Abstract
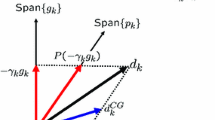
Although quasi-Newton algorithms generally converge in fewer iterations than conjugate gradient algorithms, they have the disadvantage of requiring substantially more storage. An algorithm will be described which uses an intermediate (and variable) amount of storage and which demonstrates convergence which is also intermediate, that is, generally better than that observed for conjugate gradient algorithms but not so good as in a quasi-Newton approach. The new algorithm uses a strategy of generating a form of conjugate gradient search direction for most iterations, but it periodically uses a quasi-Newton step to improve the convergence. Some theoretical background for a new algorithm has been presented in an earlier paper; here we examine properties of the new algorithm and its implementation. We also present the results of some computational experience.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.C. Allwright, “Improving the conditioning of optimal control problems using simple models”, in: D.J. Bell, ed.,Recent mathematical developments in control (Academic Press, London, 1972).
W.R. Boland, E. Kamgnia and J.S. Kowalik, “A conjugate gradient optimization method invariant to nonlinear scaling”, Report TR 245, Department of Mathematical Sciences, Clemson University, Clemson, SC (1977).
A.G. Buckley, “Extending the relationship between the conjugate gradient and BFGS algorithms”,Mathematical Programming, to appear.
C.G. Broyden, “The convergence of a class of double rank algorithms, Part I”,Journal of the Institute of Mathematics and its Applications 7 (1971) 76–90.
R. Fletcher and M.J.D. Powell, “A rapidly convergent descent method for minimization”,The Computer Journal 7 (1963).
R. Fletcher, “A new approach to variable metric algorithms”,The Computer Journal 13 (1970) 317–322.
R. Fletcher, “Conjugate direction methods”, in: W. Murray, ed.,Numerical methods for unconstrained optimization (Academic Press, London, 1972) pp. 73–86.
M.R. Hestenes and E.L. Stiefel, “Methods of conjugate gradients for solving linear systems”,Journal of Research of the National Bureau of Standards 49 (1952) 409–436.
D.M. Himmelblau,Applied nonlinear programming (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1972).
L. Nazareth, “A relationship between the BFGS and conjugate gradient algorithms”, AMD Tech. Memo 282, Argonne National Laboratory (1977).
E. Polak,Computational methods in optimization: A unified approach (Academic Press, New York, 1971).
M.J.D. Powell, “Restart procedures for the conjugate gradient method”,Mathematical Programming 12 (1977) 241–254.
M.J.D. Powell, “Some convergence properties of the conjugate gradient method”,Mathematical Programming 11 (1976) 42–49.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was supported by the National Research Council of Canada grant number A-8962.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buckley, A.G. A combined conjugate-gradient quasi-Newton minimization algorithm. Mathematical Programming 15, 200–210 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01609018
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01609018