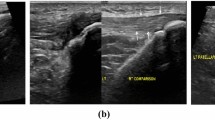
Abstract
Repetitive blunt trauma or single severe trauma to the hypothenar region may lead to traumatic thrombosis of the distal ulnar artery (hypothenar hammer syndrome, HHS). In the sports-related literature we found and analysed isolated cases attributed to injuries sustained during sporting activities such as baseball, badminton, handball, football, frisbee, softball, karate, weight-lifting and hockey. Further, we report the case of an amateur golf player with ischaemic symptoms of his left hand, where angiography revealed filling defects in the digital arteries associated with a corkscrew-like configuration of the distal ulnar artery. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan demonstrated, at the level of the hamulus ossis hamati, accessory fibres of m. palmaris brevis forming a sling around the ulnar artery. Treatment by resection of the ulnar artery. Treatment by resection of the thrombosed a. ulnaris segment and replacement with an autologous vein graft resulted in complete relief of symptoms. Histological sections revealed partially organized thrombi adherent to the intimal surface with fragmentation of the internal elastic membrane, indicating a traumatic genesis. As the mechanism of injury, we suspected intensive golf playing with the grip style and subsequent motions leading to pressure injury of the hypothenar area and the underlying ulnar artery. Contraction of the anomalous muscle belly may have additionally compressed the artery, slowing down the arterial flow and promoting thrombosis. In most reported cases including our own, it took a relatively long time until the cause of the disease as traumatic was found and accepted. The initial repetitive blunt or single severe trauma initiaing the HHS can easily be overlloked or ignored. After intimal damage of a. ulnaris, the beginning of symptoms may be prolonged and mislead one into thinking the cause is a collagen or vasospastic disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Butsch LB, Janes JM (1962) Injuries of the superficial palmar arch. J Trauma 3: 504–516
Carneirio RS, Mann RJ (1979) Occlusion of the ulnar artery associated with an anomalous muscle: a case report. J Hand Surg 4: 412–414
Conn J, Bergan JJ, Bell J (1970) Hypothenar hammer syndrome: postraumatic digital ischemia. Surgery 68: 1122–1128
Dodds GA, Hale D, Jackson T (1990) Incidence of anatomic variants in Guyon's canal. J. Hand Surg [Am] 15: 352–355
Gaylis H, Kushlick AR (1976) The hypothenar hammer syndrome. South Afr Med J 50: 125–127
Girven KS, Puckett CL, Kleinert HE (1978) Ulnar artery thrombosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 61: 405–411
Girven ML (1958) Palmar intramural thrombosis in the ulnar artery. Calif Med 89: 424–425
Hammond DC, Matloub HS, Yousif NJ, Sanger JR (1993) The corkscrew sign in hypothenar hammer syndrome. J Hand Surg [Br] 18: 767–769
Jackson JP (1954) Traumatic thrombosis of the ulnar artery in the palm. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 36: 438–439
Kleinert HE, Volianitis GJ (1965) Thrombosis of the palmar arterial arch and its tributaries: etiology and newer concepts in treatment. J. Trauma 5: 447–457
Kartihner MM, Wilcox WC (1976) Thrombolysis of palmar and digital arterial thrombosis by intraarterial thrombolysin. J Hand Surg 1: 67–74
Koga Y, Seki T, Caro LD (1993) Hypothenar hammer syndrome in a young female badminton player. Am J Sports Med 21: 890–892
Koman LA, Urbaniak JR (1981) Ulnar artery insufficiency; a guide to treatment. J Hand Surg 6: 16–24
Lawrence RR, Wilson JN (1965) Ulnar artery thrombosis in the palm: case reports. Plast Reconstr Surg 36: 604–608
Lowrey CW, Chadwick RO, Waltman EN (1976) Digital vessel trauma from repetitive impact in baseball catchers. J Hand Surg 1: 236–238
McCarthy WJ, Yao JST, Schafer MF, Nuber G, Flinn WR, Blackburn D, Suker RS (1989) Upper extremity arterial injury in athletes. J Vasc Surg 9: 317–327
Paaby H, Stadil F (1968) Thrombosis of the ulnar artery. Acta Orthop Scand 39: 336–345
Porubsky GL, Brown SI, Urbaniak JR (1986) Ulnar artery thrombosis: a sports-related injury. Am J Sports Med 14: 170–175
Pribyl CL, Moneim MS (1994) Anomalous hand muscle found in the Guyon's canal at exploration for ulnar artery thrombosis. Clin Orthop 306: 120–123
Rosen S von (1934) Ein Fall von Thrombose in der Arteria ulnaris nach Einwirkung stumpfer Gewalt. Acta Chir Scand 73: 500–505
Schneider M, Creutzig A, Alexander K (1995) Traumatisch bedingte Durchblutungsstörungen der Hände. Med Klinik 90: 225–228
Weeks PM, Young VL (1982) Ulnar artery thrombosis and ulnar nerve compression associated with an anomalous hypothenar muscle. Plast Reconstr Surg 69: 130–131
Zeiss J, Jakab E, Khimji T, Imbriglia J (1992) The ulnar tunnel at the wrist (Guyon's canal): normal MR anatomy and variants. AJR 158: 1081–1085
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müller, L.P., Rudig, L., Kreitner, K.F. et al. Hypothenar hammer syndrome in sports. Knee Surg, Sports traumatol, Arthroscopy 4, 167–170 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01577412
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01577412