Summary
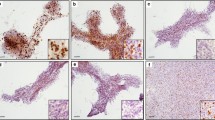
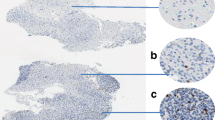
Rapid detection of the proliferating potential of 37 human brain tumors was attempted using squash preparations stained by a silver colloid technique for argyrophilic protein associated with nucleolar organizer regions (AgNORs). Less than 1 h was required for staining. The mean number of AgNORs in cell nuclei of malignant or recurrent brain tumors (16 cases) including meningeal sarcoma, recurrent meningioma, recurrent craniopharyngioma, anaplastic astrocytoma, glioblastoma multiforme and metastatic brain tumor was 3.18, and the number for benign brain tumors (21 cases) including meningioma, neurinoma, pituitary adenoma, benign astrocytoma, ependymoma, and adenoma of lachrymal gland was 1.85. The former value was significantly greater than the latter value (P<0.001). These results indicate that quantitative analysis of AgNORs in brain neoplastic cells, using squash preparations, is useful to differentiate malignant from benign tumors within 1 h. Thus, this method provides rapid and useful information about the proliferative potential of human brain tumors even during operation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AgNOR:
-
argyrophilic protein associated with nucleolar organizer regions
References
Boldy DAR, Crocker J, Ayres JG (1989) Application of the Ag-NOR method to cell imprints of lymphoid tissue. J Pathol 157:75–79
Boon AP, Sharii H (1989) Value of AgNOR method in predicting recurrence of meningioma. J Clin Pathol 42:1002–1003
Burger PC, Shibata T, Kleihues P (1986) The use of the monoclonal antibody Ki-67 in the identification of proliferating cells. Am J Surg Pathol 10:611–617
Crocker J, Nar P (1987) Nucleolar organizer regions in lymphomas. J Pathol 151:111–118
Egan MJ, Raaft F, Crocker J, Smith K (1988) Nucleolar organizer regions in fibrous proliferations of childhood and infantile fibrosarcoma. J Clin Pathol 41:31–33
Gerdes J, Schwab U, Lemke H, Stein H (1983) Production of a mouse monoclonal antibody reactive with a human nuclear antigen associated with cell proliferation. Int J Cancer 31:13–20
Hall PA, Crocker J, Watts A, Stansfeld AG (1988) A comparison of nucleolar organizer region staining and Ki-67 immunostaining in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Histopathology 12:373–381
Hara A, Hirayama H, Sakai N, Yamada H, Tanaka T, Mori H (1990) Correlation between nucleolar organizer region staining and Ki-67 immunostaining in human gliomas. Surg Neurol 33:320–324
Hara A, Hiryama H, Sakai N, Yamada H, Tanaka T, Mori H (1991) Nucleolar organizer region scores and Ki-67 labeling index in high-grade gliomas and metastatic brain tumors. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 109:37–41
Howat AJ, Giri DD, Cotton DWK, Slater DN (1989) Nucleolar organizer regions in spitz nevi and malignant melanomas. Cancer 63:474–478
Kajiwara K, Nishizaki T, Orita T, Nakayama H, Aoki H, Ito H (1990) Silver colloid staining technique for analysis of glioma malignancy. J Neurosurg 73:113–117
Lische MA, Smetana K, Olson MOJ, Busch H (1984) Protein C23 and B23 are the major nucleolar silver staining proteins. Life Sci 25:701–708
McNicol AM, Colgan J, McMeekin W, Teasdale GM (1989) Nucleolar organizer regions in pituitary adenomas. Acta Neuropathol 77:547–549
Ochs RL, Busch H (1984) Further evidence that phosphoprotein C23 (110kD/pH5.1) is the nucleolar silver staining protein. Exp Cell Res 152:260–265
Ostertag CB, Volk B, Shibata T, Burger P, Kleihues P (1987) The monoclonal antibody Ki-67 as a marker for proliferating cells in stereotactic biopsies of brain tumors. Acta Neurochir 89:117–121
Ploton D, Menager M, Heannesson P, Himber G, Pigeon F, Adnet JJ (1986) Improvement in the staining and visualization of the argyrophilic proteins of the nucleolar organizer region at the optical level. Histochem J 18:5–14
Shibata T, Burger PC (1987) The use of the monoclonal antibody Ki-67 in detection of the growth fraction in pediatric brain tumors. Childs Nerv Syst 3:364–367
Tanaka T, Takeuchi T, Nishikawa A, Takami T, Mori H (1989) Nucleolar organizer regions in hepatocarcinogenesis induced byN-2-fluorenylacetamide in rats: comparison with immunohisto-chemistry using a monoclonal antibody against bromodeoxy-uridine. Jpn J Cancer Res (Gann) 80:1047–1051
Williams MA, Kleinschmidt JA, Krohne G, Franke WW (1982) Argyrophilic nuclear and nucleolar proteins ofXenopus laevis oocytes identified by gel electrophoresis. Exp Cell Res 137:341–351
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hara, A., Sakai, N., Yamada, H. et al. Rapid detection of proliferating potential in human brain tumors by nucleolar organizer region staining on squash preparations. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 117, 510–514 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01613280
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01613280