Summary
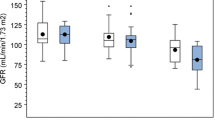
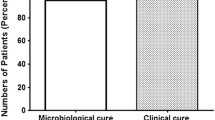
The efficacy, tolerance and pharmacokinetics of the new aminoglycoside antibiotic sisomicin, have been studied in 29 elderly male patients with varying degrees of renal function impairment and suffering from complicated urinary tract infections. The antibiotic was equally effective in patients with normal and impaired renal function and a cure (negative urine culture at one week follow-up) of 56% was obtained. There was little apparent toxicity with the dosage regimens used, although serum creatinine values were statistically but not clinically significantly increased in some patients following treatment. Serum half-lives of sisomicin were prolonged in cases of impaired renal function but accumulation of antibiotic could be prevented by varying dosing intervals between 8 and 24 hours based on serum creatinine values. There was good correlation between serum creatinine and sisomicin serum half-life values and a practical method is described for dose adjustment based on the relationship between serum half-lives and serum creatinine concentrations.
Zusammenfassung
Die Wirksamkeit, Verträglichkeit und Pharmakokinetik des neuen Aminoglykosid-Antibiotikums Sisomicin wurde an 29 älteren männlichen Patienten mit unterschiedlichen Graden der Nierenfunktionsstörung untersucht, die an komplizierten Harnwegsinfektionen litten. Das Antibiotikum war bei Patienten mit normaler und gestörter Nierenfunktion im gleichen Maße wirksam und in 56% der Fälle wurde eine Heilung erzielt (negative Harnkultur bei der Kontrolluntersuchung nach einer Woche). In den angewandten Dosierungen zeigte sich nur eine unbedeutende Toxizität, obgleich bei einigen Patienten die Serumkreatininwerte im Anschluß an die Behandlung statistisch, jedoch nicht klinisch signifikant erhöht waren. In Fällen von Nierenfunktionsstörung waren die Halbwertszeiten von Sisomicin im Serum verlängert, doch konnte eine Kumulation des Antibiotikums durch Variieren der Dosierungsintervalle zwischen 8 und 24 Stunden auf der Grundlage der Serumkreatininwerte verhindert werden. Es bestand eine gute Wechselbeziehung zwischen den Serumkreatininwerten und den Halbwertszeiten von Sisomicin im Serum und es wird eine praktische Methode zur Anpassung der Dosis auf der Grundlage des Verhältnisses zwischen Halbwertszeiten im Serum und Kreatininkonzentrationen im Serum beschrieben.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Welling, P. G., Mosegaard, A., Madsen, P. O. Sisomicin treatment of complicated urinary tract infections: Effcacy, tolerance and pharmacokinetics. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 14 (1974) 567–573.
Maher, F. T., Tauxe, W. N. Renal clearance in man of pharmaceuticals containing radioactive iodine. J. Amer. med. Ass. 207 (1969) 97–104.
Bauer, W. A., Kirby, W. M. M., Sherris, J. C., Turck, M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Amer. J. Clin. Path. 36 (1966) 493–496.
Wagner, J. G., Northam, J. I. Estimation of volume of distribution and half-life of a compound after rapid intravenous injection. J. Pharm. Sci. 56 (1967) 529–531.
Gyselynck, A.-M., Forrey, A., Cutler, R.: Pharmacokinetics of gentamicin: Distribution and plasma and renal clearance. J. Inf. Dis. 124 (1971) Suppl 70–76.
Investigator's Brochure: Informational material for the investigational drug sisomicin. Schering Corporation, Bloomfield, New Jersey (1972).
Naber, K. G., Westenfelder, S. R., Madsen, P. O. Pharmacokinetics of the aminoglycoside antibiotic tobramycin in humans. Antimicrob. Ag. Chemother. 3 (1973) 469–473.
Dettli, L., Spring, P., Habersang, R.: Drug dosage in patients with impaired renal function. Post Grad. Med. J. 46 (1970) Suppl 32–35.
Welling, P. G., Craig, W. A., Amidon, G. L., Kunin, C. M. Pharmacokinetics of cefazolin in normal and uremic subjects. Clin. Pharm. Therap. 15 (1974) 344–353.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mosegaard, A., Welling, P.G., Tse, F.L.S. et al. Treatment with sisomicin of complicated urinary tract infections in patients with varying degrees of renal function impairment. Infection 3, 143–147 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01641336
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01641336