Summary
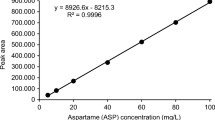
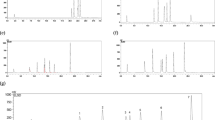
A sensitive high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) assay was developed for the qualitative and quantitative determination of carbohydrate sweeteners and organic acids in oral fluid. To separate these compounds, an ion-moderated partition resin HPLC column (Aminex HPX-87H) was used. All components of the HPLC system were interconnected using stainless steel capillary tubing. Isocratic elution with 0.01 N sulfuric acid provided the profile of both compound classes. The compounds were detected using a refractive index detector. The method employed computerized data collection and integration (Omega-2 system) with a detection sensitivity of 0.1 µg compound per HPLC assay (80 µl). This method is useful in caries research, because it detects minute amounts of sugars and organic acids in oral fluid during clearance studies of various foods in the mouth.
Zusammenfassung
Eine empfindliche HPLC-Methode wurde für die qualitative und quantitative Analyse von Kohlehydraten und organischen Säuren in Mundflüssigkeiten (Speichel und Zahnplaque) entwickelt. Für die Trennung dieser Verbindungen wurde eine Aminex HPX-87H (Bio-Rad) Chromatographie-Säule verwendet. Alle Komponenten des HPLC-Systems waren mit Edelstahl-Kapillaren verbunden. Die isokratische Elution beider Verbindungs-Klassen erfolgte mit 0,01 n Schwefelsäure. Alle Verbindungen wurden mit einem RI-(Refraktion-Index-) Detektor gemessen. Die Ergebnisse wurden mit einem PC-gestütztem Auswertesystem automatisch gesammelt und integriert. Die zeitbedingte Abnahme der Konzentration von Kohlehydraten im Munde einerseits und die Produktion von organischen Säuren durch Bakterien der Mundhöhle andererseits können mit dieser empfindlichen HPLC-Methode bis zu einer Genauigkeit von 0,1 µg Substanz per Analyse (80 µl) bestimmt werden.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dodds MWJ, Edgar WM (1988) The relationship between plaque pH, plaque acid anion profiles, and oral carbohydrate retention after ingestion of several “reference foods” by human subjects. J Dent Res 67:861–865
Linke HAB, Arav L (1989) Carbohydrate clearance and acid production after ingestion of various foods. J Dent Res 68:Spec Issue, 215
Linke HAB, Arav L, Chiu P-M, Moss SJ (1989) Oral clearance and acid production of foods containing either cooked starch or carbohydrate sweeteners. Caries Res 23:430
Nelson N (1944) A photometric adaptation of the Somogyi method for the determination of glucose. J Biol Chem 153:375–380
Schwarzenbach R (1982) High-performance liquid chromatography of carboxylic acids. J Chromatogr 251:339–358.
Shaw PE (1988) Handbook of Sugar Separations in Foods by HPLC. CRC Press Inc, Boca Raton, FL
Somogyi M (1952) Notes on sugar determination. J Biol Chem 195:19–23
Weatherell JA, Strong M, Robinson C, Nakagaki H, Ralph JP (1989) Retention of glucose in oral fluid at different sites in the mouth. Caries Res 23:399–405
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Linke, H.A.B., Moss, S.J. Quantitation of carbohydrate sweeteners and organic acids in human oral fluid using HPLC analysis. Z Ernährungswiss 31, 147–154 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01623073
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01623073