Summary
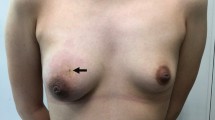
Soft tissue locations ofBrucella are a rare finding. We report the isolation ofBrucella melitensis from a suspected breast tumour of a woman who also showed signs of uveitis. Three weeks after surgical drainage and despite antimicrobial therapy a new abscess developed on the other breast whose culture also yieldedBrucella. As observed, unusual localization of brucellosis without previous penetrating injury may be the only manifestation of chronic infection.
Zusammenfassung
Weichteilaffektionen durchBrucella sind selten. Wir berichten über eine Frau mit Verdacht auf Mammatumor und Uveitis, bei derBrucella melitensis aus der entzündlichen Schwellung isoliert wurde. Trotz antimikrobieller Therapie und chirurgischer Ausräumung des entzündlichen Gewebes entstand auf der anderen Seite ebenfalls ein Abszeß, aus demBrucella isoliert wurde. Der Fall zeigt, daß ohne penetrierendes Trauma als einzige Manifestation einer chronischen Brucella-Infektion ein Brucelloseherd mit ungewöhnlicher Lokalisation auftreten kann.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouza, E., Garcia de la Torre, M., Parras, F., Guerrero, A., Rodriguez-Creixems, M., Gobernado, J. Brucellar meningitis. Rev. Infect. Dis. 9 (1987) 810–822.
Ariza, J., Gudiol, F., Valverde, J., Pallares, R., Fernández-Viladrich, P., Rufi, G., Espadaler, L., Fernandez-Nogues, F. Brucellar spondylitis: A detailed analysis based on current findings. Rev. Infect. Dis. 7 (1985) 656–664.
Young, E. J. Human brucellosis. Rev. Infect. Dis. 5 (1983) 821–842.
Ariza, J., Servitje, O., Pallarés, R., Fernández-Viladrich, P., Rufi, G., Peyri, J., Gudiol, F. Characteristic cutaneous lesions in patients with brucellosis. Arch. Dermatol. 125 (1989) 380–383.
Buchanan, T. M., Faber, L. C., Feldman, R. A. Brucellosis in the United States, 1960–1972: an abattoir-associated disease. I: clinical features and therapy. Medicine (Baltimore) 53 (1974) 403–413.
Garcia-Rodriguez, J. A., Garcia-Sánchez, J. E., Canut, A., Marin, A., Garcia-Santos, T. Absceso cutáneo porBrucella melitensis: una manifestación excepcional. Rev. Esp. Microbiol. Clin. 4 (1989) 108–110.
Mikolich, D. J., Boyce, J. M. Brucella species. In:Mandell, G. L., Douglas, R. G. Jr., Bennett, J. E. (eds.): Principles and practice of infectious diseases. Churchill Livingstone Inc., New York 1990, pp. 1735–1742.
Spink, W. W. The nature of brucellosis. University of Minnesota Press, Minneapolis 1956, pp. 145–190.
Ariza, J., Gudiol, F., Pallares, R., Rufi, G., Fernández-Viladrich, P. Comparative trial of co-trimoxazole versus tetracycline-streptomycin in treating human brucellosis. J. Infect. Dis. 152 (1985) 1358–1359.
Dhar, R., Dhar, P. M., Gafoor, M.: Recurrent epidermal cyst infection caused byBrucella melitensis in a diabetic patient. J. Clin. Microbiol. 26 (1988) 1040–141.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gasser, I., Almirante, B., Fernández-Pérez, F. et al. Bilateral mammary abscess and uveitis caused by brucella melitensis — Report of a case. Infection 19, 44–45 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01643759
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01643759