Abstract
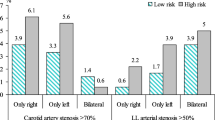
The objective of this study was to determine the predictive values of multiple atherosclerotic risk factors in using routine carotid duplex scanning for patients with peripheral vascular disease, even in the absence of any sign of carotid disease. From 1998 through 2000, 108 patients admitted for peripheral vascular reconstruction to our institution were preoperatively screened for carotid artery stenosis. Patients were examined for neurologic status and cervical bruits. As atherosclerotic risk factors, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, smoking, sex and age, coronary artery disease (CAD), coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG), and previous vascular operation were recorded, preoperative ankle-brachial pressure indexes (ABI) were calculated. All patients underwent routine carotid color duplex examinations preoperatively. Eighty five patients (78.7%) had mild (<50%) or no carotid artery stenosis, and 23 patients (21.3%) had significant (≥50%) carotid artery stenosis. Age (≥60 years), coronary artery disease, and carotid bruit were individual factors, and the combination of age ≥55 and hyperlipidemia had a significant value in predicting presence of ≥50% stenosis of one or both carotid arteries by univariate analysis. By multivariate logistic regression analysis, however, only carotid bruit was associated with carotid artery stenosis of ≥50% (p<0.001). Screening for asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis is indicated in patients with only carotid artery bruit and might be indicated in elderly patients with peripheral vascular disease. Routine screening or carotid artery stenosis in all patients is not an effective strategy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
National Center for Health Statistics (1984) Monthly vital statistics report. 1984;33(suppl):9.
Barnes RW, Liebman PR, Marszalek PB, Kirk CL, Goldmen MH (1981) The naturel history of asymptomatic carotid disease in patients undergoing cardiovascular surgery. Surgery 90:1075–1083.
Klop RBJ, Eikelboom BC, Taks ACJM (1991) Screening of the internal carotid arteries in patients with peripheral vascular disease by colour-flow duplex scanning. Eur J Vasc Surg 5:41–45.
Executive Committee for the Asymptomatic Carotid Atherosclerosis Study (1995) Endarterectomy for asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis. JAMA 273:1421–1428.
Hobson RW, Weiss DG, Fields WS, et al. (1993) Efficacy of carotid endarterectomy for asymptomatic carotid stenosis. N Endl J Med 328:221–227.
Gentile AT, Taylor LM, Moneta GL, Porter JM (1995) Prevalence of asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis in patients undergoing infrainguinal bypass surgery. Arch Surg 130:900–904.
Strandness DE Jr (1993) Extracranial arterial disease. In: Duplex Scanning in Vascular Disorders, Strandness DE Jr (ed). Raven Press: New York, pp 113–158.
Berens ES, Kouchoukos NT, Murphy SF, Wareing TH (1992) Preoperative carotid artery screening in elderly patients undergoing cardiac surgery. J Vasc Surg 15:313–323.
Ramsey DE, Miles RD, Lambeth A, Summer DS (1987) Prevalence of extracranial carotid artery disease: a survey of an asymptomatic population with noninvasive techniques. J Vasc Surg 5:584–588.
Colgan MP, Strode GR, Sommer JD, Gibbs JL, Summer DS (1988) Prevalence of asymptomatic carotid disease: results of duplex scanning in 348 unselected volunteers. J Vasc Surg 8:674–678.
Ahn SS, Baker JD, Walden K, Moore WS (1991) Which asymptomatic patients should undergo routine carotid duplex scan? Am J Surg 162:180–183.
Turnipseed WD, Berkoff HA, Belzer FO (1980) Postoperative stroke in cardiac and peripheral vascular disease. Ann Surg 192:365–368.
Fowl RJ, Maroch JG, Love M, et al. (1991) Prevalence of hemodynamically significant stenosis of the carotid artery in an asymptomatic veteran population. Surg Gynecol Obstet 172:13–16.
Busuttil RW, Baker JD, Davidson RK, Machleder HI (1981) Carotid artery stenosis: Hemodynamic significance and clinical course. JAMA 245:1438–1445.
Moore DJ, Miles RD, Gooley NA, Summer DS (1985) Noninvasive assessment of stroke risk in asymptomatic and nonhemispheric patients with suspected carotid disease. Ann Surg 212:491–503.
Norris JW, Zhu CZ, Bornstein WM, Chambers BR (1991) Vascular risks of asymptomatic carotid stenosis. Stroke 22:1485–1490.
Hertzer NR, Beven EG, Young JR, O'Hara PJ, Gray RA, Ruschhaupt WF (1984) Incidental asymptomatic carotid bruits in patients scheduled for peripheral vascular reconstruction: results of cerebral and coronary angiography. Surgery 96:535–543.
Marek J, Mills JL, Harvich J, Cui H, Fujitani RM (1996) Utility of routine carotid duplex screening in patients who have claudication. J Vasc Surg 24:572–579.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Posacioğlu, H., İslamoğlu, F., Çalkavur, T. et al. Predictive values of risk factors in carotid duplex scanning before peripheral vascular surgery. International Journal of Angiology 10, 250–253 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01637043
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01637043