Abstract
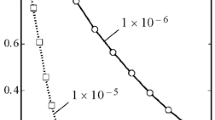
The calculation of the Zener stress involves two parts (1) the determination of the force between a particle and a grain boundary, and the shape of the resulting dimple on the grain boundary and (2) the statistical problem of summing the forces over the boundary. Calculations of the forces from spherical, needle-shaped and plate shaped particles are used to estimate the Zener stress by means of a point obstacle model and statistical dimple model. The results are compared with experimental determinations of stable grain sizes, with a computer simulation growth and with experimental measurements of retarded primary recrystallisation. When the particles are non-spherical or inhomogeneously distributed the Zener stress is anisotropic; this effect has been observed experimentally.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith C. S.: Trans. AIME175 (1948) 15.
Stüwe H. P.:in Recrystallisation of Metallic Materials (ed. Haessner F.). Dr. Riederer Verlag, Stuttgart, 1971, p. 21.
Hazzledine P. M., Hirsch P. B., Louat N.:in First RISØ International Symposium on Metallurgy and Materials Science (eds. Hansen N., Jones A. R., Leffers T.). RISØ, Röskilde, 1980, p. 159.
Hellman P., Hillert M.: Scand. J. Metall.4 (1975) 211.
Wörner C. H., Cabo A.: Scr. Metall.18 (1984) 565.
Louat N.: Acta Metall.30 (1982) 1291.
Louat N.: Philos. Mag. A47 (1983) 903.
Nes E., Ryum N., Hunderi O.: Acta Metall.33 (1985) 11.
Ashby M. F., Harper J., Lewis J.: Trans. AIME245 (1969) 413.
Wold K. J., Chambers F. M.: J. Aust. Inst. Met.13 (1968) 79.
Ryum N., Hunderi O., Nes E.: Scr. Metall.17 (1983) 1281.
Wörner C. H., Cabo A.: Acta Metall.35 (1987) 2801.
Hillert M.: Scr. Metall.18 (1984) 1431.
Wörner C. H., Cabo A., Hillert M.: Scr. Metall.20 (1986) 829.
Chan H. M., Humphreys F. J.: Acta Metall.32 (1984) 235.
Hillert M.: Acta Metall.13 (1965) 227.
Gladman T.: Proc. R. Soc. A294 (1964) 298.
Hunderi O., Ryum N.: Acta Metall.29 (1981) 1737.
Srolovitz D. J., Anderson M. P., Grest G. S., Sahni P. S.: Acta Metall.32 (1984) 1429.
Lindinger R. J., Gibson R. C., Brophy J. H.: Trans. ASM62 (1969) 230.
Watts B. M., Stowell M. J., Baikie B. L., Owen D. G. E.: Met. Sci.10 (1976) 198.
Gladman T., Pickering F. B.: J. Iron and Steel Institute205 (1967) 653.
Haroun N. A.: J. Mater. Sci.15 (1980) 2816.
Tweed C. J., Hansen N., Ralph B.: Met. Trans. A14 (1983) 2235.
Tweed C. J., Ralph B., Hansen N.: Acta Metall.32 (1984) 1407.
Elst R., van Humbeeck J., Delay L.:in 7th RISØ International Symposium on Metallurgy on Materials Science (eds. Hansen N., Juul Jensen D., Leffers T., Ralph B.). RISØ, Roskilde, 1986, p. 309.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hazzledine, P.M. Grain boundary pinning in two-phase materials. Czech J Phys 38, 431–443 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01605420
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01605420