Abstract
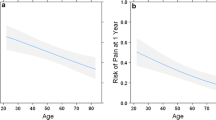
Pain is common after inguinal herniorrhaphy. The objective of our study was to evaluate the significance of various clinical factors on the level of post-operative pain after ambulatory inguinal herniorrhaphy. Between January, 1996 and December, 1998, 239 ambulatory inguinal hernia repair patients were recruited. Operative techniques included nylon darn (n=152), modified Bassini repair (n=56), and prolene mesh hernioplasty (n=30). Linear analogue pain scores-ranging in value from o to 10- were assessed by telephone interviews on the first and third post-operative days. Uni-variate and multi-variate analyses were performed to identify the significant independent determinant factors affecting the severity of post-operative pain. Clinical factors studied were age, sex, operative technique, hernia anatomy and post-operative complication(s). By uni-variate analysis, patients of age≤50 years and indirect inguinal hernia were associated with a significantly higher pain score on the first postoperative day 1. On post-operative day 3, patients of age≤50 years, with an indirect inguinal hernia and modified Bassini repair reported a significantly higher pain score. Following inguinal herniorrhaphy, multiple regression analysis showed that age was the only independent predictive factor of pain score on post-operative days 1 and 3. In conclusion, post-operative pain was not affected by surgical technique, sex, hernia anatomy and post-operative morbidity. Only age had a significant influence on the post-operative pain score following ambulatory inguinal herniorrhaphy. Therefore, the age of a patient should be taken into consideration when prescribing post-operative analgesics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellville JW, Forrest WH, Miller E, Brown BW (1971) Influence of age on pain relief from analgesics: A study of postoperative patients. JAMA 217:1835–1841
Callesen T, Bech K, Andersen J, Nielsen R, Roikjaer O, Kehlet H (1999) Pain after primary inguinal herniorrhaphy: influence of surgical technique. J Am Coll Surg 188:355–359
Callesen T, Bech K, Nielsen R, Andersen J, Hesselfeldt P, Roikjaer O, Kehlet H (1998) Pain after groin hernia repair. Br J Surg 85:1412–1414
Callesen T, Kehlet H (1997) Postherniorrhaphy pain. Anesthesiology 87:1219–30
Filipi CJ, Gastron-Johansson F, McBride PJ, Murayama K, Gerhardt J, Cornet DA, Lund RJ, Hirai D, Graham R, Patil K, Fitzgibbons R, Gaines RD (1996) An assessment of pain and return to normal activity: Laparoscopoic herniorrhaphy vs open tension-free Lichtenstein repair. Surg Endosc 10:983–986
Kawji R, Feichter A, Fuchsjager N, Kux M (1999) Postoperative pain and return to activity after five different types of inguinal herniorrhaphy. Hernia 3:31–35
Kehlet H, Dahl JB (1993) The value of multimodal or balanced analgesia in postoperative pain treatment. Anesth Analg 77:1048–1056
Johansson B, Hallerback B, Stubberod A (1997) Preoperative local infiltration with ropivacaine for postoperative pain relief after inguinal hernia repair. Eur J Surg 163:371–378
Juul P, Christensen K (1999) Randomized clinical trial of laparoscopic versus open inguinal hernia repair. Br J Surg 86:316–319
Lichtenstein IL, Shulman AG, Amid PK, Montllor MM (1989) The tension-free hernioplasty. Am J Surg 157:188–193
Liem MS, Van der Graaf Y, Van Steensel CJ, Boelhouwer RU, Clevers GJ, Meijer WS, Stassen LP, Vente JP, Weidema WF, Schrijvers AJ, Van Vroonhovenet JM (1997) Comparison of conventional anterior surgery and laparoscopic surgery for inguinal-hernia repair. N Engl J Med 336:1642–1647
MRC Laparoscopic Groin Hernia Trial Group (1999) Laparoscopic versus open repair of groin hernia: a randomized comparison. Lancet 354:185–190
Moore AK, Vilderman S, Lubenskyi W, McCans J, Fox GS (1990) Differences in epidural requirements between elderly and young patients after abdominal surgery. Anesth Analg 70:316–320
Nehra D, Gemmell L, Pye JK (1995) Pain relief after inguinal hernia repair: a randomized doubleblind study. Br J Surg 82:1245–1247
Prior MJ, Williams EV, Shukla HS, Phillips S, Vig S, Lewis M (1998) Prospective randomized controlled trial comparing Lichtenstein with modified Bassini repair of inguinal hernia. J R Coll Surg Edinb 43:82–86
Ready LB, Chadwick HS, Ross B (1987) Age predicts effective epidural morphine dosage after abdominal hysterectomy. Anesth Analg 66:1215–1218
Smedberg SG, Broom AE, Gullmo A (1984) Ligation of the hernial sac? Surg Clin North Am 64:299–306
Spittal MJ, Hunter SJ (1992) A comparison of bupivacaine instillation and inguinal field block for control of pain after herniorrhaphy. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 74:85–88
Veering BT, Burm AG, van Kleef JW, Hennis PJ, Spierdijk J (1987) Epidural anesthesia with bupivacaine: Effects of age on neural blockade and pharmacokinetics. Anesth Analg 66:589–593
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lau, H., Lee, F. Determinant factors of pain after ambulatory inguinal herniorrhaphy: a multi-variate analysis. Hernia 5, 17–20 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01576159
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01576159