Summary
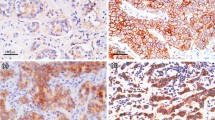
In this investigation, 83 human mammary carcinomas were examined for the expression of oestrogen receptor (ER), epidermal growth factor receptor (EGF-R), epidermal growth factor (EGF), transforming growth factor alpha (TGF-α), c-erbB-2, histological grade, mitotic index and nodal status, all of which are reportedly prognostically significant factors (Bloom and Richardson 1957; Baak et al. 1985; Wright et al. 1989). ER expression was biochemically recognized in 43.4% of mammary carcinomas, and EGF-R, EGF, TGF-α and c-erbB-2 were histochemically recognized in 25.3, 14.5, 27.7 and 18.0% of mammary carcinomas examined respectively, using conventional sections of buffered formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue and monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies. There were significant relationships between negative ER and positive EGF-R or TGF-α; positive EGF-R and TGF-α; positive EGF-R and c-erbB-2; and positive c-erbB-2 and TGF-α. The single changes which were the negative ER and the positive c-erbB-2 correlated with histological grade and mitotic index. Co-expression of EGF-R and TGF-α correlated with positive nodal status. Therefore, the present investigation indicates that the negative ER, single expression of c-erbB-2 and co-expression of EGF-R and TGF-α are important markers which contribute indirectly to prognosis, which reconfirms previous findings on the former two while adding the new finding that immuno-histochemical demonstration of expression of EGF-R and TGF-α may provide useful information for selecting the appropriate treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali IU, Campbell G, Lidereau R, Callahan R (1988) Amplification of c-erbB-2 and aggressive human breast tumors? Science 240:1795–1796
Baak JPA, Dop HV, Kurver PHJ, Hermans J (1985) The value of morphometry to classic prognosticators in breast cancer. Cancer 56:374–382
Berger MS, Locher GW, Saurer S, Gullick WJ, Waterfield MD, Groner B, Hynes NE (1988) Correlation of c-erbB-2 gene amplification and protein expression in human breast carcinoma with nodal status and nuclear grading. Cancer Res 48:1238–1243
Bloom HGJ, Richardson WW (1957) Histologic grading and prognosis in breast cancer. Br J Cancer 11:655–669
Borg A, Tandon AK, Sigurdsson H, Clark GM, Ferno M, Fuqua SAW, Killander D, McGuire WL (1990) HER-2/neu amplification predicts poor survival in node-positive breast cancer. Cancer Res 50:4332–4337
Dazzi H, Hasleton PS, Thatcher N, Barnes DM, Wilkes S, Swindell R, Lawson RAM (1989) Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGF-R) in non-small cell lung cancer. Use of archival tissue and correlation of EGF-R with histology, tumour size, node status and survival. Br J Cancer 59:746–749
Derynck R (1986) Transforming growth factor-α: structure and biological activities. J Cell Biochem 32:203–204
Dickson RB, Bates SE, Mcmanaway ME, Lippman ME (1986) Characterization of estrogen responsive transforming activity in human breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 46:1707–1713
Dotzlaw H, Miller T, Karvelas J, Murphy LC (1990) Epidermal growth factor gene expression in human breast cancer biopsy samples: relation to estrogen and progesterone receptor gene expression. Cancer Res 50:4204–4208
Gullick WJ, Downward J, Parker PJ, Whittle N, Kris R, Schlessinger J, Ullrich A, Waterfield MD (1985) The structure and function of EGFr studied by using anti-synthetic peptide antibodies. Proc R Soc Lond 226:127–134
Gullick WJ, Marsden JJ, Whittle N, Ward B, Bobrow L, Waterfield MD (1986) Expression of epidermal growth factor receptors on human cervical, ovarian, and vulval carcinomas. Cancer Res 46:285–292
Gullick WJ, Berger MS, Bennett PLP, Rothbard JB, Waterfield MD (1987) Expression of the c-erbB-2 protein in normal and transformed cells. Int J Cancer 40:246–254
Gusterson BA, Machin LG, Gullick WJ, Gibbs NM, Powles TJ, Elliott C, Ashley S, Monaghan P, Harrison S (1988) c-erbB-2 expression in benign and malignant breast disease. Br J Cancer 58:453–457
Jungsil Ro, Naggar A, Ro JY, Blick M, Frye D, Fraschini G, Fritsche H, Hortobagyi G (1989) c-erbB-2 Amplification in node-negative human breast cancer. Cancer Res 49:6941–6944
King CR, Kraus MH, Aaronson SA (1985) Amplification of a novel v-erbB-related gene in human mammary carcinoma. Science 229:974–976
Knight WAIII, Livingston RB, Gregory EJ, McGuire WL (1977) Estrogen receptor as an independent prognostic factor for early recurrence in breast cancer. Cancer Res 37:4669–4671
Marquardt H, Hunkapiller MW, Hood LE, Twardzik DR, De Larco JE, Stephenson JR, Todaro GJ (1983) Transforming growth factors produced by retrovirus-transformed rodent fibroblasts and human melanoma cells: amino acid sequence homology with epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:4684–4688
Matsumoto K, Ochi H, Nomura Y, Takatani O, Izuo M, Okamoto R, Sugano H (1978) Progesterone and estrogen receptors in Japanese breast cancer. In: McGuire WL (ed) Hormones, receptors, and breast cancer. Raven Press, New York, pp 43–58
McGuire WL, Dickson RB, Osborne CK, Salomon D (1988) The role of growth factors in breast cancer. A panel discussion. Breast Cancer Res Treat 12:159–166
Meyers SL, O'Brien MT, Smith T, Dudley JP (1990) Analysis of theint-1,int-2, c-myc, andneu oncogene in human breast carcinoma. Cancer Res 50:5911–5918
Mizukami Y, Nonomura A, Yamada T, Kurumaya H, Hayashi M, Koyasaki N, Taniya T, Noguchi M, Nakamura S, Matubara F (1990) Immunohistochemical demonstration of growth factors, TGF-α, TGF-β, IGF-I andneu oncogene product in benign and malignant human breast tissues. Anticancer Res 10:1115–1126
Okamoto S, Oka T (1984) Evidence for physiological function of epidermal growth factors: pregestational sialoadenectomy in mice decreases milk production and increases offspring mortality during lactation period. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:6059–6063
Osborne CK, Artega CL (1990) Autocrine and paracrine growth regulation of breast cancer: clinical implications. Breast Cancer Res Treat 15:3–11
Real FX, Retting WJ, Chesa PG, Melamed MR, Old LJ, Mendelsohn J (1986) Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor in human cultures cells and stage of differentiation. Cancer Res 46:4726–4731
Reynolds FH Jr, Todaro GJ, Fryling C, Stephenson JR (1983) Human transforming growth factors induce tyrosine phosphorylation of EGF receptors. Nature 292:259–262
Roberts MM, Rubens RD, King RJB (1978) Oestrogen receptors and the response to endocrine therapy in advanced breast cancer. Br J Cancer 38:431–436
Sainsbury JRC, Malcolm AJ, Appleton DR, Farndon JR, Harris AL (1987a) Presence of epidermal growth factor receptor as an indicator of poor prognosis in patients with breast cancer. J Clin Pathol 38:1225–1228
Sainsbury JRC, Farndon JR, Needham GK, Malcolm AJ, Harris AL (1987b) Epidermal-growth-factor receptor status as predictor of early recurrence of and death from breast cancer. Lancet 1:1398–1402
Schechter AL, Hung MC, Vaidyanathan L, Weinberg RA, Feng TLY, Francke U, Ullrich A, Coussens L (1985) Theneu gene: anerbB-homologous gene distinct from and unlinked to the gene encoding the EGF-receptor. Science 229:976–978
Semba K, Kamata N, Toyoshima K, Yamamoto T (1985) A verbB-related proto-oncogene, c-erbB-2, is distinct from the cerbB-1/epidermal growth factor receptor gene and is amplified in a human salivary gland adenocarcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:6497–6501
Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ, Ullrich A, McGuire WL (1987) Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science 235:177–183
Sorvillo JM, McCormack ES, Yanez L, Valenzuela D, Reynolds FH (1990) Preparation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies specific for human transforming growth factor. Oncogene 5:377–386
Sporn MB, Todaro GJ (1980) Autocrine secretion and malignant transformation of cells. N Engl J Med 303:878–880
Spyratos F, Delarue JC, Andrieu C, Lidereau R, Champeme MH, Hacene K, Brunet M (1990) Epidermal growth factors and prognosis in primary breast cancer. Cancer Res Treat 17:83–89
Taylor JM, Mitchell WM, Cohen S (1972) Epidermal growth factor: physical and chemical properties. J Biol Chem 247:5928–5934
Thor AD, Schwartz LH, Koerner FC, Edgerton SM, Skates SJ, Yin S, McKenzie SJ, Panicali DL, Marks PJ, Fingert HJ, Wood WC (1989) Analysis of c-erbB-2 expression in breast carcinoma with clinical follow-up. Cancer Res 49:7147–7152
Tsuda H, Hirohashi S, Shimosato Y, Hirota T, Tsugane S, Yamamoto H, Miyajima N, Toyoshima K, Yamamoto T, Yokota J, Yoshida T, Sakamoto H, Terada M, Sugimura T (1989) Correlation between long-term survival in breast cancer patients and amplification of two putative oncogene-coamplification units:hst-1/int-2 and c-erbB-2/ear-1. Cancer Res 49:3104–3108
Uehara T, Kaneko Y, Kanda N, Yamamoto T, Higashi Y, Nomoto C, Izumo T, Takayama S, Sakurai M (1990) c-erbB-2 and c-erbA-1 (ear-1) gene amplification and c-erbB-2 protein expression in Japanese breast cancers: their relationship to the histology and other disease parameters. Jpn J Cancer Res 81:620–624
Venter DJ, Tuzi NL, Kumar S, Gullick WJ (1987) Overexpression of the c-erbB-2 oncoprotein in human breast carcinomas: immunohistological assessment correlates with gene amplification. Lancet II:69
Vijver MJ van de, Peters JL, Mooi WJ, Lomans J, Palesio O, Nesse R (1988) Neu-protein overexpression in breast cancer: association with comedo-type ductal carcinoma in situ and limited prognostic value in stage II breast cancer. N Engl J Med 319:1239–1245
Wright C, Angus B, Nicholson S, Sainbury JRC, Cairns J, Gullick WJ, Kelly P, Harris AL, Horne CHW (1989) Expression of c-erbB-2 oncoprotein: a prognostic indicator in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 49:2087–2090
Yamada Y, Yoshimoto M, Murayama Y, Ebuchi M, Mori S, Yamamoto T, Sugano H, Toyoshima K (1989) Association of elevated expression of the c-erbB-2 protein with spread of breast cancer. Jpn J Cancer Res 80:1192–1198
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Umekita, Y., Enokizono, N., Sagara, Y. et al. Immunohistochemical studies on oncogene products (EGF-R, c-erbB-2) and growth factors (EGF, TGF-α) in human breast cancer: their relationship to oestrogen receptor status, histological grade, mitotic index and nodal status. Vichows Archiv A Pathol Anat 420, 345–351 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01600214
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01600214