Abstract
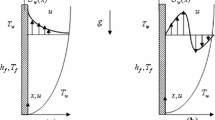
The problem of mixed convection over a semi-infinite vertical flat plate is studied by the method of series truncation for both cases when buoyancy adds and opposes the main flow. The present analysis is valid from leading edge to far downstream. The solutions show that the results are very accurate over an entire flow regime spanning from pure forced convection to moderately large free convection flows. In the buoyancy dominated limit the heat transfer is underestimated by 4 percent and skin friction is overestimated by 22 percent.
Zusammenfassung
Das Problem der gemischten Konvektion entlang einer vertikalen ebenen Platte wurde untersucht mit Hilfe der Methode der abgebrochenen Reihen, um Ergebnisse für kleine und mittlere Reynoldszahlen zu geben, verglichen mit den Grenzschicht-Resultaten in der Literatur, die fürRe→∞ gültig sind. Es wurde gefunden, dass die Methode gute Ergebnisse gibt für alle drei Regionen (erzwungene Konvektion dominierend im Nahgebiet, freie Konvektion dominierend im Ferngebiet, und das Zwischengebiet) in die das Strömungsfeld bei Grenzschichtrechnungen aufgeteilt worden ist; nicht nur für genügend grosseR x sondern auch für sehr kleine Werte vonR x .
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. M. Sparrow, R. Eichhorn andJ. L. Gregg,Combined Forced and Free Convection in a Boundary Layer Flow, Phys. Fluids2, 319–328 (1959).
J. H. Merkin,The Effect of Buoyancy Forces on the Boundary-Layer Flow Over a Semi-infinite Vertical Flat Plate in a Uniform Stream, J. Fluid Mech.34, 439–450 (1969).
E. M. Sparrow andJ. L. Gregg,Buoyancy Effects in Forced Convection Flow and Heat Transfer, J. Appl. Mech.26, 133–134 (1959).
A. A. Szewczyk,Combined Forced and Free-convection Laminar Flow, J. Heat Transfer86, 501–507 (1964).
R. C. Gunnes andB. Gebhart,Combined Forced and Natural Convection Flow for the Wedge Geometry, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer8, 43–53 (1965).
S. Eshghy,Forced Flow Effects on Free Convection Flow and Heat Transfer, J. Heat Transfer86, 290–291 (1964).
J. R. Lloyd andE. M. Sparrow,Combined Forced and Free Convection Flow on Vertical Surface, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer13, 434–438 (1970).
G. Wilks,Combined Forced and Free Convection on Vertical Surfaces, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer16, 1958–1964 (1973).
P. H. Oosthuizen andR. Hart,A Numerical Study of Laminar Combined Convective Flow Over Flat Plates, J. Heat Transfer95, 60–63 (1973).
R. T. Davis,Laminar Incompressible Flow Past a Semi-infinite Flat Plate, J. Fluid Mech.27, 691–704 (1967).
R. E. Bellman andR. E. Kalaba,Quasi-linearization and Nonlinear Boundary-value Problems, Rand Corporation, California (1965).
H. Schlichting,Boundary Layer Theory, McGraw-Hill, London (1968).
N. K. Banthiya andN. Afzal. To be published.
S. Kaplun,The Role of Coordinate System in Boundary Layer Theory, Z. angew. Math. Phys.5, 111–135 (1954).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Afzal, N., Banthiya, N.K. Mixed convection over a semi-infinite vertical flat plate. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics (ZAMP) 28, 993–1004 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01601667
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01601667