Abstract
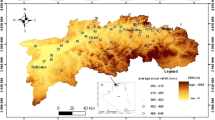
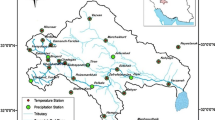
The paper treats the problem of interpolating annual runoff from regular streamflow measurements in a regional scale applying objective methods. These methods are adapted to point processes like temperature and precipitation. Modifications are needed to account for the fact that streamflow is an integrated process following the hierarchical structure of river systems. The most straightforward method is therefore to relate the interpolation to the existing river network. For theoretical reasons it is preferable to interpolate the lateral inflow rather than the flow in the river itself. Procedures for the interpolation with the different approaches are developed and discussed. Special attention is put on the question how the equation of continuity can be satisfied. The Laagen drainage basin in southern Norway is used as a test area. The data consist of annual observations of streamflow and digital map information on river networks and drainage basin boundaries.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnell, N. 1991: Producing grid maps of average annual runoff:some preliminary results. Institute of Hydrology, Wallingford
Baumgartner, A.; Reichel, E. 1975: World Water Balance. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Creutin, J.D.; Obled, C. 1982: Objective analysis and mapping techniques for rainfall fields: An objective comparison. Water Resour. Res. 18(2), 413–439
Eastman, J.R. 1991: IDRISI: A grid-based geographic analysis system. Version 3.2.2. Clark University, Graduate school of Geography, Worcester, Massachusetts, USA.
Eliassen, A. 1954: Provisional report on calculation of spatial covariance and autocorrelation of the pressure field. Rep no 5. Videnskapsakademiet Institutt for Vaer og Klimaforskning, Oslo
Forsman, A. 1976: Water balance maps of the Nordic countries. Vannet i Norden, No. 4
Gandin, L.S. 1963: Objektivnyi analyz meteorologicheskikh polei. Gidrometeoizdat. Leningrad
Gandin, L.S.; Kagan, P.L. 1976: Statisticheskie metody interpretatsii meteorologicheskikh dannykh. Gidrometeoizdat, Leningrad
Gottschalk, L. 1993: Correlation and covariance of runoff. Stochastic Hydro. Hydraul. 7, 95–101
Kolmogorov, A. 1941: Interpolated and extrapolated stationary random sequences. Izvestia AN SSSR, seria matematichecheskaya 5(2), 85–95
Korzun, V.I. 1978: World water balance and water resources of the Earth. UNESCO, Studies and Reports in Hydrology 25
NVE (Norwegian Water Resources and Energy Administration). 1987: Directorate of water resources, hydrology department. Runoff Map of Norway (1930–1960), Oslo
Wiener, N. 1949: Extrapolation, interpolation and smoothing of stationary time series. John Wiley, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gottschalk, L. Interpolation of runoff applying objective methods. Stochastic Hydrol Hydraul 7, 269–281 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01581615
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01581615