Summary
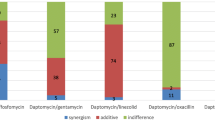
Infections with multiresistant strains ofStaphylococcus aureus andStaphylococcus epidermidis pose severe clinical problems. The drug of choice in such cases, vancomycin, is potentially ototoxic and nephrotoxic and this may give rise to additional problems in the patient. Fosfomycin has been shown to be nephroprotective when given with vancomycin and with other nephrotoxic drugs. We report the inhibitory and bactericidal activity of fosfomycin and vancomycin alone and in combination against 26 clinically relevant strains ofS. aureus and 48 strains ofS. epidermidis. In most instances these two drugs showed indifferent or additive effects, synergism or antagonism was only rarely observed. Assessment of the bactericidal action of the combination revealed similar effects. The combination of fosfomycin and vancomycin may, therefore, be beneficial in clinical situations where the nephrotoxic effect of vancomycin cannot be tolerated.
Zusammenfassung
Infektionen mit multiresistentenStaphylococcus epidermidis- oderStaphylococcus aureus-Stämmen stellen schwerwiegende klinische Probleme dar. Weitere Probleme können sich daraus ergeben, daß Vancomycin, das Mittel der Wahl, ein ototoxisches und nephrotoxisches Potential besitzt. Von Fosfomycin ist bekannt, daß es vor den nephrotoxischen Wirkungen des Vancomycin und anderer verschiedener Substanzen schützen kann. Wir berichten hier über die inhibitorische und bakterizide Wirksamkeit von Vancomycin und Fosfomycin allein und in Kombination gegenüber 26S. aureus- und 48S. epidermidis-Isolaten aus klinischem Material. Dabei zeigte die Kombination meist indifferente oder additive Effekte, während Synergismus oder Antagonismus nur selten beobachtet wurden. Wenn die bakterizide Wirkung der Kombination gemessen wurde, waren die Ergebnisse ähnlich. Die Kombination aus Vancomycin und Fosfomycin kann daher in klinischen Situationen, wo die potentiell nierenschädigende Wirkung des Vancomycin nicht toleriert werden kann, von Nutzen sein.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Watanakunakorn, C. Treatment of infections due to methicillin-resistantStaphylococcus aureus. Ann. Intern. Med. 97 (1982) 376–378.
Alvarez, S., Jones, M., Berk, S. L. In vitro activity of fosfomycin, alone and in combination against methicillin-resistantStaphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 28 (1985) 689–690.
Baron, D., Drugeon, H. Fosfomycine Sem. Hôp. 61 (1985) 2341–2349.
Graninger, W., Leitha, T., Havel, M., Georgopoulos, A. In vitro activity of fosfomycin against methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistantStaphylococcus aureus. Infection 12 (1984) 293–295.
Haag, R. Efficacy of penicillin-G, flucloxacillin, cefazolin, fusidic acid, vancomycin, rifampicin and fosfomycin in muscular infections in mice due toStaphylococcus aureus. Infection 14 (1986) 38–43.
Olay, T., Vicente, M. V., Rodríguez, A., Mayer, K. H. Estudios sobre actividadin vitro de fosfomicina sola y en asociación con otros antibióticos frenteStaphylococcus resistentes a meticilina. Rev. Esp. de Microbiol. Clin. 1 (1986) 49–52.
Rodríguez, A., Vicente, M. V., Olay, T. Comparison of fosfomycin and vancomycin therapy for experimental endocarditis due to methicillin-resistantStaphylococcus epidermidis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. 4 (1986) 603–605.
Duncker, D., Ullmann, U. Activity of 18 antimicrobial agents against multiresistant strains ofStaphylococcus aureus isolated from intensive care patients. Infection 13 (1985) 240–242.
Marre, R., Schulz, E., Hedtke, D., Sack, K. Influence of fosfomycin and tobramycin on vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity. Infection 13 (1985) 190–192.
Stevens, D. L., Jones, C. Use of trehalose-mannitol-phosphatase agar to differentiateStaphylococcus epidermidis andStaphylococcus saprophyticus from other coagulase-negative staphylococci. J. Clin. Microbiol. 20 (1984) 977–980.
Thornsberry, C. Methicillin-resistant (heteroresistant) staphylococci. Antimicrob. Newslett. 1 (1984) 43–50.
Gatermann, S. Plasmid fingerprinting of methicillin-resistantStaphylococcus aureus strains isolated in Hamburg. Infection 15 (1987) 459–462.
Haag, R., Hoffmann, R. Investigations on the bactericidal activity of fosfomycin using the membrane filter-agar dilution method and the time kill technique. Zbl. Bakt. Hyg. A 260 (1985) 260–272.
Haag, R., Vömel, W. Einflüsse auf die Aktivität von Fosfomycinin vitro. Immun. Infekt. 7 (1979) 202–209.
Krogstadt, D., Moellering, P. C. Combinations of antibiotics, mechanisms of interaction against bacteria. In:Lorian, V. (ed.): Antibiotics in laboratory medicine. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, London 1980, pp. 298–341.
Iwantscheff, A. In-vitro activity of fosfomycin against differentStaphylococcus species. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 21 (1988) 379–384.
Sack, K., Schulz, E., Marre, R., Kreft, B. Fosfomycin protects against tubulotoxicity induced by cis-diaminedichlorplatin and cyclosporin A in the rat. Klin. Wochenschr. 65 (1987): 525–527.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gatermann, S., Marre, R. & Schulz, E. The microbiological efficacy of the combination of fosfomycin and vancomycin against clinically relevant staphylococci. Infection 17, 35–37 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01643498
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01643498