Summary
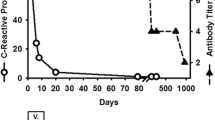
Using the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), we studied the IgG and IgM antibody titers in various groups of pediatric patients (n=81) infected with gram-negative organisms. Unlike the control group (n=12), IgG antibodies were detected in only five (all under four months of age) of 19 children with sepsis. We assume that either the IgG antibodies are used up during the infection, or the lack of IgG antibodies results in a disposition to sepsis; the latter is more probable. Seventeen of 18 patients with urinary tract infections and proven renal involvement were IgM-positive. This indicates a permanent antigen stimulus, possibly in the form of a fixed antigen complex. Because of the heterogeneity of the groups studied, no overall statements can be made for the 93 children studied, some of whom were studied repeatedly. These children included 17 with tracheal colonization, 17 with recurrent urinary tract infections without proven renal changes and six with wound infections.
Zusammenfassung
Bei verschiedenen Gruppen von Patienten einer Kinderklinik (n=81), die mit gramnegativen Keimen infiziert waren, wurden mittels Enzym-gebundenem Immunsorbent-Test (ELISA) die Antikörper-Titer gegen Lipoid A im IgG- und IgM-Bereich untersucht. Hierbei zeigte sich, daß — im Gegensatz zur Kontrollgruppe (n=12) — bei 19 Kindern mit Sepsis nur in fünf Fällen, alle jünger als vier Monate, IgG-Antikörper nachzuweisen waren. Es wird vermutet, daß entweder bei der Infektion IgG-Antikörper verbraucht werden oder, was wahrscheinlicher ist, daß das Fehlen von IgG-Antikörpern zu einer Sepsis-Disposition führt. Bei Harnwegsinfektion mit sicherer Nierenbeteiligung waren 17 von 18 Patienten IgM-positiv. Dies weist auf einen permanenten Antigenstimulus, vielleicht in Form eines fixierten Antigenkomplexes, hin. Weitere 17 Kinder wiesen eine Tracheal-Kolonisation mit gramnegativen Keimen auf, 17 litten an rekurrierender Harnwegsinfektion ohne nachgewiesene Nierenbeteiligung, sechs an Wundinfektionen. Wegen der Heterogenität der untersuchten Gruppen ist für die Gesamtgruppe der 93 z. T. wiederholt untersuchten Kinder eine pauschale Beurteilung nicht möglich.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Westphal, O. Bacterial endotoxins. Transact. Colleg. Int. Allerg., 10th Symp., Copenhagen 1974. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol. 49 (1975) 1–43.
Lüderitz, O., Galanos, C., Lehmann, V., Nurminen, M., Rietschel, E. T., Rosenfelder, G., Simon, M., Westphal, O. Lipid A: Chemical structure and biological activity. J. Infect. Dis. 128 (1973) S 17-S 29.
Galanos, C., Lüderitz, O., Westphal, O. Preparation and properties of antisera against the lipid-A component of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Eur. J. Biochem. 24 (1971) 116–122.
Simon, G., Reindke, S., Marget, W. Lipoid-A-Antikörpertiter bei Pyelonephritis und anderen Infektionen mit gramnegativen Bakterien. Infection 2 (1974) 178–184.
Schuurs, A. H. W. M., van Weemen, B. K. Enzyme-immunoassay. Clin. Chim. Acta 81 (1977) 1–40.
Engvall, E., Perlmann, P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, ELISA. III. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J. Immunol. 109 (1972) 129–135.
Wichmann, U., Marget, W. Parameter zur Diagnose akuter Schübe von chronischer Pyelonephritis im Kindesalter. Arch. Kinderheilkunde 182 (1971) 240–247.
Westenfelder, M., Galanos, C., Madsen, P. O., Marget, W. Pathological activities of lipid A: Experimental studies in relation to chronic pyelonephritis. In:Schlesinger, D. (ed.): Microbiology. American Society of Microbiology, Washington, D. C. 1977, pp. 277–279.
Freudenberg, M. A., Bøg-Hansen, T. C., Back, U., Galanos, C. Interaction of lipopolysaccharides with plasma high-density lipoprotein in rats. Infect. Immun. 28 (1980) 373–386.
Ziegler, E. J., McCutchan, J. A., Fierer, J., Glauser, M. P., Sadoff, J. C., Douglas, H., Braude, A. I. Treatment of gramnegative bacteremia and shock with human antiserum to a mutantEscherichia coli. N. Engl. J. Med. 307: (1982) 1225–1230.
Marget, W., Reindke, B. Neuere Beobachtungen zur Frage der Pathogenese der nichtobstruktiven chronischen Harnweginfektionen. Med. Klin. 69 (1974) 1767–1773.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marget, W., Weiß, M. & Ruhland, B. Lipid a antibody determinations using ELISA on patients at a children's hospital: A preliminary report. Infection 11, 84–86 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01641072
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01641072