Erwachsenen gefunden. Die Inzidenz der Infektion war in den Monaten August und September (16 Fälle) am höchsten. Sowohl epidemiologische Gesichtspunkte als auch die klinische Bedeutung dieser Befunde werden diskutiert.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Mai Nguyen, X. Intestinale Cryptosporidiose: Eine seltene Durchfallserkrankung beim Menschen. Schweiz. Med. Wochenschr. 115 (1985) 1205–1208.
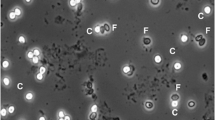
Hendriksen, S. A., Pohlenz, J. F. L. Staining of cryptosporidia by a modified Ziehl-Neelsen technique. Acta Vet. Scand. 22 (1981) 594–596.
Casemore, D. P., Jackson, B. Sporidic cryptosporidiosis in children. Lancet II (1983) 679.
Hunt, D. A., Shannon, R., Palmer, S. R., Jephcott, A. E. Cryptosporidiosis in an urban community. Br. Med. J. 289 (1984) 814–816.
Harari, D. M., West, B., Dwyer, B. Cryptosporidium as cause of laryngotracheitis in an infant. Lancet I (1986) 1207.
Shamid, N. S., Rahman, A. S. M. H., Anderson, B. C., Mata, L. J., Sanyal, S. C. Cryptosporidiosis in Bangladesh. Brit. Med. J. 290 (1985) 114–115.
Current, W. L., Reese, N. C., Ernst, J. V., Bailey, W. S., Hegman, M. B., Weinstein, W. M. Human cryptosporidiosis in immunocompetent and immunodeficient persons. N. Engl. J. Med. 308 (1983) 1252–1257.
Benett, M., Baxby, D., Blundell, N., Gaskell, C. J., Hart, C. A., Kelly, D. F. Cryptosporidiosis in the domestic cat. Vet. Rec. 116 (1985) 73–74.
Cryptosporidiosis among children attending day-care centres. MMWR 33 (1984) 599–601.
Heidl, M. Hering, L., Scholz, H. Kryptosporidiose bei Kindern. Infection 14 (1986) 173–176.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, X.M. Cryptosporidial diarrhoea in children. Infection 15, 444–446 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01647228
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01647228