Summary
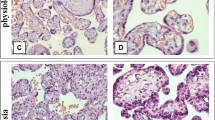
Human normal dura mater containing arachnoid villi were examined for their expression of glutathione S-transferase placental type (GST-π), a detoxifying enzyme, using an immunohistochemical method. All of the arachnoid villi and arachnoid cells in five normal cases were found to have expression of GST-π, although no positive reaction for the enzyme was present in other tissues of the dura mater. The results show a possible role for arachnoid tissues in protecting human brain from hazardous xenobiotics in the cerebrospinal fluid. Twenty-six meningiomas were also examined for expression of the enzyme. Tissues of meningotheliomatous meningiomas were always positive for expression of the enzyme. Transitional meningiomas also showed the expression in their meningotheliomatous components. No staining reaction of GST-π was recognized in fibroblastic meningiomas except for two cases with a tendency to meningotheliomatous differentiation. The findings suggest a functional similarity between the arachnoid tissues and meningotheliomatous components of meningiomas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chasseaud LF (1979) The role of glutathione and glutathione S-transferases in the metabolism of chemical carcinogens and other electrophilic agents. Adv Cancer Res 29:175–274
Di Ilio C, Del Boccio G, Aceto A, Casaccia R, Mucilli F, Federici G (1988) Elevation of glutathione transferase activity in human lung tumor. Carcinogenesis 9:335–340
Hayes JD (1983) Rat liver glutathione S-transferases. A study of the structure of the basic YbYb-containing enzymes. Biochem J 213:625–633
Jakoby WB (1978) The glutathione S-transferases: a group of multifunctional detoxification proteins. Adv Enzymol 46:383–414
Kitahara A, Soto K (1981) Immunological relationship among subunits of glutathione S-transferases A, AA, B and ligandin and hybrid formation between AA and ligandin by guanidine hydrochloride. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 103:943–950
Kitahara A, Satoh K, Sato K (1983) Properties of the increased glutathione S-transferase A form in rat preneoplastic hepatic lesions induced by chemical carcinogens. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 112:20–28
Kodate C, Fukushi A, Narita T, Kudo H, Soma Y, Sato K (1986) Human placental form of glutathione S-transferase (GST-π) as a new immunohistochemical marker for human colonic carcinoma. Jpn J Cancer Res 77:226–229
Mannervik B (1985) The isozymes of glutathione transferase. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol 57:357–417
Mannervik B, Jensson H (1982) Binary combinations of four protein subunits with different catalytic specificities explain the relationship between six basic glutathione S-transferases in rat liver cytosol. J Biol Chem 257:9909–9912
Russell DS, Rubinstein LJ (1989) Tumor of the meninges and related tissues. In: Russell DS, Rubinstein LT (eds) Pathology of tumors of the nervous system, 5th edn. Edward Arnold, London, pp 449–532
Sato K (1988) Glutathione S-transferases and hepatocarcinogenesis. Jpn J Cancer Res 79:556–572
Sato K, Kitahara A, Satoh K, Ishikawa T, Tatematsu M, Ito N (1984) The placental form of glutathione S-transferase as a new marker protein for preneoplasia in rat chemical hepatocarcinogenesis. Gann 75:199–202
Satoh K, Kitahara A, Soma Y, Inaba Y, Hatayama I, Sato K (1985) Purification, induction, and distribution of placental glutathione transferase: a new marker enzyme for preneoplastic cells in the rat chemical hepatocarcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:3964–3968
Shiratori Y, Soma Y, Maruyama H, Sato S, Takano A, Sato K (1987) Immunohistochemical detection of the placental form of glutathione S-transferase in dysplastic and neoplastic human uterine cervix lesions. Cancer Res 47:6808–6809
Sternberger LA, Hardy PH, Cuculis JJ, Meyer HG (1970) The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry. Preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem 18:315–333
Tatematsu M, Aoki T, Kagawa M, Mera Y, Ito N (1988) Reciprocal relationship between developmental glutathione S-transferase positive liver foci and proliferation of surrounding hepatocytes in rats. Carcinogenesis 9:221–225
Tatematsu M, Mera Y, Ito N, Satoh K, Sato K (1985) Relative merits of immunohistochemical demonstration of placental, A, B and C forms of glutathione S-transferase and histochemical demonstration ofγ-glutamyl transferase as markers of altered foci during liver carcinogenesis in rats. Carcinogenesis 6:1621–1626
Tateoka N, Tsuchida S, Soma Y, Sato K (1987) Purification of glutathione S-transferases in human kidney. Clin Chim Acta 266:207–218
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hara, A., Yamada, H., Sakai, N. et al. Immunohistochemical expression of glutathione S-transferase placental type (GST-π), a detoxifying enzyme, in normal arachnoid villi and meningiomas. Vichows Archiv A Pathol Anat 417, 493–496 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01625729
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01625729