Summary
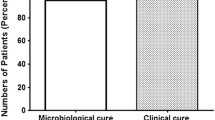
Ceftibuten is an orally active third generation cephalosporin with increased potency against members of theEnterobacteriaceae. In this study, 74 women with acute uncomplicated urinary tract infection (UTI) were enrolled in an open study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of this new antibiotic. Patients were treated with 400 mg ceftibuten once daily for seven days and followed for four to six weeks after cessation of therapy. All pathogens were eradicated during treatment, including five coagulase-negative staphylococci that were resistant to ceftibuten. At five to nine days posttreatment, 93% of patients were cured. Of the five recurrent infections, four patients had a relapse and one had a reinfection. By four to six weeks post-treatment, five additional patients had recurrent infections. The overall cure rate was 85% in this study. Most ceftibuten-associated adverse effects were mild and involved the gastrointestinal tract. Diarrhea was the most commonly reported side effect. Of the eight (11%) patients who developed diarrhea, three had a positive latex agglutination test forClostridium difficile. The diarrhea resolved in all patients without sequelae. Ceftibuten was effective and generally safe in the treatment of women with acute uncomplicated UTI. The high incidence of diarrhea observed in this study is a concern.
Zusammenfassung
Ceftibuten ist ein Oralcephalosporin der dritten Generation mit erhöhter Aktivität gegenEnterobacteriaceae-Arten. Die Wirksamkeit und Sicherheit dieses neuen Antibiotikums wurden in einer offenen Studie bei 74 Frauen mit akuter, unkomplizierter Harnwegsinfektion geprüft. Die Patientinnen erhielten sieben Tage lang eine einmal tägliche Dosis von 400 mg Ceftibuten oral. Nach Ende der Therapie wurden vier bis sechs Wochen lang Nachuntersuchungen vorgenommen. In allen Fällen war eine Erregereradikation nachzuweisen, darunter waren auch fünf Fälle, bei denen koagulase-negative Staphylokokken mit Resistenz gegen Ceftibuten aus dem Urin isoliert worden waren. Eine Heilung war fünf bis neun Tage nach Behandlungsende bei 93% der Patientinnen eingetreten. Rezidive wurden in einem von fünf Fällen auf eine Reinfektion zurückgeführt, in vier Fällen durch den ursprünglichen Keim. Vier bis sechs Wochen nach Therapie hatten weitere fünf Patientinnen erneut Infektionsschübe entwickelt. Insgesamt kam es in dieser Studie zu einer Heilungsrate von 85%. Nebenwirkungen, die unter der Therapie mit Ceftibuten auftraten, waren meistens leicht und betrafen den Gastrointestinaltrakt. Die häufigste Nebenwirkung war Diarrhoe. Der Latex-Agglutinationstest fürClostridium difficile war in drei von acht Fällen mit Diarrhoe (11% des Gesamtkollektivs) positiv. Bei Frauen mit akuter, unkomplizierter Harnwegsinfektion erwies sich die Therapie mit Ceftibuten als wirksam und im allgemeinen sicher. Bedenken ergeben sich aus der hohen Diarrhoerate in dieser Studie.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jones, R. N., Barry, A. L. Antimicrobial activity, spectrum, and recommendations for disk diffusion susceptibility testing of ceftibuten (7432-S; SCH 39720), a new orally administered cephalosporin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 32 (1988) 1576–1582.
Bragman, S. G. L., Casewell, M. W. Thein vitro activity of ceftibuten against 475 clinical isolates of gram-negative bacilli, compared with cefuroxime and cefadroxil. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 25 (1990) 221–226.
Jones, R. N., Barry, A. L., andthe Collaborative Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Group Ceftibuten (7432-S, SCH 39720): comparative antimicrobial activity against 4735 clinical isolates, beta-lactamase stability and broth microdilution quality control guidelines. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 7 (1988) 802–807.
Nakashima, M., Uematsu, T., Takiguchi, Y., Mizuno, A., Iida, M., Yoshida, T., Yamamoto, S., Kitagawa, K., Oguma, T., Ishii, H., Yamada, H. Phase 1 clinical studies of 7423-S, a new oral cephalosporin: safety and pharmacokinetics. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 28 (1988) 246–252.
Shiba, K., Shimada, J., Saito, A., Miyahara, T.: The effect of food or probenecid on the pharmacokinetics of ceftibuten. In:Rubinstein, E., Adam, D. (eds.): Recent Advances in Chemotherapy. Proceedings of the 16th International Congress of Chemotherapy, Jerusalem 1989, p. 176.1–176.2
Kumazawa, J., Nagayama, A.: Open clinical trials of ceftibuten in the field of urology. In:Rubinstein, E., Adam, D. (eds.): Recent advances in chemotherapy. Proceedings of the 16th International Congress of Chemotherapy, Jerusalem, 1989, p. 179.1–179.2
Neu, H. D., Chin, N., Labthavikul, P. Comparativein vitro study and β-lactamase stability of FR 17027, a new orally active cephalosporin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 26 (1984) 174–180.
Brittain, D. C., Scully, B. E., Hirose, T., Neu, H. C. The pharmacokinetic and bactericidal characteristics of oral cefixime. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 38 (1985) 590–594.
Wise, R., Nye, K., O'Neill, P., Wostenholme, M., Andrews, J. M. Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of ceftibuten. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 34 (1990) 1053–1055.
Irvani, A., Richard, G. A., Johnson, D., Bryant, A. A double-blind multicenter comparative study of the safety and efficacy of cefixime versus amoxicillin in the treatment of acute urinary tract infections in adult patients. Am. J. Med. 95 (Suppl. 3A) (1988) 17A-23A.
Tally, F. P., Desjardins, R. E., McCarthy, E. F., Cartwright, K. Safety profile of cefixime. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 6 (1987) 976–980.
Kammer, R. B., Jackson, T. P.: Comparison of the efficacy and safety of ceftibuten (SCH 39720) and cefaclor in the treatment of acute lower respiratory infections. In: Abstracts of the 7th Mediterranean Congress of Chemotherapy, Barcelona, 1990, Abstract 182, p. 53.
George, W. L. Antimicrobial agent-associated colitis and diarrhea: historical background and clinical aspects. Rev. Infect. Dis. 6 (Suppl. 1) (1984) S208-S213.
deLalla, F., Privitera, G., Ortisi, G., Rizzardini, G., Santoro, D., Pagano, A., Rinaldi, E., Scarpellini, P. Third generation cephalosporins as a risk factor forClostridium difficile-associated disease: a four-year survey in a general hospital. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 23 (1989) 623–631.
Golledge, C. L., McKenzie, T., Riley, V. Extended spectrum cephalosporins andClostridium difficile. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 23 (1989) 929–931.
Finegold, S. M., Ingram-Drake, L., Gee, R., Reinhardt, J., Edelstein, M. A. C., MacDonald, K., Wexler, H. Bowel flora changes in humans receiving cefixime (CL 284, 635) or cefaclor. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 31 (1987) 443–446.
Nakashima, M., Iida, M., Yoshida, T., Kitagawa, T., Oguma, T., Ishii, H.: Pharmacokinetics and safety of 7423-S in healthy volunteers. In: Program and Abstracts of the 26th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, New Orleans, 1986, Abstract 591, p. 205.
Bennett, R. G., Laughon, B. E., Mundy, L. M., Bobo, L. D., Gaydos, C. A., Greenough, W. B., Bartlett, J. G. Evaluation of a latex agglutination test forClostridium difficile in two nursing home outbreaks. J. Clin. Microbiol. 27 (1989) 889–893.
Sherman, M. E., DeGirolami, P. C., Thorne, G. M., Kimber, J., Eichelberger, K. Evaluation of a latex agglutination test for diagnosis ofClostridium difficile-associated colitis. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 89 (1988) 228–233.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stein, G.E., Christensen, S. & Mummaw, N. Treatment of acute uncomplicated urinary tract infection with ceftibuten. Infection 19, 124–126 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01645584
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01645584