Summary
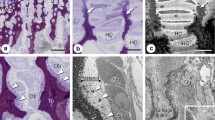
Nuclear inclusions, identical to those characteristic of Paget's disease of bone, were observed in giant cells in four of eight cases of primary oxalosis. The giant cells containing nuclear inclusions were directly involved in phagocytosis of large oxalate crystals in the context of typical foreign body granulomas in the bone marrow. Cytochemically, all of them exhibited strong tartrateresistant acid phosphatase activity, and a proportion of them also tartrate-resistant acid ATPase. The inclusions consisted of typical arrays of filamentous material as described in Paget's disease, admixed with variable proportions of electron-dense material closely reminiscent of nucleolar pars fibrillaris and fibrillary centres. These data indicate: (a) the occurrence of Paget-like inclusions in a bone disease unrelated to Paget's disease, not causally related to viral infection, and resulting from an inborn metabolic derangement; and (b) the occurrence of Paget-like inclusions in foreign body giant cells as opposed to osteoclasts. We suggest that the occurrence of paramyxovirus-like nuclear inclusions in either osteoclasts or giant cells may represent an epiphenomenon of cell fusion and giant cell formation whenever appropriate stimuli act on latently infected precursor cells. Further-more, our data suggest that nucleoli may represent the specific site of virus-like inclusion formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abelanet R, Daudet-Monsac M, Laoussadi S, Forest M, Vacher-Lavenu MC (1986) Frequency and diagnostic value of the virus-like filamentous inclusions in giant cell tumour of bone, not associated with Paget's disease. Virchows Arch [A] 410:65–68
Andersson G, Marks SC (1989) Tartrate-resistant acid ATPase as a cytochemical marker for osteoclasts. J Histochem Cytochem 37:115–117
Andersson G, Ek-Rylander B, Hammarstrom LE, Lindskog S, Toverud SU (1986) Immunocytochemical localization of a tartrate-resistant and vanadate-sensitive acid nucleotide tri- and diphosphatase. J Histochem Cytochem 34:293–298
Andersson G, Lidunger A, Ek-Rylander B (1989) Isolation and characterization of skeletal acid ATPase — a new osteoclast marker? Connect Tissue Res 20:151–158
Aparisi T, Arborgh B, Ericsson JLE (1979) Giant cell tumour of bone. Variations in patterns and appearance of different cell types. Virchows Arch [A] 381:159–178
Basle MF, Russell WC, Goswani KAA, Rebel A, Giraudon P, Wild F, Filman R (1985) Paramyxovirus antigens in osteoclasts from Paget's bone tissue detected by monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Virol 66:2103–2110
Basle MF, Fournier JG, Rosenblatt S, Rebel A, Bouteille M (1986) Measles virus RNA detected in Paget's disease bone tissue by in situ hybridization. J Gen Virol 67:907–913
Beneton MNC, Harris S, Kanis JA (1987) Paramyxovirus-like nuclear inclusions in two cases of pycnodysostosis. Bone Dis Relat Res 8:211–217
Benhamou CL, Pierre D, Geslin N, Viala JF, Maitre F, Chavassieux P, Edouard C, Meunier PJ (1987) Primary bone oxalosis: the roles of oxalate deposits and renal osteodystrophy. Bone 8:59–64
Bianco P, Costantini M, Dearden LC, Bonucci E (1987) Expression of tartrate resistant acid phosphatase in bone marrow macrophages. Basic Appl Histochem 31:433–440
Bianco P, Ballanti P, Bonucci E (1988) Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase activity in rat osteoblasts and osteocytes. Calcif Tissue Int 43:167–171
Breed A, Chesney R, Friedman A, Gilbert E, Langer L, Lattoraca R (1981) Oxalosis-induced bone disease: a complication of transplantation and prolonged survival in primary hyperoxaluria. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 63:310–316
Canavese C, Salomone M, Massara C, Portigliatti Barbos M, Cadario A, Pavan I, Marangella M, Petrarulo M, Rotolo U (1990) Primary oxalosis mimicking hyperparathyroidism diagnosed after long-term hemodialysis. Am J Nephrol 10:344–349
Chambers TJ (1985) The pathobiology of the osteoclast. J Clin Pathol 38:241–252
Chaplin AJ (1977) Histopathological occurrence and characterization of calcium oxalate: a review. J Clin Pathol 30:800–811
El Labban NG (1984) Ultrastructural study of intranuclear tubulo-filaments in a giant cell tumor of bone in a patient with Paget's disease. J Oral Pathol 13:650–660
Gherardi G, Lo Cascio V, Bonucci E (1980a) Fine structure of nuclei and cytoplasm of osteoclasts in Paget's disease of bone. Histopathology 4:63–74
Gherardi G, Poggi A, Sisca S, Calderaro V, Bonucci E (1980b) Bone oxalosis and renal osteodystrophy. Arch Pathol Lab Med 104:105–111
Gordon MT, Anderson DC, Sharpe PT (1991) Canine distemper virus localized in bone cells of patients with Paget's disease. Bone 12:195–201
Harvey L, Gray T, Beneton MNC, Douglas DL, Kanis JA, Russell RGG (1982) Ultrastructural features of the osteoclasts from Paget's disease of bone in relation to a viral etiology. J Clin Pathol 35:771–779
Hodgkinson A, Zarembski PM (1968) Oxalic acid metabolism in man: a review. Calcif Tissue Res 2:115–132
Howatson AF, Fornasier VL (1982) Microfilaments associated with Paget's disease of bone: comparison with nucleocapsids of measles virus and respiratory syncytial virus. Intervirology 18:150–159
Kahn AJ (1990) The viral etiology of Paget's disease of bone: a new perspective. Calcif Tissue Int 47:127–129
Lagier R, Revell P, Schoenboerner A (1982) Calcium oxalate deposition in growing bone: anatomical and radiological study in a case of primary oxalosis. Metab Bone Dis Relat Res 4:49–59
Mills BG, Singer FR (1976) Nuclear inclusions in Paget's disease of bone. Science 194:201–202
Mills BG, Singer FR (1987) Critical evaluation of viral antigen data in Paget's disease of bone. Clin Orthop 217:16–25
Mills BG, Singer FR, Weiner LP, Holst PA (1980) Cell cultures from bone affected by Paget's disease. Arthritis Rheum 23:1115–1120
Mills BG, Singer FR, Weiner LP, Holst PA (1981) Immunohistological demonstration of respiratory syncitial virus antigens in Paget's disease of bone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:1209–1212
Mills BG, Singer FR, Weiner LP, Suffin SC, Stabile E, Holst P (1984) Evidence for both respiratory syncytial virus and measles virus antigens in the osteoclasts of patients with Paget's disease of bone. Clin Orthop 183:303–311
Mills BG, Holst PA, Stabile EK, Adams JS, Rude RK, Fernie BF, Singer FR (1985) A viral antigen-bearing cell derived from culture of Paget's bone cells. Bone 6:257–268
Mills BG, Yabe H, Singer FR (1988) Osteoclasts in human osteopetrosis contain viral-nucleocapside nuclear inclusions. J Bone Miner Res 3:101–106
Mirra JM (1985) Pathogenesis of Paget's disease based upon viral etiology. Clin Orthop 217:162–170
Nijweide PJ, Burger EH, Feyen JH (1986) Cells of bone: proliferation, differentiation and hormonal regulation. Physiol Rev 66:855–886
Nijweide PJ, Hagenaars CE, Modderman WE, Mulder RJP (1990) The cell lineage of the osteoclast. In: Cohn DV, Glorieux FH, Martin TJ (eds) Calcium regulators and bone metabolism. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 415–424
O'Driscoll JB, Anderson DC (1985) Past pets and Paget's disease. Lancet II:919–921
Ralston SH, Digiovine FS, Gallacher SJ, Boyle IT, Duff GW (1991) Failure to detect paramyxovirus sequences in Paget's disease of bone using the polymerase chain reaction. J Bone Miner Res 6:1243–1248
Rebel A, Malkani K, Basle M, Bregeon C (1974a) Particularités ultrastructurales des osteoclasts de la maladie de Paget. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic 41:767–771
Rebel A, Malkani K, Basle M (1974b) Anomalies nucleaires de la maladie osseuse de Paget. Nouv Presse Med 3:1299–1301
Rebel A, Basle M, Pouplard A, Malkani K, Filmon R, Lepatezour A (1980a) Bone tissue in Paget's disease of bone. Ultrastructure and immunocytology. Arthritis Rheum 23:1104–1114
Rebel A, Pouplard A, Filmon R, Basle M, Kouyoumdjian S, Lepatezour A (1980b) Viral antigens in osteoclasts from Paget's disease of bone. Lancet II:344–346
Schajowicz F, Ubios AM, Santini Araujo E, Cabrini RL (1985) Virus-like intranuclear inclusions in giant cell tumor of bone. Clin Orthop 201:247–250
Singer FR (1980) Paget's disease of bone: a slow virus infection? Calcif Tissue Int 31:185
Welsh RA, Mayer AT (1970) Nuclear fragmentations and associated fibrils in giant cell tumors of bone. Lab Invest 22:63–72
Williams HE, Lloyd HS Jr (1972) Primary hyperoxaluria. In: Stanbury JB, Wyngaarder JB, Fredrickson DS (eds) The metabolic basis of inherited disease. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 196–219
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bianco, P., Silvestrini, G., Ballanti, P. et al. Paramyxovirus-like nuclear inclusions identical to those of Paget's disease of bone detected in giant cells of primary oxalosis. Vichows Archiv A Pathol Anat 421, 427–433 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01606916
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01606916